Which of the following statements is true regarding learning difficulties? This question delves into the multifaceted nature of learning difficulties, exploring their impact on individuals and the various factors that contribute to their development. Join us as we unravel the complexities of this topic, shedding light on the challenges and opportunities that accompany learning difficulties.
Learning difficulties encompass a wide range of conditions that affect an individual’s ability to learn and process information. These difficulties can manifest in various ways, impacting reading, writing, math, and other cognitive skills. Understanding the nature of learning difficulties is crucial for providing effective support and interventions to individuals who face these challenges.
Definition and Types of Learning Difficulties
Learning difficulties refer to a wide range of conditions that affect an individual’s ability to acquire, process, retain, and use information effectively. These difficulties can manifest in different ways and impact individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
There are numerous types of learning difficulties, each with its unique characteristics. Some of the most common types include:
Dyslexia, Which of the following statements is true regarding learning difficulties
Dyslexia is a language-based learning difficulty that primarily affects the ability to read, write, and spell. Individuals with dyslexia may struggle with phonological processing, decoding, and fluency, leading to difficulties in reading comprehension and written expression.
Dyscalculia
Dyscalculia is a mathematical learning difficulty that affects the ability to understand and apply mathematical concepts. Individuals with dyscalculia may struggle with number sense, calculation, and problem-solving, leading to difficulties in mathematics and related subjects.
Dysgraphia
Dysgraphia is a writing-based learning difficulty that affects the ability to produce legible and coherent written work. Individuals with dysgraphia may struggle with handwriting, spelling, grammar, and organization, leading to difficulties in written communication and academic performance.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects attention, focus, and self-control. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with paying attention, staying organized, and controlling impulsive behaviors, leading to difficulties in academic, social, and behavioral settings.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
ASD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social communication, interaction, and behavior. Individuals with ASD may struggle with understanding social cues, engaging in reciprocal conversations, and developing relationships, leading to difficulties in social and educational settings.
Causes and Risk Factors
Learning difficulties are a broad range of conditions that affect a person’s ability to learn and process information in the same way as others. The causes of learning difficulties can be complex and varied, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and cognitive factors.
Genetic Factors
- Research has identified several genes associated with learning difficulties, including those involved in language processing, memory, and attention.
- Genetic disorders such as Down syndrome and fragile X syndrome can also lead to learning difficulties.
Environmental Factors
- Exposure to environmental toxins, such as lead or mercury, can damage the developing brain and lead to learning difficulties.
- Prenatal exposure to alcohol or drugs can also have a negative impact on cognitive development.
- Socioeconomic status can also play a role, with children from disadvantaged backgrounds being more likely to experience learning difficulties due to factors such as poor nutrition, lack of access to educational resources, and exposure to stress.
Cognitive Factors
- Cognitive factors, such as processing speed, working memory, and attention, can also contribute to learning difficulties.
- Children with slow processing speed may struggle to keep up with the pace of learning, while those with poor working memory may have difficulty retaining information.
- Attention deficits can also interfere with learning, as children may have difficulty focusing and staying on task.
Risk Factors
- Family history of learning difficulties
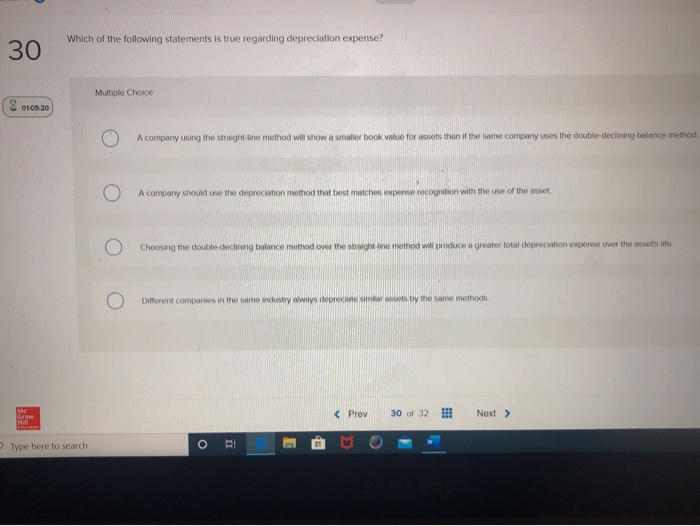
- Low socioeconomic status
- Premature birth
- Exposure to environmental toxins
- Prenatal exposure to alcohol or drugs
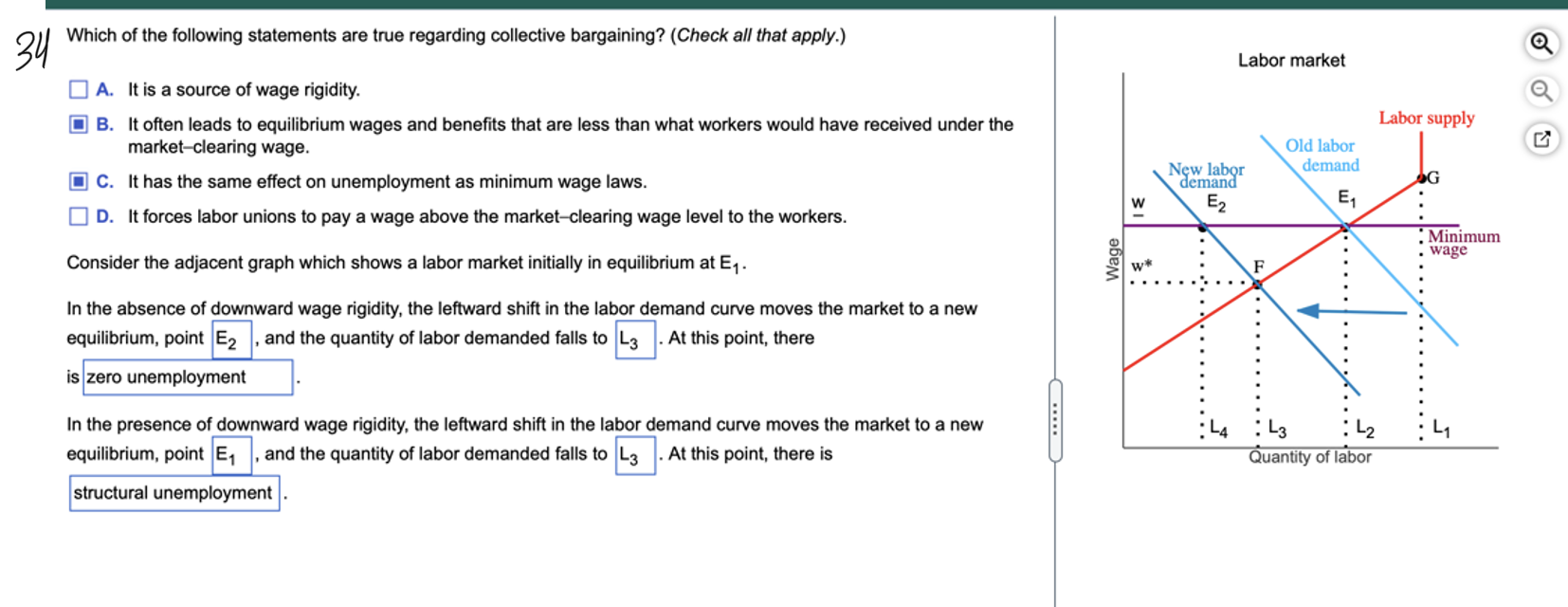
It’s important to note that learning difficulties are not the result of a single cause, but rather a combination of factors. By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with learning difficulties, we can better identify and support children who may be struggling with learning.
Identification and Assessment
Identifying and assessing learning difficulties is crucial for providing appropriate support and interventions. This involves a multidisciplinary approach, utilizing various methods and professionals.
Screening tests are often used as an initial step to identify potential learning difficulties. These tests provide a broad overview of a child’s skills and can help narrow down areas for further assessment.
Cognitive assessments delve deeper into a child’s cognitive abilities, including their memory, attention, language, and problem-solving skills. These assessments can help identify specific strengths and weaknesses that may contribute to learning difficulties.
Educational evaluations focus on a child’s academic performance and progress. They assess a child’s reading, writing, and math skills, as well as their ability to access and use information in an educational setting.
Professionals Involved
The identification and assessment process typically involves a team of professionals, each with their own expertise:
- Teachers: Classroom teachers can provide valuable observations about a child’s behavior, academic progress, and areas of difficulty.
- Psychologists: Psychologists conduct cognitive assessments to evaluate a child’s intellectual abilities and identify any underlying cognitive factors that may contribute to learning difficulties.
- Speech-language pathologists: Speech-language pathologists assess and treat communication disorders, which can impact a child’s ability to learn and participate in educational activities.
4. Interventions and Support
Individuals with learning difficulties can benefit from various interventions and support systems tailored to their specific needs. These interventions aim to address the challenges they face and promote their academic, social, and emotional well-being.
Support for students with learning difficulties may include:
Educational Interventions
- Specialized instruction:Providing tailored teaching methods, materials, and pacing to accommodate different learning styles.
- Assistive technology:Utilizing tools like computers, speech-to-text software, and audiobooks to enhance learning and communication.
- Peer support:Establishing peer tutoring or study groups to foster collaboration and provide emotional support.
- Multi-sensory learning:Incorporating visual, auditory, and kinesthetic activities to engage multiple senses and enhance retention.
Therapeutic Interventions
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT):Helping students develop coping mechanisms, improve problem-solving skills, and manage anxiety related to learning.
- Speech-language therapy:Addressing communication challenges, improving fluency, and enhancing comprehension.
- Occupational therapy:Developing fine motor skills, coordination, and sensory processing abilities.
Environmental Modifications
- Reduced distractions:Creating a quiet and organized learning environment to minimize distractions and improve focus.
- Preferential seating:Providing students with seating arrangements that minimize distractions and optimize attention.
- Extended time:Allowing additional time for completing assignments, tests, and exams to reduce anxiety and promote thoroughness.
Other Support Systems
- Parental involvement:Encouraging parents to actively participate in their child’s education and provide support at home.
- School counselors:Providing emotional support, guidance, and resources to students and families.
- Community organizations:Offering additional support services, such as tutoring, mentoring, and social skills groups.
Legal and Ethical Considerations

Individuals with learning difficulties have specific legal rights and protections that safeguard their access to education and support. The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a federal law that mandates the provision of free and appropriate public education (FAPE) for all students with disabilities, including those with learning difficulties.
IDEA ensures that students receive individualized education plans (IEPs) tailored to their specific needs and that they are provided with appropriate accommodations and supports to succeed in school.
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in the education and support of individuals with learning difficulties. Confidentiality is paramount, and all personal information about a student’s disability must be kept private. Equity is another key consideration, ensuring that all students have equal access to resources and opportunities regardless of their learning difficulties.
Finally, access to resources is essential, and schools and other service providers must ensure that individuals with learning difficulties have access to the necessary resources to support their education and development.
Legal Rights and Protections
- Individuals with learning difficulties have the right to a free and appropriate public education (FAPE) under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA).
- IDEA mandates the development of individualized education plans (IEPs) for students with learning difficulties, outlining their specific needs and accommodations.
- Students with learning difficulties are entitled to appropriate accommodations and supports to help them succeed in school, such as assistive technology, preferential seating, and extra time on tests.
Ethical Considerations
- Confidentiality is crucial, and all personal information about a student’s disability must be kept private.
- Equity is essential, ensuring that all students have equal access to resources and opportunities regardless of their learning difficulties.
- Access to resources is vital, and schools and other service providers must ensure that individuals with learning difficulties have access to the necessary resources to support their education and development.
Technology and Assistive Devices
Technology has become an integral part of our lives, and it can play a vital role in supporting individuals with learning difficulties. Assistive devices and technologies can help them overcome challenges, enhance their learning, and improve their communication.
There are a wide range of technologies and devices available that can assist individuals with learning difficulties. These include:
Text-to-Speech Software
- Converts written text into spoken audio, making it easier for individuals with dyslexia or other reading difficulties to access information.
- Can also help with language learning and pronunciation.
Speech-to-Text Software
- Transcribes spoken words into written text, making it easier for individuals with dysgraphia or other writing difficulties to take notes or create written work.
- Can also be used for dictation and language learning.
Mind Mapping Software
- Helps individuals with visual learning styles to organize and visualize information.
- Can be used for brainstorming, note-taking, and studying.
Adaptive Learning Software
- Tailors learning content to the individual’s needs and pace, making it easier for them to learn at their own level.
- Can provide personalized feedback and support.
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices
- Provide alternative ways for individuals with speech difficulties to communicate.
- Can range from simple picture boards to complex electronic devices.
Future Directions and Research
The field of learning difficulties is constantly evolving, with new research and advancements emerging all the time. These advancements are helping us to better understand learning difficulties and develop more effective interventions and support for individuals who experience them.
One of the most important areas of future research is the development of early identification and intervention strategies. Early identification is key to ensuring that individuals with learning difficulties receive the support they need as early as possible, which can make a significant difference in their long-term outcomes.
Emerging Technologies
Another important area of research is the use of technology to support individuals with learning difficulties. Technology can be used to provide individualized instruction, support communication, and promote social interaction. As technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective ways to use it to support individuals with learning difficulties.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to develop new tools for identifying and assessing learning difficulties.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are being used to create immersive learning experiences that can be tailored to the needs of individual learners.
- Assistive technology devices, such as speech-to-text software and text-to-speech software, are becoming increasingly sophisticated and affordable, making them more accessible to individuals with learning difficulties.
FAQ Section: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Regarding Learning Difficulties
What are the common types of learning difficulties?
Learning difficulties can manifest in various ways, including dyslexia, dyscalculia, dysgraphia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
What causes learning difficulties?
The causes of learning difficulties can be genetic, environmental, or cognitive. Factors such as premature birth, family history, and socioeconomic status can also contribute to the development of learning difficulties.
How are learning difficulties diagnosed?
Learning difficulties are typically diagnosed through a combination of screening tests, cognitive assessments, and educational evaluations conducted by professionals such as teachers, psychologists, and speech-language pathologists.