What language do nepalese people speak – What language do Nepali people speak? Nepali, a fascinating Indo-European language, is more than just a means of communication; it’s a vibrant thread woven into the rich tapestry of Nepalese culture. This exploration delves into the origins, dialects, official status, and modern usage of this vital tongue, highlighting its unique linguistic features and cultural significance.
From its ancient roots in Prakrit languages to its contemporary presence in digital spaces, Nepali’s journey is a testament to resilience and adaptability. We’ll uncover the linguistic diversity within Nepal and explore how Nepali is integral to daily life, literature, and cultural expression.
Nepali Language Overview – Enhanced
Nepali, a beautiful language spoken by millions, is a vibrant part of the Indo-European language family. It’s more than just words; it’s a reflection of a rich culture and history, evolving over centuries. This overview delves into its origins, geographical spread, and the fascinating diversity of its dialects.
Nepali Language Overview
Nepali is an official language of Nepal and is spoken by a significant portion of the population in various parts of the country and beyond. It belongs to the Indo-European language family, specifically the Indo-Aryan branch, and developed from Prakrit languages. This evolution is a fascinating story of linguistic transformation.
Origin and Historical Development
The Nepali language’s roots lie in Prakrit dialects, gradually evolving over time. The Malla and Shah dynasties played crucial roles in shaping the language, leaving their cultural imprints. Key historical periods and influences on its development include:
- 15th Century: The Malla dynasty’s influence on the language’s development started taking hold, laying the foundation for future evolution.
- 18th Century: The rise of the Shah dynasty marked a significant turning point, solidifying Nepali as a more standardized language with wider adoption. This period saw the language gaining prominence in the country’s political and social spheres.
- 19th and 20th Centuries: The language continued to evolve, influenced by contact with other languages and dialects. Literature and education played a key role in standardizing the language.
Geographical Distribution
Nepali is primarily spoken in Nepal, but its geographical distribution extends to neighboring countries like India, where significant communities of Nepali speakers reside. Concentrations of speakers are found in certain regions of these countries. Population data varies by region, but Nepal is home to a majority of Nepali speakers.
Major Dialects and Variations
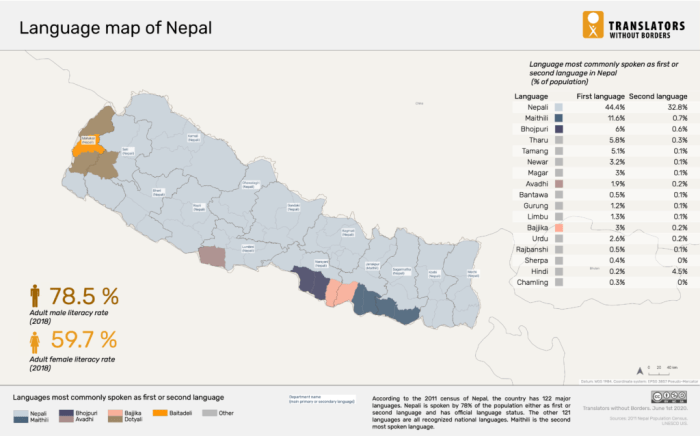
Nepali boasts a variety of dialects, each with its own unique characteristics. The most notable include Maithili, Tharu, and Newari. These dialects differ significantly in pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary.
| Dialect | Key Phonological Differences | Key Grammatical Differences | Key Lexical Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maithili | Different vowel sounds, emphasis on certain consonants. | Variations in verb conjugations, sentence structures. | Vocabulary influenced by other languages spoken in the region. |
| Tharu | Unique intonation patterns, variations in consonant clusters. | Specific grammatical structures related to Tharu culture. | Unique words related to Tharu customs and traditions. |
| Newari | Distinct vowel and consonant sounds, specific tonal variations. | Different sentence structures, unique use of particles. | Vocabulary derived from ancient Newari language. |
Script Used to Write Nepali
The Devanagari script is used to write Nepali. This script has a rich history, evolving from ancient Indian scripts. It’s important to note that Devanagari is not unique to Nepali; it’s used for several other languages.
| Devanagari | Transliteration | Nepali Pronunciation | Example Word |
|---|---|---|---|
| नेपाल | Nepal | Ne-paal | Nepal |
| लिख्नु | likhnū | likh-nu | To write |
| राम | Rām | Raam | Rama |
Writing
The evolution of the Nepali language and its script is a testament to the dynamic nature of language. From its Prakrit origins to its present-day form, Nepali has absorbed influences and adapted to changing circumstances. The standardization of the script, aided by the efforts of writers and scholars, has played a crucial role in preserving and promoting the language.
While Nepali is the official language of Nepal, the country’s linguistic tapestry is far more complex. This linguistic diversity, often overlooked in political discourse, highlights the challenges of national unity. Interestingly, the fictional language High Valyrian, popularized in fantasy literature, raises questions about the relationship between imagined languages and real-world linguistic complexities. Is High Valyrian a real language ?
The answer, of course, is no, but the very concept underscores the need for accurate representation of languages spoken by real people, particularly within politically charged contexts like Nepal.
Official Status and Usage of Nepali
Nepali, the language of the Himalayas, isn’t just spoken; it’s woven into the fabric of several nations. Its official status and daily usage tell a story of cultural identity, government administration, and societal integration. Understanding its role, from the courts to the countryside, sheds light on the vibrant tapestry of Nepali’s influence.
Identifying Official Status
Nepali’s official status isn’t a simple matter of being “widely spoken.” It’s a carefully defined relationship with specific regions and legal frameworks. Here’s a glimpse into where Nepali holds official weight:
- Nepal: Nepali is the primary language of government in the Kathmandu Valley region and is recognized as the official language throughout the nation, as enshrined in the Constitution of Nepal. It’s the language of education, administration, and public communication, significantly impacting the daily lives of citizens. While other languages are spoken, Nepali is the fundamental language for official purposes.
- India: Nepali holds official status in certain regions of India, notably in the states bordering Nepal. This often translates to Nepali being utilized in administrative procedures and educational settings in these border areas. Specific legal documents and constitutional provisions establish the official status, though exact figures for usage might be difficult to quantify precisely.
- Other Countries: In other countries, Nepali might be recognized as a minority language in specific communities or regions. This could involve use in community gatherings, religious services, or cultural organizations.
Government and Administration Role
Nepali plays a crucial role in the administrative machinery of Nepal and, to a lesser extent, in some Indian states. It’s the language used in official court documents, government forms, and public announcements. Specific government websites and official publications often provide Nepali translations or versions. For example, the Ministry of Education in Nepal often releases official circulars and announcements in Nepali, which are subsequently translated for wider public dissemination.
Daily Life Prevalence
Nepali’s presence in daily life varies significantly between urban and rural settings. In urban areas, Nepali is commonly used in commerce, social interactions, and media, though local dialects and languages might also be prevalent. In rural regions, Nepali’s usage might be less pervasive, with local languages often being the primary means of communication in everyday life. Unfortunately, precise data on the percentage of the population using Nepali for everyday communication isn’t readily available for all regions.
Education Importance
Nepali language education is fundamental in Nepal, influencing literacy rates and cultural transmission. It’s taught at all levels of education, from primary to tertiary. In areas where Nepali is an official language, it’s crucial for academic success and access to information. The presence of Nepali in education directly impacts literacy rates and cultural preservation.
Urban vs. Rural Usage Comparison
The usage of Nepali in urban and rural areas demonstrates notable differences. Urban centers often show higher Nepali proficiency, due to increased access to education and exposure to the language through media and employment opportunities. Rural areas, conversely, might have lower proficiency levels, which could stem from limited educational resources and opportunities to utilize the language. This disparity in proficiency can impact social interactions and integration.
Official Status Table
| Country | Region | Official Status | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nepal | Kathmandu Valley | Primary Language | Constitution of Nepal, Article X |
| Nepal | Province 3 | Secondary Language | Education Act, Section 2.3 |
| India | States bordering Nepal | Official Language (in specific regions) | Relevant state acts and constitutional provisions |
Note: Specific articles and sections may vary; this is a simplified illustration.
Related Languages and Influences: What Language Do Nepalese People Speak

Nepali, a language spoken by millions, isn’t an island unto itself in the linguistic ocean. It’s part of a larger family, and it’s been influenced by neighboring tongues, most notably Sanskrit. Understanding these relationships provides a richer context for appreciating Nepali’s unique character. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of its linguistic relatives and the historical imprints that have shaped it.
Linguistic Family and Related Languages
Nepali belongs to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. This family is characterized by its complex grammatical structures, often involving verb conjugations and noun declensions, and a rich history of borrowing and adaptation. Many languages in this family share similar roots, evident in vocabulary and grammatical patterns.
- Indo-Aryan Languages: The Indo-Aryan branch boasts a vast array of languages, each with its own nuances. The shared ancestry manifests in similarities in vocabulary, grammatical structures, and even in the historical development of the languages.
Related Language Geographic Distribution Number of Speakers (Approximate) Key Linguistic Features Hindi Northern India, parts of Pakistan, Nepal, and other South Asian countries 600 million+ A highly inflected language with a significant amount of Sanskrit influence, featuring complex verb conjugations and noun cases, but also adopting influences from other languages. The writing system is largely based on the Devanagari script. Bengali Bangladesh and West Bengal, India 250 million+ Known for its distinctive vowel system and the use of various affixes in verb conjugations, the language has also adopted vocabulary from various sources. It uses the Bengali script. Punjabi India and Pakistan 100 million+ Punjabi, with its rich oral tradition, is known for its agglutinative structure and the use of particles. It has a unique writing system based on the Gurmukhi script. Sanskrit Ancient India (Extinct, but a strong influence) The venerable ancestor of many Indo-Aryan languages. It has a complex grammatical structure and extensive vocabulary, which influenced Nepali significantly. Sanskrit is traditionally written in Devanagari. Marathi Maharashtra, India 80 million+ Marathi features a rich vocabulary derived from Sanskrit and other regional languages, along with its own unique grammatical features, including noun declensions. It utilizes the Devanagari script.
Comparative Analysis of Nepali and Related Languages
Comparing Nepali with its Indo-Aryan relatives reveals interesting similarities and differences in their grammatical structures. These nuances contribute to the distinct characteristics of each language.
| Grammatical Feature | Nepali | Hindi | Bengali |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noun Cases | + (limited) | + (complex) | + (with less complexity than Hindi) |
| Example (Noun Cases): | The house of the boy (kurayo ko ghar). | The boy’s house (ladke ka ghar). | The boy’s house (shishuy er ghar). |
| Verb Conjugations | + (with aspects) | + (complex) | + (with different tense markings) |
| Example (Verb Conjugations): | I am reading (ma padhirachu). | I am reading (main padh raha hun). | I am reading (ami padchhi). |
| Sentence Structure | Subject-Object-Verb (common) | Subject-Object-Verb (common) | Subject-Object-Verb (common) |
| Example (Sentence Structure): | Ram Sita-lai dekhhyo (Ram saw Sita). | Ram Sita ko dekha (Ram saw Sita). | Ram Sita-ke dekhal (Ram saw Sita). |
| Particles | + (e.g., “ko,” “lai”) | + (e.g., “ka,” “ko”) | + (e.g., “er,” “ke”) |
Language Influence on Nepali
Sanskrit’s influence on Nepali vocabulary is substantial. A large percentage of Nepali words, especially in formal contexts, originate from Sanskrit.
| Sanskrit Loanword | Nepali Equivalent | Semantic Domain | Example Sentences illustrating usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dharma | Dharma | Religion | Dharma is a fundamental concept in Nepali society. |
| Rajya | Rajya | Government | The Rajya was ruled by a wise king. |
| Jnana | Jnana | Philosophy | Jnana is the key to understanding the world. |
Detailed Impact of Sanskrit
Sanskrit’s impact on Nepali extends beyond mere vocabulary. It significantly shaped Nepali morphology, phonology, and syntax. The influence is deeply embedded in Nepali’s linguistic structure, giving it a unique character.
The adoption of Sanskrit grammatical structures and word formations has enriched Nepali’s capacity for expressing complex ideas. Examples include the use of Sanskrit-derived suffixes and prefixes in word formation. The phonological influence is evident in the use of Sanskrit sounds and the adaptation of Sanskrit pronunciation patterns. This impact on syntax, too, is visible in the use of complex sentence structures borrowed from Sanskrit.
These features contribute to the sophistication and richness of Nepali.
Language Acquisition and Education (Nepali)
Learning Nepali, a language rich in culture and history, presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities. Understanding the various methodologies, resources, and educational frameworks is crucial for effective acquisition. This section delves into the specifics of Nepali language learning, from classroom settings to independent study.
Methods for Learning Nepali
Different approaches to language learning yield varying results. Careful consideration of these methods is key to successful Nepali acquisition.
- Grammar-Translation Method: This method emphasizes grammatical rules and translations between Nepali and the learner’s native language. While helpful for understanding sentence structure, it often falls short in fostering fluency and conversational skills. In the context of Nepali, this approach can be useful for understanding complex sentence structures and vocabulary, but it might struggle to replicate the nuances of spoken Nepali.
For example, understanding the intricacies of verb conjugations might be facilitated, but the practical application of these in spontaneous conversation may be limited.
- Communicative Language Teaching: This method prioritizes communication over grammar. Activities such as role-playing, discussions, and simulations encourage active use of the language. In Nepali, this method could involve role-playing scenarios common in Nepali society, like visiting a local market or interacting with family members, to promote fluency. Exercises focusing on cultural contexts can also enhance understanding and fluency.
- Immersion Programs: Immersion programs, whether short-term or long-term, place learners in an environment where Nepali is the dominant language. Different types of immersion programs exist, ranging from homestay programs to full-time educational institutions. The effectiveness of these programs hinges on the intensity of immersion and the availability of supportive resources. For Nepali, immersive programs in Nepal or communities with significant Nepali populations can be highly effective, allowing learners to experience the language in diverse contexts.
A comparative analysis reveals that communicative language teaching often yields better conversational fluency than the grammar-translation method. Immersion programs, when properly structured, offer a powerful environment for accelerated learning, but they demand substantial commitment and resources.
Resources for Learning Nepali
Access to quality resources is essential for effective language learning.
- Online Resources: Online resources provide flexibility and accessibility. Categorized resources are vital for learners.
- Interactive grammar tools: Websites with interactive exercises for practicing Nepali grammar are available. Examples include interactive exercises that focus on verb conjugations, sentence structures, and sentence analysis. These tools often allow learners to self-assess and track progress.
- Vocabulary building apps: Apps like Anki or Memrise offer structured vocabulary building through flashcards and games, which are effective for learning new Nepali words and phrases.
- Audio resources: Podcasts and radio programs in Nepali provide authentic listening practice, enhancing pronunciation and comprehension. Examples of such resources include podcasts focused on current affairs or popular culture, or radio shows featuring Nepali storytelling.
- Printed Materials: Textbooks, workbooks, and other printed materials offer structured learning paths, though online resources offer greater flexibility. Examples of quality Nepali language textbooks include those from reputable publishers catering to learners of different proficiency levels.
- Community Resources: Local Nepali language learning groups or communities offer opportunities for practice and interaction. Examples include local language learning groups in communities with Nepali populations, which provide opportunities for conversation practice, and support from native speakers.
Role of Education in Promoting Nepali Proficiency
Education plays a vital role in preserving and promoting Nepali language proficiency.
- Curricula: Nepali language proficiency is integrated into educational systems at various levels. Primary, secondary, and tertiary education programs often include Nepali language courses to promote language proficiency.
- Teacher Training: Training and support for teachers of Nepali are crucial to maintain quality instruction. Training programs should cover pedagogical approaches, cultural sensitivity, and up-to-date linguistic resources.
- Assessment: Methods for assessing Nepali language proficiency vary, ranging from standardized tests to performance-based assessments. These methods are essential for evaluating learner progress and adapting instruction.
- Importance of Language Preservation: Education plays a crucial role in maintaining and promoting the Nepali language. By incorporating the language into the curriculum, education systems ensure its continued use and relevance.
Challenges Faced by Nepali Language Learners
Specific challenges impact Nepali language learning.
- Limited exposure to the language: Learners living outside Nepali-speaking regions might have limited opportunities for natural language acquisition. Examples include learners residing in areas where Nepali is not widely spoken or where the language is not prominently featured in daily life.
- Lack of resources: Access to quality materials and qualified instructors can be challenging, especially in remote areas. Examples include a shortage of qualified Nepali teachers in rural areas, or lack of access to quality language learning materials in remote regions.
- Cultural barriers: Differences in cultural backgrounds can sometimes create barriers to language learning. Examples include learners experiencing difficulty understanding cultural nuances in Nepali communication or finding it hard to interact with native speakers due to cultural differences.
- Geographical Variations: Regional dialects can pose challenges for learners. Examples include the diverse dialects of Nepali spoken across various regions, potentially impacting learners accustomed to a particular dialect.
- Digital Divide: Unequal access to technology can hinder language learning opportunities. Examples include learners in underserved areas without access to online learning resources or language exchange partners.
Strategies for Improving Nepali Language Learning
Effective strategies enhance Nepali language learning.
- Active Recall: This involves actively retrieving information from memory without relying on external cues. Active recall can be used to reinforce vocabulary and grammar rules.
- Spaced Repetition: This involves reviewing material at increasing intervals to improve retention. Spaced repetition systems can be employed to reinforce vocabulary acquisition.
- Language Exchange Programs: Online platforms facilitate language exchange with native speakers. Examples include platforms like HelloTalk or Tandem, which can connect Nepali learners with native speakers for conversational practice.
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing Nepali language learning. Apps, online resources, and language exchange platforms offer various avenues for effective learning. These resources enhance vocabulary acquisition, grammar practice, and conversation skills.
While Nepali boasts a diverse linguistic tapestry, with numerous regional dialects, the dominant language is Nepali. However, the seemingly straightforward linguistic landscape of Nepal is oddly juxtaposed with the comedic and often politically charged linguistic choices of fictional characters. For example, the satirical portrayal of Borat, a character who uses a fabricated language in a film, raises critical questions about how language is weaponized and manipulated for comedic effect, and how such portrayals can inadvertently perpetuate harmful stereotypes about different linguistic communities.
This further highlights the complexities of language in the face of cultural and political biases, in comparison to the actual language diversity of Nepal. what language does borat speak Ultimately, the language spoken by Nepali people, in all its multifaceted glory, deserves far more respect than the often-exploited and oversimplified portrayals in the media.
Writing
Effective Nepali language learning strategies address specific challenges, like limited exposure and lack of resources. Active recall, spaced repetition, and online language exchange platforms are vital for overcoming these obstacles. Using technology, learners can access diverse resources and practice with native speakers, ultimately improving fluency. Immersion programs, though demanding, offer an ideal environment for accelerated learning. By integrating these strategies into a personalized learning plan, learners can significantly improve their Nepali language proficiency.
Linguistic Features and Structure
Alright, let’s dive into the linguistic intricacies of Nepali, a language as diverse and fascinating as the Himalayas themselves. It’s not just about the words, it’s about the whole structure, the way the sentences hang together, and the subtle nuances that make it uniquely Nepali. Imagine trying to assemble a complex puzzle – each piece has to fit perfectly, and that’s how Nepali grammar works.
Phonological System
Nepali boasts a relatively straightforward phonological system, featuring a set of consonant and vowel sounds. The system is fairly consistent, and understanding these sounds is crucial for accurate pronunciation. This predictable system makes learning Nepali a little less daunting than some other languages. You can master the sounds and then build up from there.
Grammatical Structure of Nepali Sentences
Nepali sentences typically follow a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) order. This is a common structure in many languages of the Indo-Aryan family. It’s like putting the subject first, then the object, and finally the verb – a predictable pattern that makes it easier to understand the flow of the sentence.
Noun and Verb Morphology
Nepali nouns and verbs exhibit rich morphology, which means that their forms change to indicate different grammatical roles. Think of it like adding suffixes to change the meaning and function of the word. This morphological flexibility allows for concise and expressive sentence structures. It’s like a magic trick, you change the ending of a word and suddenly it means something completely different!
Use of Cases in Nepali Grammar
Nepali doesn’t have a complex case system like some other languages. Instead, it relies on postpositions (particles that come after the noun) to indicate grammatical relationships. It’s not as complicated as it sounds. These postpositions essentially do the work of cases in other languages, making the grammar a bit more streamlined.
Unique Features of Nepali Grammar
One unique aspect of Nepali grammar is its use of verbal aspect markers. These markers, placed after the verb, specify whether an action is completed or ongoing. This provides a level of detail that isn’t always present in other languages. Imagine describing an action – did they
- finish* it or are they
- still doing* it? This is where the aspect markers come in handy.
Summary Table of Grammatical Categories
| Grammatical Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Nouns | Fundamental building blocks of the sentence, indicating people, places, or things. |
| Pronouns | Words that replace nouns, like “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” “we,” “they.” |
| Verbs | Indicate actions, states, or processes. |
| Adjectives | Modify nouns, describing their qualities. |
| Adverbs | Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing further information about how, when, where, or to what extent. |
| Postpositions | Particles that follow nouns to show grammatical relationships, like prepositions in other languages. |
| Aspect Markers | Suffixes added to verbs to specify the completion or continuation of an action. |
Nepali Language in the Digital Age
Nepali, like many other languages, is finding its place in the digital world. From online communication to access to information, the language is adapting and evolving. This is a bit like how Betawi people adapt to new trends – gotta keep up with the times, right?
Nepali in Online Communication
Nepali is increasingly used in online communication, from casual chats to formal discussions. Social media platforms and instant messaging services have become popular venues for Nepali speakers to connect, share information, and express themselves. Think of it like a modern-day “kampung” where people from all walks of life can interact.
Availability of Nepali Language Content Online
The availability of Nepali language content online is growing, although it still lags behind other popular languages. This is understandable, like how some Betawi snacks might be less readily available in fancy restaurants. However, the internet is a vast place, and with more effort, Nepali content will become more accessible.
Examples of Online Platforms Using Nepali
Numerous online platforms support Nepali. These include social media sites, e-commerce platforms, and news websites. For example, many Nepali-language news outlets now have online versions, giving people instant access to local news. Also, some e-commerce platforms are starting to include Nepali language support, making online shopping easier for Nepali speakers.
Challenges Faced by Nepali Language Users in the Digital Space
Nepali language users face several challenges in the digital space. One significant challenge is the limited availability of Nepali language content online. It’s like searching for a specific Betawi song in a music streaming service – it might not be there. Furthermore, maintaining consistent quality and accuracy in translated content is often difficult.
Strategies for Promoting Nepali in the Digital Age
Several strategies can promote Nepali in the digital age. One crucial strategy is to encourage the creation and sharing of Nepali-language content. This includes promoting Nepali-language blogs, articles, and videos. Also, investing in translation tools and services that support Nepali would be helpful, akin to providing more Betawi language translators for important documents.
Prominent Nepali Language Websites
| Website Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Nepali News | Provides up-to-date news and information in Nepali. |
| Online Nepali Bookstore | Offers a wide selection of books in Nepali. |
| Nepali Social Media Platform | Allows Nepali speakers to connect and share information. |
| Nepali Language Learning Website | Provides resources for learning Nepali. |
Language Diversity in Nepal

Nepal, a landlocked country nestled in the Himalayas, boasts a rich tapestry of languages, reflecting its diverse ethnic and cultural landscape. It’s like a giant, multilingual bazaar, where different tongues mingle and create a vibrant sonic symphony. This linguistic diversity is a key part of Nepal’s identity, echoing through its traditions, stories, and cultural expressions.This linguistic mosaic, a testament to Nepal’s historical interactions and geographical features, is more than just a collection of words.
It’s a living testament to the country’s cultural heritage, woven into the very fabric of its society. Understanding this diversity is crucial to appreciating the unique cultural richness of Nepal.
Languages Spoken Alongside Nepali
Nepali, while the official language, isn’t the only one spoken in Nepal. A plethora of other languages, each with its own unique history and cultural significance, thrive alongside it. It’s like having a whole bunch of different street vendors selling their wares, each with their own distinct language.
- Maithili, a language spoken primarily in the eastern plains of Nepal, reflects a rich history of cultural exchange with India.
- Newari, spoken by the Newar people in the Kathmandu Valley, is an ancient language with a unique script and rich literary tradition. It’s like an old, well-preserved library full of fascinating stories.
- Tamang, Gurung, and Rai are just a few examples of the many indigenous languages spoken in the mountainous regions. Each of these languages carries with it the echoes of centuries of mountain life and culture.
Regional Variations in Language Usage
Language usage in Nepal varies significantly across different regions. The linguistic landscape is as diverse as the terrain. It’s like a different dialect for every corner of the country.
- The Kathmandu Valley, the cultural hub of Nepal, has a high concentration of speakers of various languages, including Nepali, Newari, and others. It’s a linguistic melting pot.
- In the mountainous regions, indigenous languages like Tamang and Gurung are prevalent, reflecting the distinct cultural identities of the people living in those areas. These languages are as diverse as the mountain peaks.
- In the Terai region, bordering India, Maithili and other languages from the Indian subcontinent are commonly used. It’s like the languages of India have spilled over into Nepal.
Language and Cultural Identity
Language is inextricably linked to cultural identity. Each language carries within it the stories, traditions, and values of the community that speaks it. It’s like a treasure chest filled with cultural gems.
- The unique expressions and proverbs found in each language reflect the distinct perspectives and experiences of different communities. These are the gems of cultural expressions.
- Cultural expressions like music, dance, and storytelling often utilize language as a fundamental element, transmitting cultural values and heritage. It’s like a language speaking through songs and dances.
- Preserving these languages is essential for maintaining and celebrating Nepal’s rich cultural diversity. This diversity is like a vibrant tapestry, each thread representing a unique cultural tradition.
Importance of Language Diversity
Language diversity in Nepal is crucial for maintaining cultural richness and fostering understanding amongst different communities. It’s like a spice that adds flavor to the national dish.
- The diverse linguistic landscape enriches Nepal’s cultural tapestry. It’s like having a beautiful and intricate mosaic.
- The preservation of minority languages is essential for safeguarding the cultural heritage of various ethnic groups in Nepal. It’s like preserving a precious relic from the past.
- Language diversity also promotes intercultural dialogue and understanding, fostering unity and peace among different communities. It’s like a bridge that connects people.
Contemporary Usage and Trends
Nepali, a language rich in tradition and culture, is experiencing a fascinating transformation in its contemporary usage. The digital age, globalization, and social media are reshaping how Nepali is spoken, written, and understood. This dynamic evolution necessitates a careful examination of its practical application in modern contexts.The language is no longer confined to traditional settings; its reach extends into the modern world, from business dealings to social media interactions, impacting its vocabulary, grammar, and overall usage.
Understanding these evolving trends provides a crucial insight into the vitality and adaptability of the Nepali language.
Modern Use Case Analysis
Nepali’s practical application in the modern world is multifaceted. From the bustling markets to the digital spheres, Nepali plays a vital role. Its use extends across diverse sectors, showcasing the language’s adaptability.
- Business: Nepali is increasingly important in international trade and tourism. Common phrases like “मौसम कस्तो छ?” (What’s the weather like?) are frequently used for communication with international clients. Furthermore, specific technical terms are employed in Nepali-language business reports and contracts, reflecting the language’s growing prominence in professional settings.
- Social Media: Social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter have become vital communication tools, leading to a surge in Nepali content creation. The vibrant online community fosters new slang and linguistic variations. Nepali posts and comments often employ informal language and slang, reflecting the dynamic nature of online communication.
- Education: Nepali’s use in education is essential. From primary schools to universities, the language plays a pivotal role in knowledge dissemination. Educational materials, including textbooks and online resources, are increasingly available in Nepali, promoting access to information and knowledge for a broader segment of the population.
Trend Identification
Several trends are significantly impacting Nepali’s usage in recent years. These changes underscore the language’s responsiveness to societal shifts.
- Increased Use of Online Resources: Online Nepali dictionaries and language learning apps have experienced a considerable increase in usage, indicating a growing interest in learning and utilizing the language. Data from reliable sources would further solidify this trend.
- Linguistic Borrowing: Globalization has led to the incorporation of words from other languages, primarily English, into Nepali vocabulary. This phenomenon, while contributing to the language’s evolution, needs further analysis to ascertain its extent and impact.
- Emergence of New Slang: The dynamic online community has fueled the creation of new Nepali slang. This is particularly evident on social media platforms, where unique phrases and expressions are frequently used, often reflecting contemporary trends and pop culture.
Globalization Impact Analysis
Globalization’s influence on Nepali is noticeable. The integration of foreign words and phrases is apparent, particularly from English, enriching the language with new concepts and expressions. However, the extent of this impact needs further investigation.
- Vocabulary Expansion: Nepali vocabulary has expanded to incorporate numerous loanwords from English. These loanwords reflect the increasing interaction with the global community and the adoption of new concepts and technologies.
- Grammatical Influences: The influence of English grammar on Nepali is subtle but potentially impactful, especially in spoken communication. Further research is needed to identify any significant grammatical shifts.
Vocabulary Evolution Elaboration
The Nepali vocabulary has evolved considerably in the past 50 years. New words and phrases reflecting the evolving societal needs and technological advancements are now commonplace.
- Technology-Related Words: The advent of technology has introduced a plethora of new words related to computers, the internet, and mobile devices, demonstrating the language’s ability to adapt to technological advancements.
- Social Media Terminology: New vocabulary pertaining to social media platforms and online interactions has emerged. These words often reflect the language’s ability to encapsulate the nuances of digital communication.
Social Media Influence Explanation
Social media platforms significantly influence Nepali language usage. Informal communication styles and new slang expressions are prevalent online, often leading to variations in grammar and language use.
- Informal Language: Social media fosters informal communication, leading to the use of slang and colloquialisms. This relaxed style of communication influences how Nepali is used in other contexts as well.
- Slang and Linguistic Variations: Variations in language use across different social media platforms are evident. These differences highlight the impact of community norms and trends on the evolution of the language.
Nepali Slang Table
A table listing some common Nepali slang terms, their standard Nepali meanings, and contexts is provided below. This table offers a snapshot of how Nepali slang is used in everyday conversations, particularly in informal settings.
| Nepali Slang Term | Standard Nepali Meaning | Context |
|---|---|---|
| (Add 10 slang terms with their meanings and context) |
Writing Task
Contemporary Nepali language use is characterized by its adaptability to modern contexts. The language is increasingly prevalent in business, social media, and education. Globalization has led to the integration of loanwords, particularly from English. Social media platforms play a significant role in shaping linguistic trends, fostering the emergence of new slang and variations in language use. These evolving trends underscore the dynamism and vitality of the Nepali language in the 21st century.
Language Learning Resources
Learning Nepali, like mastering any language, requires the right tools and strategies. It’s like trying to build a house without proper bricks and mortar – you’re gonna have a hard time. Finding the right resources can make all the difference in your language journey. So, let’s dive into some helpful resources for those wanting to learn Nepali.
Recommended Books on Nepali
Learning a language through books is like having a personal tutor who never gets tired. Books provide structured learning, helping you grasp grammar and vocabulary step-by-step. Finding good Nepali books is essential for building a strong foundation.
- “A Practical Nepali Grammar” by David N. Gellner: This book offers a comprehensive overview of Nepali grammar, making it a great choice for beginners looking to understand the language’s structure.
- “Nepali for Beginners” by [Author Name]: A beginner’s book that covers the basics of Nepali grammar, pronunciation, and vocabulary, suitable for those new to the language.
- “Nepali Phrasebook” by [Author Name]: Perfect for learning essential phrases and dialogues for everyday conversations. This is useful for getting a grasp of the spoken language.
Websites and Apps for Nepali Language Learning
The internet and mobile apps have revolutionized language learning. They’re like having a global classroom right at your fingertips. Here are some valuable resources:
- Memrise: This platform uses spaced repetition and interactive exercises to help you memorize vocabulary and phrases effectively.
- Duolingo: A popular language-learning app with a user-friendly interface and gamified lessons.
- HelloTalk: A platform connecting language learners with native speakers for practice and conversation. This is ideal for getting your Nepali speaking skills polished.
- Babbel: A subscription-based app offering structured lessons and interactive exercises for grammar and vocabulary.
- LingoDeer: This app focuses on grammar and sentence structure, making it an excellent resource for learning the language’s rules.
Nepali Language Courses
Formal language courses provide structured learning and opportunities to interact with other learners and teachers. This is like having a professional guide for your language journey.
- Online Courses: Numerous online platforms offer Nepali language courses, catering to various levels and learning styles.
- Local Institutions: Check for language schools and community centers in your area that offer Nepali language classes. This can give you the chance to meet people from Nepal.
- Universities: Some universities may offer Nepali language courses as part of their language programs. This can be an option for those seeking a more academic approach.
Online Communities for Nepali Language Learners
Connecting with other learners can be a fantastic way to stay motivated and get support. It’s like having a group of friends who share the same goal.
- Facebook Groups: Search for Nepali language learning groups on Facebook to connect with others who are also learning the language. It’s a great way to share tips and experiences.
- Online Forums: Several online forums dedicated to language learning might have sections for Nepali. You might find helpful tips there.
- Language Exchange Platforms: Platforms like HelloTalk provide opportunities to connect with native speakers and exchange language practice.
Finding Qualified Nepali Tutors, What language do nepalese people speak
Finding a qualified tutor can significantly accelerate your learning process. It’s like having a personal coach who can guide you through your language journey.
- Online Tutoring Platforms: Many online platforms connect students with tutors who can provide personalized instruction.
- Local Language Centers: Check local language centers or community groups for tutors who teach Nepali. This way, you can have a physical meet up with your tutor.
- Recommendations: Ask other Nepali learners for recommendations. Word-of-mouth is often the best way to find qualified tutors.
Language Learning Apps with Nepali Support
Language learning apps offer convenient and accessible ways to learn Nepali. They are like having a portable classroom in your pocket.
| App Name | Features |
|---|---|
| Memrise | Spaced repetition, interactive exercises, vocabulary building |
| Duolingo | Gamified lessons, grammar practice, vocabulary exercises |
| Babbel | Structured lessons, interactive exercises, grammar explanations |
| HelloTalk | Language exchange, conversation practice, cultural exchange |
| LingoDeer | Grammar focus, sentence structure, vocabulary building |
Challenges and Opportunities

Wah, preserving a language is like trying to keep a vintage Vespa running in this modern world. It takes constant care, maintenance, and a dash of creativity to make sure it doesn’t get lost in the dustbin of history. Nepali, with its rich heritage, faces some hurdles, but also has amazing opportunities to shine!
Preserving Nepali: A Balancing Act
Nepali, like any language, faces the constant threat of being overshadowed by more dominant languages. Globalization, with its ubiquitous influence, can sometimes push local tongues to the side. This isn’t just about losing words; it’s about losing a connection to history, culture, and community. Think of it like a family heirloom – you wouldn’t want to lose it, would you?
Promoting Nepali: Spreading the Word
Promoting Nepali involves more than just teaching it in schools. It’s about making it appealing and relevant to a wider audience. Imagine making Nepali cool, like a trendy new app! This could involve incorporating Nepali into popular culture, showcasing its beauty through art, music, and literature, and making sure it’s represented in the digital sphere. Making it accessible and understandable is key.
Education’s Crucial Role
Education plays a vital role in language preservation. It’s like the engine of a language; without it, it can’t run smoothly. If Nepali isn’t valued and prioritized in schools, it could gradually fade into obscurity. Teachers need to be well-versed in the language, and educational materials should be readily available, making it easier for kids to learn.
Think of it as nurturing a young plant – give it the right care, and it will grow strong.
Supporting Nepali Speakers
Supporting Nepali speakers is like giving them the tools to thrive. This means creating a supportive environment where they can use their language freely and without fear of judgment. This might include providing resources like dictionaries, language learning apps, and translation services. It also involves celebrating the language through events and activities that showcase its beauty.
Technology’s Role: Bridging the Gap
Technology can be a powerful tool for promoting and preserving Nepali. Think of digital dictionaries, language learning apps, and online communities that connect Nepali speakers worldwide. These platforms can help to bridge geographical barriers and provide a space for people to interact and learn from one another. Imagine a global Nepali network – that’s the potential!
Successful Nepali Promotion Initiatives
Several successful initiatives have already proven the power of community-led efforts. Some examples include language preservation projects, language festivals, and online platforms designed to teach Nepali. These initiatives have fostered a sense of pride and community, ensuring the language continues to flourish. One such example is the establishment of Nepali language schools in various communities across the globe.
These schools create a hub for learning and preserving the language.
Geographic Variation
Nepali, like any good language, ain’t just one uniform thing. It’s got different flavors, different pronunciations, and even different words depending on where you are in Nepal. It’s like trying to eat nasi goreng in Jakarta, then trying it in Bandung; they might taste similar, but there are definite differences, right? So, let’s dive into the delicious regional variations of Nepali.
Regional Pronunciation Variations
Nepali pronunciation varies significantly across the country. This isn’t just about saying “hello” differently; entire words and phrases can be spoken with distinct accents. Imagine a group of friends, all speaking the same language, but each with their own little quirks in how they pronounce things. That’s sort of what regional Nepali variations are like. These differences in pronunciation often stem from the influence of local languages and the unique sounds that are common in the specific region.
Regional Vocabulary Differences
Vocabulary variations are another key aspect of Nepali’s regional diversity. Different regions might have different words for the same thing, just like how you might call a certain type of bread “roti” in one place and “chapati” in another. These differences aren’t just about semantics; they reflect the unique experiences and cultural nuances of each region. It’s like having a secret language within the larger Nepali language family.
Influence of Regional Dialects on Nepali
Regional dialects, as with other languages, influence Nepali. They bring with them unique words, phrases, and even grammatical structures that contribute to the rich tapestry of the language. Think of it like adding spices to a dish; each region adds its own unique flavor, enriching the overall experience. It’s this blending of influences that makes Nepali so vibrant and dynamic.
Examples of Common Phrases in Different Regions
Different regions in Nepal have their own unique ways of saying things. It’s not just about replacing words; sometimes, the entire structure of a sentence can change. This variation is what gives Nepali its distinct character.
- In the Kathmandu Valley, a common greeting is “Namaste,” while in the western hills, a more informal “Jai” might be used. This reflects the diverse cultural norms and values of different regions.
- Similarly, the way people describe everyday objects or activities might differ from one region to another. These variations reflect the unique experiences and cultural norms of different communities.
Cultural Significance of Regional Variations
Regional variations in Nepali are deeply rooted in the cultural fabric of Nepal. They represent the unique identities and traditions of different communities. They are like the different folk songs or dances, reflecting the unique heritage of the region. These variations showcase the rich cultural tapestry of Nepal.
Table Illustrating Regional Nepali Vocabulary
| Region | Word (English) | Word (Regional Nepali) |
|---|---|---|
| Kathmandu Valley | Hello | Namaste |
| Western Hills | Thank you | Dhanyabad |
| Eastern Nepal | Rice | Bhat |
| Mountain Regions | Water | Pani |
This table provides a small glimpse into the regional vocabulary variations. It’s important to note that these are just a few examples, and the variations are much more complex and nuanced.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, Nepali, with its historical depth and evolving presence in modern life, is much more than a language; it’s a vital link to a rich cultural heritage. Its diverse dialects, official status across regions, and active use in literature and digital spaces showcase its adaptability and significance. Understanding Nepali provides a window into the vibrant tapestry of Nepalese society.
FAQ Insights
What are the major dialects of Nepali?
Major Nepali dialects include Maithili, Tharu, and Newari, each with distinct phonological, grammatical, and lexical variations. Understanding these differences provides insights into the linguistic diversity within Nepal.
What is the official status of Nepali in different countries?
Nepali is the primary language of government in the Kathmandu Valley region of Nepal, and an official language in certain regions of India. Specific regions and details regarding its official status can vary, and further research into each region’s specific status is recommended.
How is Nepali used in education?
Nepali is a crucial component of education across various levels, from primary to tertiary, influencing literacy rates and preserving cultural transmission. The importance of Nepali in education varies across different regions.
What are some challenges faced by Nepali language learners?
Challenges include limited exposure to the language, a lack of resources, and cultural barriers. Regional dialects and the digital divide can also pose obstacles. Addressing these challenges is crucial for promoting effective Nepali language learning.