What type of tool is the hazard vulnerability analysis? This question opens up a fascinating realm of inquiry into the methods and techniques used to assess the susceptibility of communities and ecosystems to natural and human-induced hazards. By exploring the concept of hazard vulnerability analysis, we embark on a journey to understand how these tools empower us to mitigate risks, enhance resilience, and promote sustainable development.
Hazard vulnerability analysis serves as a vital instrument for disaster preparedness, risk management, and land-use planning. It equips decision-makers with the knowledge to identify vulnerable areas, prioritize mitigation strategies, and allocate resources effectively. As we delve into the intricacies of this field, we will uncover the types of tools available, the methodologies employed, and the challenges encountered in conducting hazard vulnerability analysis.
Definition of Hazard Vulnerability Analysis: What Type Of Tool Is The Hazard Vulnerability Analysis

Hazard vulnerability analysis is a systematic process of identifying and assessing the potential impacts of hazards on a community or region. It involves evaluating the likelihood and severity of different types of hazards, as well as the vulnerability of the community to these hazards.
A hazard vulnerability analysis is a tool that helps identify and assess the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with a particular hazard. Like the paint bucket tool in an image editing software, it allows you to fill in areas with specific values or colors, in this case, identifying and assessing potential risks and vulnerabilities.
Examples of different types of hazards include natural hazards (e.g., earthquakes, floods, hurricanes), technological hazards (e.g., industrial accidents, transportation accidents), and societal hazards (e.g., terrorism, civil unrest).
Purpose and Benefits
The purpose of conducting a hazard vulnerability analysis is to help communities understand their risks and vulnerabilities, and to develop strategies to reduce their vulnerability and mitigate the potential impacts of hazards.
A hazard vulnerability analysis is a tool that helps identify and assess the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with a particular hazard. It can be used to prioritize mitigation efforts and develop emergency response plans. If you’re experiencing issues with the Webroot tool, you can uninstall webroot tool and explore alternative options.
Nevertheless, hazard vulnerability analysis remains a valuable tool for assessing and managing risks associated with natural disasters and other hazards.
- Benefits of conducting a hazard vulnerability analysis include:
- Improved understanding of the risks and vulnerabilities of a community
- Identification of priority areas for risk reduction and mitigation
- Development of more effective emergency response plans
- Increased community resilience to hazards
Types of Hazard Vulnerability Analysis Tools
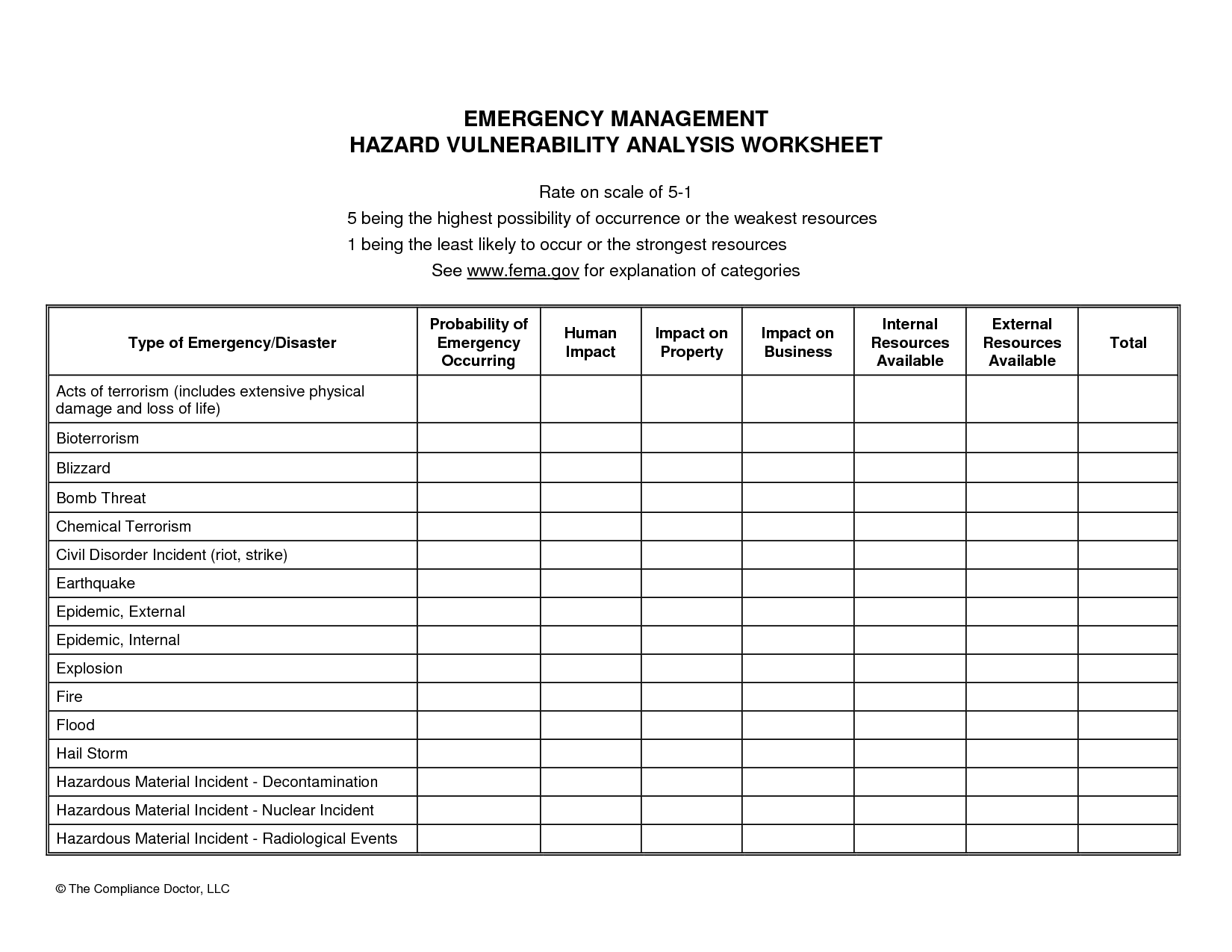
Hazard vulnerability analysis tools are diverse, each with unique capabilities and limitations. Understanding the types of tools available can help you select the most appropriate one for your specific needs.
Open-Source Tools
- HAZUS-MH:A comprehensive tool developed by FEMA for natural hazard risk assessment. It includes modules for earthquake, flood, wind, and hurricane analysis.
- OpenQuake:A platform for probabilistic seismic hazard assessment. It allows users to create and analyze seismic hazard maps.
- CatRisk:A software package for natural hazard and risk assessment. It supports various hazard types, including earthquakes, floods, and landslides.
Commercial Tools
- RMS RiskLink:A proprietary tool used by insurance companies to assess natural hazard risk. It provides detailed analysis of potential losses.
- AIR Worldwide Touchstone:Another proprietary tool used for natural hazard risk assessment. It offers advanced modeling capabilities and supports multiple hazard types.
- EQECAT:A comprehensive tool for earthquake risk assessment. It includes features for scenario-based analysis and probabilistic hazard modeling.
Methods for Conducting Hazard Vulnerability Analysis
Conducting a comprehensive hazard vulnerability analysis requires a systematic approach involving several key steps. These steps aim to identify, assess, and prioritize potential hazards and their impacts on specific communities or assets.
Various methodologies and approaches can be employed in hazard vulnerability analysis, each with its advantages and limitations. The selection of the appropriate methodology depends on the specific objectives, data availability, and resources of the analysis.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection and analysis play a crucial role in hazard vulnerability analysis. Data on hazards, exposed elements, and vulnerability factors must be gathered from various sources, including historical records, scientific studies, and stakeholder consultations.
Data analysis involves processing and interpreting the collected data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. This analysis helps in understanding the likelihood and severity of hazards, as well as the susceptibility and resilience of exposed elements.
Applications of Hazard Vulnerability Analysis

Hazard vulnerability analysis is a valuable tool for various sectors, including disaster preparedness, risk management, and land-use planning. It helps mitigate the impacts of natural and man-made hazards, making communities more resilient and sustainable.
Role in Disaster Preparedness
- Identifying vulnerable areas and populations helps disaster response teams prioritize resources and develop evacuation plans.
- Assessing infrastructure resilience helps identify critical facilities that need reinforcement or relocation to ensure continuity of essential services.
Role in Risk Management, What type of tool is the hazard vulnerability analysis
- Quantifying the potential losses from hazards helps insurance companies determine risk premiums and design mitigation strategies.
- Informing risk-based land-use planning helps avoid development in high-risk areas, reducing future losses.
Role in Land-Use Planning
- Delineating hazard zones helps regulate land use and development, preventing construction in vulnerable areas.
- Identifying safe development areas ensures the long-term sustainability of communities while minimizing disaster risks.
Challenges and Limitations of Hazard Vulnerability Analysis
Hazard vulnerability analysis is a valuable tool for assessing the potential impacts of hazards on communities and infrastructure. However, there are also some challenges and limitations associated with this type of analysis.
One challenge is the difficulty in accurately predicting the likelihood and severity of future hazards. This is due to the fact that hazards are often rare events, and there may be limited historical data available to inform the analysis. Additionally, the impacts of hazards can be highly variable, depending on factors such as the location, intensity, and duration of the event.
Another challenge is the difficulty in quantifying the vulnerability of communities and infrastructure to hazards. This is due to the fact that vulnerability is a complex concept that can be influenced by a wide range of factors, including social, economic, and environmental conditions.
Factors Affecting Accuracy and Reliability
- Data availability:The accuracy and reliability of hazard vulnerability analysis is dependent on the availability of accurate and up-to-date data. This includes data on hazards, vulnerability, and the potential impacts of hazards.
- Model selection:The choice of model used to conduct the analysis can also affect the accuracy and reliability of the results. There are a variety of different models available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Assumptions:The assumptions made in the analysis can also affect the accuracy and reliability of the results. These assumptions should be clearly stated and justified.
Addressing Challenges
There are a number of ways to address the challenges and limitations of hazard vulnerability analysis. These include:
- Using multiple data sources:By using multiple data sources, analysts can increase the accuracy and reliability of their results. This can include using historical data, scientific models, and expert opinion.
- Using a variety of models:By using a variety of models, analysts can explore the sensitivity of their results to different assumptions. This can help to identify the most robust and reliable results.
- Conducting sensitivity analysis:Sensitivity analysis can be used to identify the factors that have the greatest impact on the results of the analysis. This can help to identify the most important factors to consider when making decisions about hazard mitigation.
Best Practices for Hazard Vulnerability Analysis
Effective hazard vulnerability analysis is crucial for mitigating risks and enhancing community resilience. Here are some best practices to guide you:
Data Collection:
- Gather comprehensive data on hazards, exposed elements, and vulnerability factors.
- Utilize multiple data sources, including historical records, scientific studies, and local knowledge.
- Ensure data accuracy and reliability by verifying sources and conducting field surveys.
Analysis:
- Employ appropriate analytical techniques to assess hazard likelihood, exposure, and vulnerability.
- Consider both quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Use spatial analysis tools to identify areas at high risk and vulnerable populations.
Interpretation:
- Interpret results carefully, considering uncertainties and limitations.
- Communicate findings clearly and effectively to stakeholders.
- Identify actionable recommendations for risk reduction and vulnerability mitigation.
Stakeholder Engagement:
- Involve stakeholders throughout the process, including community members, local authorities, and emergency responders.
- Seek their input on hazard identification, vulnerability assessment, and risk management strategies.
- Foster collaboration and consensus-building to ensure that analysis results are widely accepted and supported.
Emerging Trends in Hazard Vulnerability Analysis
The field of hazard vulnerability analysis is constantly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging to improve our understanding of how vulnerable communities are to natural disasters. Some of the most important trends in hazard vulnerability analysis include:
- The use of GIS and remote sensing: GIS (geographic information systems) and remote sensing technologies allow us to collect and analyze data on a wide range of factors that can contribute to vulnerability, such as land use, population density, and infrastructure.
- The integration of climate change considerations: Climate change is expected to increase the frequency and severity of many natural disasters, so it is important to consider climate change impacts when conducting hazard vulnerability analysis.
Integration of Climate Change Considerations
Climate change is expected to have a significant impact on the frequency and severity of natural disasters, so it is important to consider climate change impacts when conducting hazard vulnerability analysis. Some of the specific ways that climate change can affect vulnerability include:
- Increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
- Causing sea levels to rise, which can increase the risk of flooding in coastal areas.
- Changing the distribution of plant and animal species, which can disrupt ecosystems and make communities more vulnerable to natural disasters.
Detailed FAQs
What are the different types of hazard vulnerability analysis tools?
Hazard vulnerability analysis tools vary widely, encompassing qualitative and quantitative approaches. Qualitative tools rely on expert judgment and stakeholder input, while quantitative tools utilize data and models to assess vulnerability.
How do you conduct a hazard vulnerability analysis?
Conducting a hazard vulnerability analysis involves several steps, including hazard identification, vulnerability assessment, risk estimation, and mitigation planning. Data collection, stakeholder engagement, and analysis are crucial components of the process.
What are the challenges associated with hazard vulnerability analysis?
Challenges in hazard vulnerability analysis include data availability, accuracy, and uncertainty; the complexity of natural and human systems; and the need for stakeholder involvement and communication.