Why did my drive letter change? It’s a question that often pops up when you connect a new device, reinstall your operating system, or even just update your drivers. The truth is, drive letters can be a bit fickle, shifting around like sand in a desert wind.
But understanding the forces at play can help you navigate these changes with ease.
Operating systems, in their quest to keep track of all your storage, assign drive letters to each drive. These letters are a simple way for the system to identify and access data. But this seemingly straightforward process can get complicated when new devices are introduced, old ones are removed, or system settings are tweaked.
Drive Letter Assignment

Operating systems assign drive letters to storage devices, including hard drives, solid-state drives, and external storage media, to identify and manage them. This system allows the operating system to easily access and organize data stored on these devices.
Drive Letter Assignment Process
Operating systems typically assign drive letters based on a combination of factors, including the order of device detection, existing drive letters, and system configuration. The order in which the operating system detects devices is crucial in drive letter assignment. Typically, the first detected storage device receives the drive letter “C,” followed by “D” for the next device, and so on.
This sequence can be influenced by factors such as the order in which devices are connected or the speed at which they are detected. The assignment process is also affected by existing drive letters. If a drive letter is already in use by a device, the operating system will assign the next available letter to the newly detected device.
System configuration settings can further influence drive letter assignment. Users can manually configure drive letters through the operating system’s Disk Management tool. This allows for customization and flexibility in managing storage devices.
Scenarios for Drive Letter Changes, Why did my drive letter change
Several scenarios can lead to changes in drive letter assignments.
- Connecting External Devices: When connecting external devices, such as USB drives or external hard drives, the operating system will assign them a drive letter based on the factors discussed earlier. The assigned drive letter will usually be the next available letter in the sequence.
For example, if a system already has drives labeled “C,” “D,” and “E,” a newly connected USB drive will be assigned the drive letter “F.”
- Re-installing Operating Systems: Re-installing an operating system can result in changes to drive letter assignments. The operating system will assign drive letters based on the order in which it detects devices during the installation process. This can lead to different drive letter assignments compared to the previous installation.
- Updating Drivers: Updating drivers for storage devices can sometimes influence drive letter assignments. If the driver update changes the way the operating system interacts with the device, it can lead to a different drive letter being assigned.
Common Causes of Drive Letter Changes
Drive letter changes are a common occurrence in Windows operating systems, often caused by various factors that impact how your computer recognizes and assigns letters to storage devices. Understanding the root causes can help you troubleshoot and resolve these changes effectively.
Yo, my drive letter just changed and I’m totally confused. Like, what’s up with that? I’m gonna have to ask my dad about it. He’s the best, you know? He’s like the ultimate tech guru.
I should totally check out this letter to the best dad in the world I found online, it’s pretty sweet. Anyway, back to my drive letter. I guess I’ll just ask my dad. He’ll probably have the answer.
Connecting or Disconnecting Devices
The most common reason for drive letter changes is connecting or disconnecting external devices, such as USB drives, external hard drives, or SD cards. When you plug in a new device, Windows assigns it a drive letter, which may conflict with the existing letter assigned to another device.
Similarly, when you disconnect a device, its drive letter becomes available, potentially causing a shift in the letters assigned to other connected devices.
System Settings Updates
System updates, including Windows updates and driver updates, can sometimes cause drive letter changes. These updates might modify the way your computer manages storage devices or introduce changes to the device driver, resulting in a reassignment of drive letters.
Multiple Devices with the Same Drive Letter
Connecting multiple external devices with the same drive letter can lead to conflicts and unpredictable behavior. Windows attempts to assign unique drive letters to each device, but if you have multiple devices with the same letter, the operating system might struggle to differentiate them, leading to confusion and potential data loss.
Determining the Cause of a Drive Letter Change
To pinpoint the specific cause of a drive letter change, follow these steps:
- Check Connected Devices:Examine the list of connected devices in File Explorer (This PC) or Disk Management (right-click “This PC” and select “Manage”). Look for any newly connected devices or devices that have been disconnected since the drive letter change occurred.
- Review Recent Updates:Check your Windows update history or device manager for any recent updates that might have been installed around the time of the drive letter change.
- Examine Disk Management:In Disk Management, look for any unusual changes in the drive letter assignments, such as multiple devices with the same letter or a drive letter assigned to a device that’s not physically connected.
Troubleshooting Drive Letter Changes

Troubleshooting drive letter changes involves identifying the root cause of the issue and applying appropriate solutions. This can be a challenging process, as drive letter changes can be triggered by various factors, including hardware malfunctions, software conflicts, or even user error.
Methods for Troubleshooting Drive Letter Changes
Several methods can be employed to diagnose and resolve drive letter changes. Each technique offers a unique approach to understanding the underlying issue and provides valuable insights into the problem.
- Checking Device Manager: This method allows users to identify potential hardware issues that might be causing drive letter changes. The Device Manager provides a comprehensive view of all connected hardware components, including storage devices. By examining the properties of the affected drive in Device Manager, users can identify any error messages, driver conflicts, or hardware malfunctions that might be responsible for the drive letter change.
- Examining Disk Management: Disk Management is a powerful tool that provides a detailed view of the hard drives and partitions on a system. This method enables users to check the drive’s status, partition configuration, and drive letter assignments. By analyzing the information in Disk Management, users can determine if the drive letter change is due to a partition resizing, a change in the drive’s status, or a conflict with other partitions.
- Verifying System Configuration: System configuration settings can significantly impact drive letter assignments. This method involves reviewing system settings, including drive letter mapping, mount points, and drive letter assignment policies. By carefully examining these settings, users can identify any conflicts or misconfigurations that might be causing the drive letter change.
Comparison of Troubleshooting Techniques
The following table summarizes the effectiveness of different troubleshooting techniques in addressing drive letter changes:
| Technique | Effectiveness | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Checking Device Manager | High | Identifies hardware issues, driver conflicts, or malfunctions that might be causing drive letter changes. |
| Examining Disk Management | Moderate | Provides a detailed view of the hard drives and partitions, allowing users to identify partition configuration issues, drive status changes, or conflicts with other partitions. |
| Verifying System Configuration | Low | Reveals system settings, including drive letter mapping, mount points, and drive letter assignment policies, which can be helpful in identifying conflicts or misconfigurations. |
Flowchart for Diagnosing and Resolving Drive Letter Issues
The following flowchart provides a step-by-step guide for diagnosing and resolving drive letter issues:
StartCheck Device Manager for hardware issuesYes, hardware issues foundResolve hardware issuesNo, hardware issues not foundExamine Disk Management for partition configuration issuesYes, partition configuration issues foundResolve partition configuration issuesNo, partition configuration issues not foundVerify system configuration for drive letter mapping, mount points, and assignment policiesYes, configuration issues foundResolve configuration issuesNo, configuration issues not foundContact technical support for further assistanceEnd
Manually Changing Drive Letters
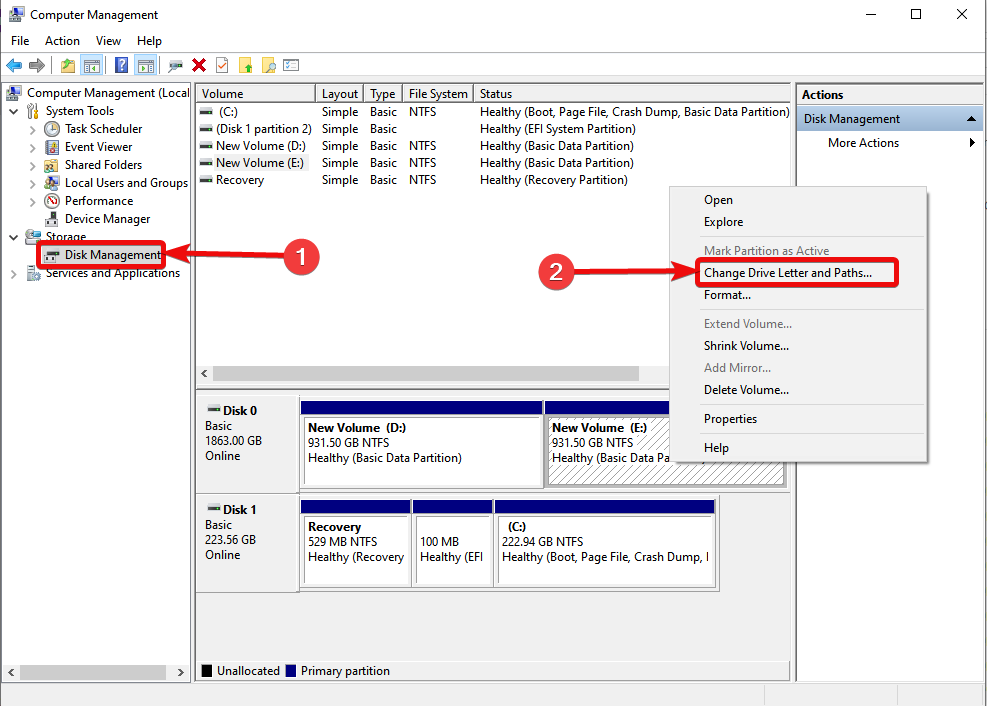
Manually changing drive letters can be useful for various reasons, such as organizing your storage or troubleshooting system issues. This section explains the process of changing drive letters using Disk Management and other system tools, along with the potential risks and best practices to follow.
Potential Risks and Limitations of Manually Changing Drive Letters
Modifying drive letters can introduce potential risks and limitations, which should be considered before proceeding.
- Data Loss:Incorrectly changing drive letters can lead to data loss, especially if the drive contains critical system files.
- System Instability:Altering drive letters can disrupt system functionality and cause instability, particularly if the drive is associated with essential operating system components.
- Application Compatibility:Some applications may rely on specific drive letters, and changing them can cause compatibility issues.
- Boot Issues:Changing the drive letter of the system drive (usually C:) can prevent the system from booting correctly.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Integrity and Preventing System Errors
To minimize risks and ensure data integrity when manually changing drive letters, follow these best practices:
- Back Up Your Data:Before making any changes, create a complete backup of all important data on the drive whose letter you intend to modify.
- Use Disk Management:Utilize the Disk Management tool built into Windows to modify drive letters. This provides a user-friendly interface and minimizes the risk of errors.
- Avoid Changing System Drive Letter:Refrain from changing the drive letter of the system drive (C:) unless absolutely necessary.
- Restart After Changes:After modifying drive letters, restart your computer to ensure the changes take effect correctly.
- Test Applications:After changing drive letters, test all applications that access the affected drive to ensure compatibility.
Preventing Drive Letter Changes: Why Did My Drive Letter Change
/change-drive-letter-5948522e3df78c537bd14bc3.png)
Drive letter changes can be disruptive, especially if they occur unexpectedly. Understanding the causes of these changes and adopting preventive measures can minimize their impact on your system. Here’s a guide to preventing drive letter changes and maintaining a consistent drive letter assignment.
Using Fixed Drive Letters
Assigning fixed drive letters can prevent unexpected changes. Fixed drive letters are permanently assigned to specific volumes, eliminating the possibility of the operating system assigning a different letter during system startup or after a device connection.
Configuring Drive Letter Assignments
Configuring drive letter assignments allows you to control the letters assigned to your drives. You can use tools like Disk Management in Windows to manage drive letter assignments, ensuring that drives are assigned the desired letters and preventing accidental changes.
Managing External Devices
External devices like USB drives or external hard drives can trigger drive letter changes. To prevent this, you can assign fixed drive letters to these devices. Additionally, disconnecting external devices when not in use can help prevent conflicts and ensure drive letter stability.
“Managing external devices is crucial to preventing drive letter changes. Assigning fixed drive letters and disconnecting them when not in use can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected changes.”
Commonly Asked Questions
What happens if two devices have the same drive letter?
When multiple devices have the same drive letter, the system might prioritize one device over another, potentially causing data access issues. It’s best to avoid assigning the same drive letter to multiple devices.
Can I manually change a drive letter without causing problems?
Yes, but it’s important to proceed with caution. Make sure you understand the potential risks and follow best practices to avoid data loss or system errors. Always back up your data before making any changes.
Is there a way to permanently fix a drive letter?
You can use fixed drive letters or configuration settings to prevent changes, but these methods might not always be compatible with all devices or situations. It’s best to consult your system documentation or seek professional advice if you have specific requirements.