What letter grade is an 82? The answer, unfortunately, isn’t as simple as a quick conversion chart. While an 82 might seem like a solid score, its translation into a letter grade can vary significantly depending on the specific grading scale used.
This ambiguity stems from the diverse approaches to grading adopted by different schools, courses, and even individual instructors.
Understanding the nuances of grading systems is crucial for students to accurately gauge their academic performance. This article delves into the complexities of letter grades, exploring the factors that influence the conversion of an 82 into a letter grade, and provides insights into how students can effectively communicate with instructors about grading expectations.
Understanding Letter Grades

Letter grades are a common method of evaluating student performance in educational settings. They provide a concise and standardized way to communicate academic achievement to students, parents, and other stakeholders.
The Purpose and Significance of Letter Grades
Letter grades serve several important purposes in education:
- Assessment of Learning:Letter grades provide a quantifiable measure of a student’s understanding of course material and their ability to apply that knowledge. They offer a clear snapshot of a student’s progress and mastery of specific skills.
- Communication of Achievement:Letter grades act as a standardized language for communicating student performance to various parties, including parents, teachers, and potential employers. They provide a concise and readily understandable representation of academic standing.
- Motivation and Feedback:Letter grades can serve as a motivating factor for students, encouraging them to strive for improvement. They also provide feedback on strengths and weaknesses, allowing students to identify areas for growth.
- Basis for Decisions:Letter grades are often used as a basis for making important decisions, such as awarding scholarships, granting admission to universities, or determining eligibility for certain programs.
Common Letter Grading Scales
Letter grading scales vary depending on the educational institution and level of study. Some common scales include:
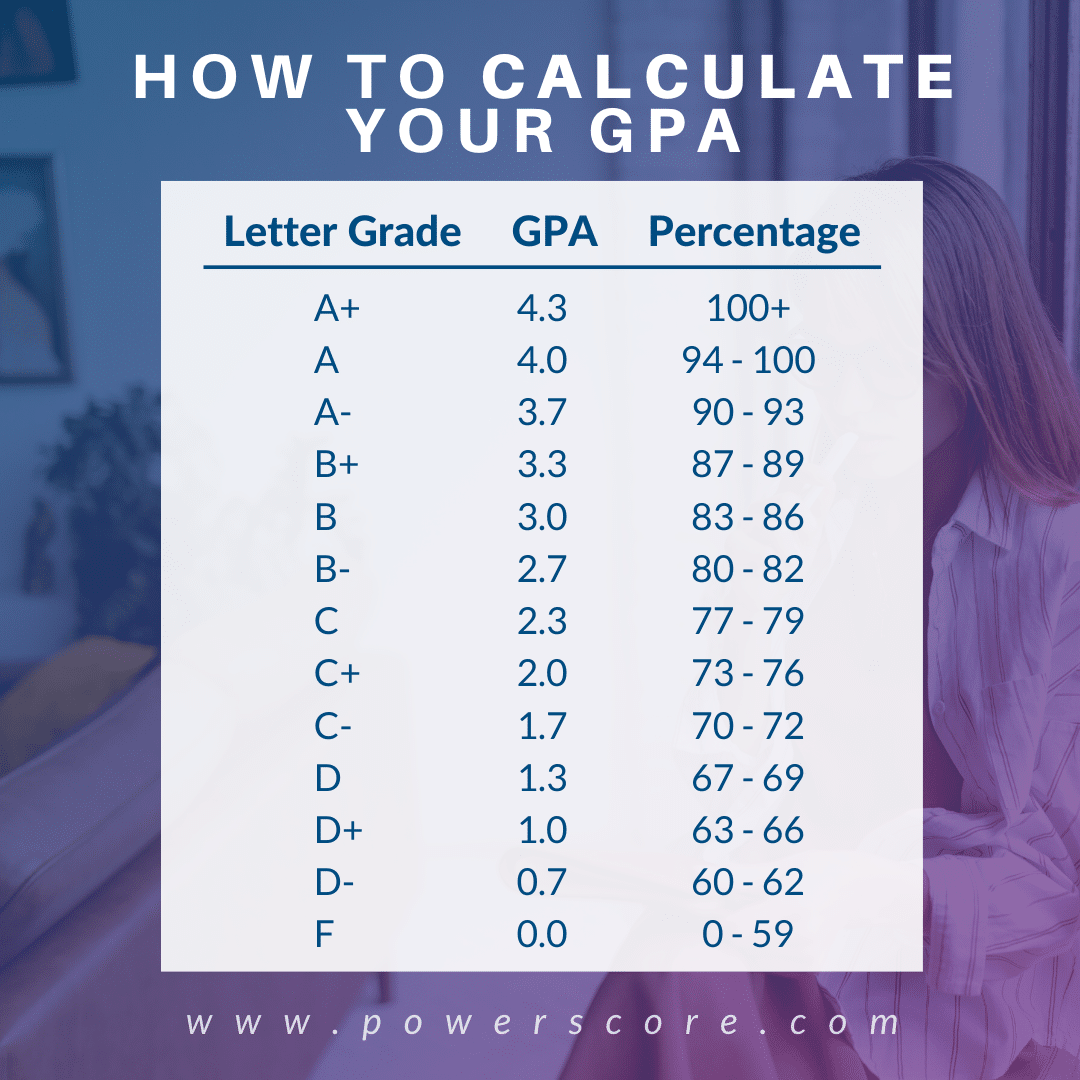
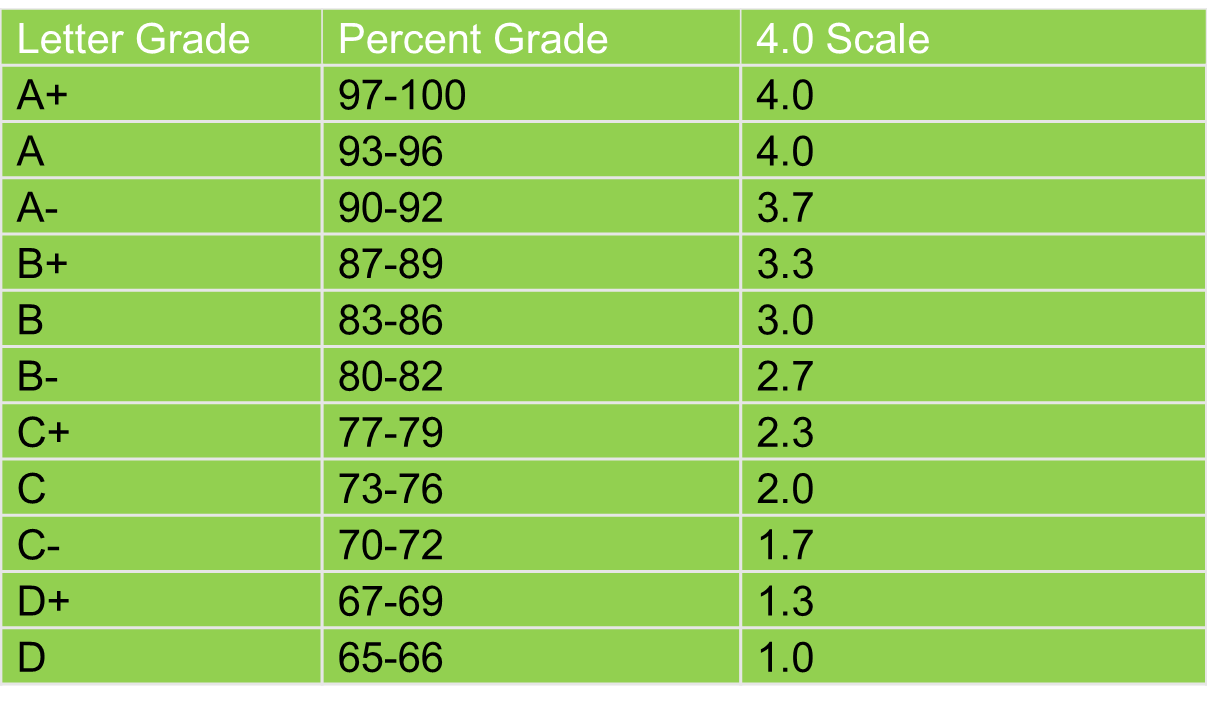
- A-F Scale:This is the most widely used grading scale, with letter grades ranging from A (highest) to F (lowest). Each letter grade typically corresponds to a specific percentage range, with A representing 90-100%, B representing 80-89%, and so on.
- 4.0 GPA System:This system assigns numerical values to letter grades, with A=4.0, B=3.0, C=2.0, D=1.0, and F=0.0. The GPA (Grade Point Average) is calculated by averaging the numerical values of all grades earned in a specific period.
Interpreting a Score of 82

An 82, in the context of a typical grading scale, sits comfortably within the “B” range. This score indicates strong performance and a good understanding of the subject matter. However, the precise letter grade assigned to an 82 can vary depending on the specific grading scale used by the instructor or institution.
Factors Influencing Letter Grade
The letter grade assigned to an 82 can be influenced by several factors:
- Grading Scale:Different institutions and instructors use different grading scales. Some may assign a “B+” to an 82, while others may assign a “B.” It’s crucial to understand the specific grading scale being used to interpret the score accurately.
- Class Average:The average score in a class can also impact the letter grade assigned. If the class average is high, an 82 may be considered a lower “B.” Conversely, if the average is low, an 82 may be considered a higher “B.”
- Curve:Some instructors use a curve to adjust grades, which can influence the letter grade assigned to an 82. A curve can raise or lower the score based on the overall performance of the class.
- Extra Credit:Extra credit opportunities can potentially raise a score of 82 to a higher letter grade. However, the impact of extra credit varies depending on the specific assignment and the instructor’s policy.
Factors Affecting Letter Grades

While a score of 82 might generally fall within the ‘B’ range, it’s crucial to understand that letter grades aren’t universally standardized. Numerous factors can influence the final grade assigned, making it essential to consider the broader context.
Grading Scales and Variations
Different educational institutions and even individual courses may employ distinct grading scales, leading to potential variations in the letter grade assigned to a score of 82.
| Grading Scale | Letter Grade for 82 |
|---|---|
| Traditional 10-Point Scale | B |
| 7-Point Scale | B+ |
| Standard Deviation-Based Scale | May vary depending on class distribution |
For instance, a traditional 10-point scale would likely assign an ‘B’ to an 82, while a 7-point scale might award a ‘B+.’ A grading system based on standard deviation could result in a different letter grade, depending on the overall distribution of scores within the class.
An 82 typically translates to a B- in most grading systems, signifying satisfactory performance. While this might not be the highest achievement, it demonstrates a solid understanding of the material. When crafting a letter of recommendation for a candidate with such a grade, it’s crucial to highlight their strengths and potential, drawing upon specific examples of their work and contributions.
Referencing resources such as how to write a letter of recommendation army can provide valuable guidance on structuring and crafting compelling recommendations. Ultimately, the letter should convey a positive assessment of the candidate’s abilities, even if their numerical grade is not exceptional.
Contextualizing the Grade: What Letter Grade Is An 82
While an 82 might seem like a solid score, it’s crucial to remember that letter grades are not always straightforward conversions of numerical scores. Several factors can influence the final letter grade, making an 82 potentially translate to a range of grades.
The final grade often reflects a broader picture than just a single numerical score.
Understanding Grading Criteria
The grading criteria used in a particular course play a significant role in determining the final letter grade. Each instructor may have their own unique system for evaluating student performance, which can vary considerably. For example, some instructors may place a heavier emphasis on exams, while others may prioritize class participation or the completion of specific projects.
Understanding the specific weight assigned to each component of the course is essential for students to accurately assess their progress and potential grade.
It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the grading rubric, syllabus, or any other documentation outlining the specific criteria and weighting of different assessments.
Impact of Additional Factors
Beyond the numerical score, several additional factors can influence the final letter grade. These factors can include:
- Class Participation:Active engagement in class discussions, asking insightful questions, and contributing valuable ideas can positively impact the final grade, even if the numerical scores are slightly lower.
- Assignments and Projects:The quality and completion of assignments and projects can significantly impact the final grade. Even if the numerical score on a test is high, poor performance on assignments can lower the overall grade.
- Attendance:Regular attendance is often a factor in determining the final grade, particularly in courses that involve frequent discussions or group work.
- Improvement and Effort:Some instructors may consider a student’s overall improvement and effort throughout the course, even if the numerical scores don’t reflect exceptional performance.
For instance, a student might receive a B+ in a course despite earning an 82 on the final exam. This could be due to consistent participation in class discussions, excellent performance on assignments, and a strong demonstration of understanding throughout the semester.
Conversely, a student with an 82 on the final exam might receive a B if they struggled with other assignments or had poor attendance.
Communicating with ors
Maintaining clear and effective communication with instructors (ors) is crucial for student success. It fosters understanding, addresses concerns, and ensures a productive learning environment. This section explores the art of communication with ors, offering strategies to navigate potential discrepancies and ensure a clear understanding of grading expectations.
Understanding Grading Policies
The grading policies of a particular course provide a framework for evaluating student performance. These policies Artikel the criteria used to assess assignments, exams, and overall participation. To understand the grading policies, students should carefully review the course syllabus. The syllabus typically includes information about:
- Weighting of assignments and exams: This clarifies the relative importance of different components of the course.
- Grading scale: This specifies the numerical range corresponding to each letter grade.
- Late submission policies: This Artikels the consequences of submitting assignments after the deadline.
- Academic integrity guidelines: This emphasizes the importance of honest work and the consequences of plagiarism.
In addition to the syllabus, students can proactively seek clarification from ors regarding any aspects of the grading policies that are unclear.
Seeking Clarification
Seeking clarification from ors about a specific grade or grading system is a proactive approach to ensuring understanding. This can be done through various channels, such as:
- Office hours: Most instructors schedule dedicated office hours to provide individualized support to students. This is an excellent opportunity to discuss specific concerns about a grade or the grading system.
- Email: Email communication allows for a written record of the discussion and can be used to follow up on inquiries.
- Course discussion forums: Some courses utilize online forums for communication. This platform can be used to ask questions about grades or grading policies, and other students might also benefit from the discussion.
When seeking clarification, students should be respectful, specific, and concise in their communication. They should clearly state their question or concern, providing relevant context or examples to support their inquiry.
Communicating Grade Expectations, What letter grade is an 82
Effective communication about grade expectations involves a two-way exchange between students and ors. Students should proactively engage with ors to understand the expectations for assignments and exams. This can be done through:
- Asking clarifying questions: Before starting an assignment, students should ask ors for clarification about the specific requirements, expectations, and assessment criteria. This ensures that their understanding aligns with the instructor’s vision.
- Seeking feedback: Students should actively seek feedback from ors on their work throughout the semester. This can be done through informal discussions, peer reviews, or formal feedback sessions. Feedback provides valuable insights into areas for improvement and helps students understand how their work aligns with the grading criteria.
- Maintaining open communication: Throughout the semester, students should maintain open communication with ors, addressing any concerns or questions that arise regarding grades or assignments. This proactive approach helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures a productive learning experience.
Open communication fosters a collaborative learning environment where students feel comfortable seeking clarification and addressing any discrepancies in grade expectations.
Detailed FAQs
What is a typical grading scale?
A typical grading scale uses letter grades like A, B, C, D, and F, with each letter corresponding to a numerical range. For example, an A might be 90-100, a B might be 80-89, and so on.
Can an 82 ever be an A?
Yes, in some cases, an 82 might be considered an A, especially if the grading scale is more lenient or if the instructor adjusts the curve.
What if my teacher doesn’t provide a specific grading scale?
If the grading scale is not explicitly defined, it’s best to reach out to the instructor directly to clarify their grading policies and expectations.
How can I improve my chances of getting a higher grade?
Focus on understanding the course material, actively participate in class, complete all assignments thoroughly, and seek help when needed. Building a strong foundation in the subject can lead to improved grades.