What is community engaged learning – Welcome to the realm of Community Engaged Learning (CEL), where the boundaries between the classroom and the community blur, fostering a dynamic exchange of knowledge, skills, and experiences. This transformative approach to education empowers students to become active participants in addressing real-world challenges while enriching the lives of those around them.
CEL initiatives encompass a wide range of activities, from service-learning projects that connect students with local organizations to community-based research that tackles pressing social issues. Through these hands-on experiences, students develop not only academic knowledge but also essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and empathy.
Definition and Overview of Community Engaged Learning (CEL)

Community Engaged Learning (CEL) is a teaching and learning approach that intentionally integrates community engagement into the curriculum. It emphasizes collaboration between students, faculty, and community partners to address real-world issues and enhance student learning.
CEL initiatives vary widely in their specific focus and implementation, but they all share the following key characteristics:
- Community-based:CEL is grounded in the community and its needs, with projects and activities designed in collaboration with community partners.
- Reciprocal:CEL benefits both the students and the community, fostering mutually beneficial relationships and shared learning experiences.
- Transformative:CEL aims to transform both students and community members through the process of engagement and shared experiences.
Examples of CEL initiatives include:
- Service-learning:Students engage in community service as part of their coursework, applying academic knowledge and skills to address real-world issues.
- Community-based research:Students conduct research in partnership with community organizations, addressing community-identified needs and contributing to local knowledge.
- Community-engaged internships:Students gain practical experience in community settings, working alongside community partners to support their work and learn from their expertise.
CEL initiatives have a positive impact on both students and communities. For students, CEL enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills, while fostering a sense of civic responsibility and social awareness. For communities, CEL provides access to academic resources and expertise, supports local initiatives, and strengthens community capacity.
Benefits of CEL for Students
Community Engaged Learning (CEL) offers students a plethora of benefits that extend beyond the classroom, enriching their academic, personal, and professional lives. Through hands-on experiences, students gain invaluable skills, broaden their perspectives, and make meaningful contributions to their communities.
Academic Benefits
CEL enhances students’ academic performance by providing practical applications of theoretical concepts. They learn to apply their knowledge to real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- Improved grades and retention rates
- Increased understanding of course material
- Development of research and writing skills
Personal Benefits
CEL fosters personal growth and development by exposing students to diverse perspectives and experiences. They develop empathy, compassion, and a sense of social responsibility.
- Increased self-awareness and confidence
- Enhanced leadership and teamwork skills
- Development of ethical and moral values
Professional Benefits
CEL prepares students for the workforce by providing practical experience in their field of study. They gain valuable skills and make connections that can enhance their career prospects.
- Development of marketable skills
- Networking opportunities with professionals
- Preparation for future leadership roles
Case Study
A study conducted at the University of California, Berkeley found that students who participated in CEL programs had higher GPAs and were more likely to graduate on time. Additionally, they reported increased confidence in their ability to apply their knowledge to real-world problems.
Methods and Approaches to CEL

Community Engaged Learning (CEL) can be implemented through various methods and approaches, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. Here are some common methods:
Service-Learning
Service-learning is a form of CEL where students engage in community service activities while reflecting on their experiences to enhance their learning. This approach combines academic learning with practical, real-world experiences, allowing students to apply their knowledge and skills while making a positive impact on the community.
Community-Based Research
Community-based research involves students collaborating with community partners to conduct research that addresses local issues and concerns. This approach emphasizes community involvement and engagement, ensuring that research is relevant and responsive to the needs of the community.
Internships
Internships provide students with opportunities to work in community organizations or agencies, gaining hands-on experience and applying their knowledge in a professional setting. Internships can expose students to different career paths and enhance their professional development.
| Method | Key Features | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service-Learning | – Combines academic learning with community service Community engaged learning is a teaching and learning strategy that intentionally integrates academic learning with community engagement and service. It allows students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world problems while making a positive impact on the community. One example of a community engaged learning program is the A Perfect Start Learning Center , which provides educational support to young children and their families in underserved communities. Through this program, students gain valuable experience in early childhood education and develop a deep understanding of the challenges faced by families in these communities.
| – Enhanced learning outcomes
| – Time constraints
|
| Community-Based Research | – Collaboration with community partners
| – Relevant and impactful research
| – Resource limitations
|
| Internships | – Hands-on experience in professional settings
| – Practical application of knowledge
| – Competition for placements
|
Challenges and Considerations in CEL: What Is Community Engaged Learning

Implementing CEL initiatives can present several challenges and considerations that need to be addressed to ensure successful outcomes. These include:
Funding
CEL programs often require additional resources to support student stipends, travel expenses, and community partnerships. Securing sustainable funding sources can be a challenge, especially in the face of budget constraints.
Logistics
Coordinating CEL experiences can be logistically complex, involving scheduling, transportation, and managing community partnerships. Balancing academic schedules with community engagement can also be a challenge for students.
Community Engagement
Building and maintaining strong community partnerships is crucial for successful CEL. This requires time, effort, and a commitment to reciprocity and mutual benefit.
Overcoming Challenges
Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning and collaboration. Some effective strategies include:
Securing Funding
Explore a diverse range of funding sources, including grants, university funds, and community partnerships. Emphasize the value and impact of CEL programs to secure support.
Streamlining Logistics
Establish clear communication channels and create flexible scheduling systems to accommodate both academic and community engagement commitments.
Fostering Community Partnerships
Engage in ongoing dialogue with community partners to understand their needs and build mutually beneficial relationships. Foster a culture of respect and reciprocity to create sustainable partnerships.
Best Practices for CEL

Community Engaged Learning (CEL) is an effective way to bridge the gap between theory and practice, fostering student learning and community impact. By following best practices, educators and community partners can maximize the benefits of CEL programs.
To ensure successful CEL programs, it’s crucial to involve the community in the design, implementation, and evaluation stages. By collaborating with community partners, educators can tailor programs to meet specific community needs and ensure that students’ learning experiences are relevant and meaningful.
Planning and Design
- Clearly define program goals and objectives that align with both academic and community needs.
- Establish a collaborative partnership with community organizations, ensuring mutual benefits and shared ownership.
- Develop a structured curriculum that integrates academic content with community-based experiences.
- Provide students with clear expectations, guidelines, and support throughout the program.
Implementation
- Foster a supportive and inclusive learning environment that values diverse perspectives.
- Provide ongoing training and support for both students and community partners.
- Encourage reflective practice and critical thinking to enhance student learning.
- Monitor and evaluate program progress regularly, making adjustments as needed.
Evaluation, What is community engaged learning
- Use a variety of evaluation methods to assess student learning outcomes, community impact, and program effectiveness.
- Collect feedback from students, community partners, and other stakeholders to inform program improvement.
- Disseminate evaluation findings to demonstrate the value and impact of the CEL program.
Role of Technology in CEL

Technology has emerged as a powerful tool in enhancing Community Engaged Learning (CEL) experiences. It offers a wide range of opportunities to facilitate communication, collaboration, and data collection, thereby enriching the learning process for students.
Through online platforms and mobile applications, students can engage in real-time discussions with community partners, access relevant resources, and share their insights. Technology also enables remote collaboration, allowing students to work together on projects and assignments from different locations.
Communication
- Video conferencing and instant messaging tools facilitate real-time communication between students, faculty, and community partners.
- Online forums and discussion boards provide platforms for asynchronous discussions and knowledge sharing.
- Social media platforms enable students to connect with community organizations and engage in online conversations.
Collaboration
- Cloud-based document sharing and collaboration tools allow students to work together on projects, share resources, and provide feedback.
- Project management software helps students track their progress, assign tasks, and manage deadlines.
- Virtual meeting spaces enable students to participate in group discussions and brainstorming sessions.
Data Collection
- Online surveys and data collection tools streamline the process of gathering data from community partners.
- Mobile apps can be used to collect GPS data, record observations, and capture images.
- Data analysis software helps students analyze and interpret data, draw conclusions, and identify trends.
Impact of CEL on Communities
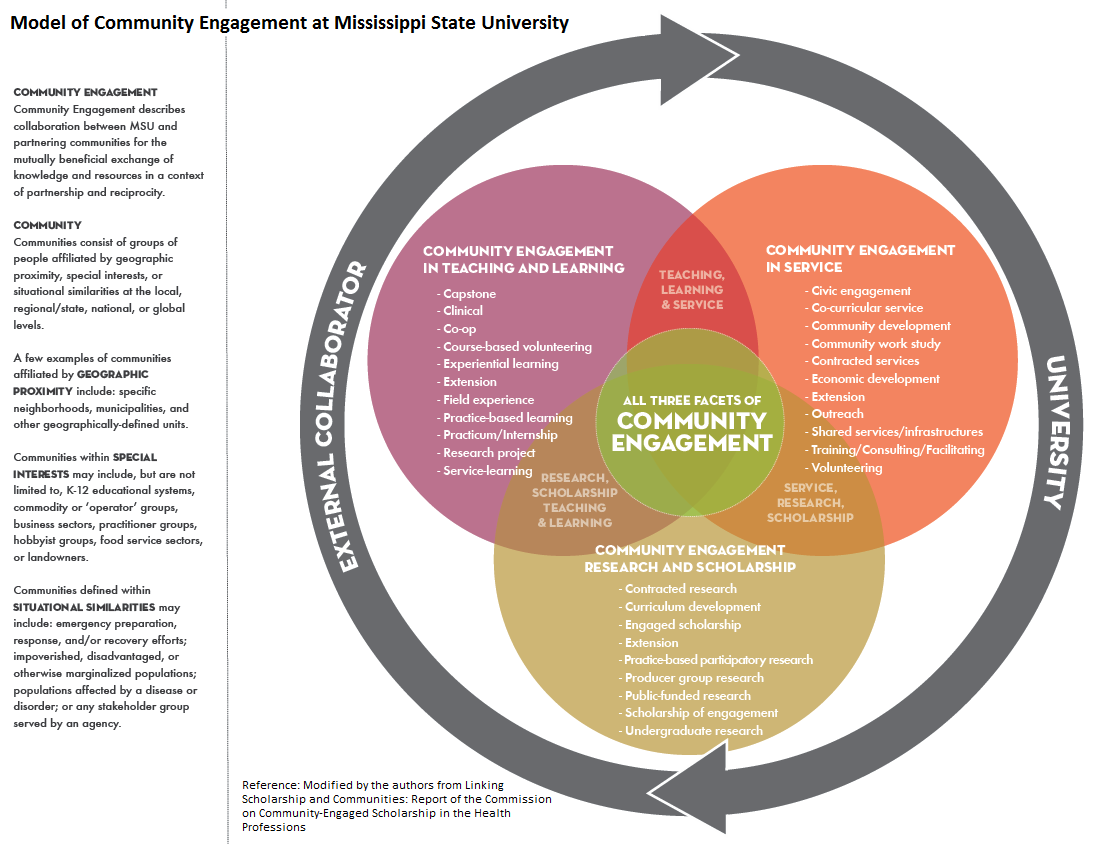
Community Engaged Learning (CEL) fosters a reciprocal relationship between educational institutions and communities, where students engage with community members to address real-world issues. This collaboration brings numerous benefits to communities, fostering positive change and empowerment.
Community engaged learning is a teaching and learning method that integrates academic study with community engagement, allowing students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world issues. If you’re interested in learning how to play pickleball, here are some resources to help you get started.
Community engaged learning fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills while making a positive impact on the community.
CEL promotes social cohesion by bridging the gap between academia and the community. Students work alongside community members, fostering understanding, empathy, and mutual respect. This interaction creates a sense of shared purpose and belonging, strengthening the fabric of the community.
Economic Development
CEL contributes to economic development by providing students with practical experience and skills that are in high demand in the job market. Students gain hands-on experience in problem-solving, communication, and collaboration, making them more competitive in the workforce. Additionally, CEL projects often focus on community-identified needs, such as workforce development or business incubation, directly contributing to local economic growth.
Community Empowerment
CEL empowers communities by giving them a voice in shaping their own future. Through collaboration with students and faculty, community members identify their needs and work together to develop solutions. This process fosters a sense of ownership and agency, empowering communities to take control of their own development.
Examples of CEL Impact
- A CEL program at a university partnered with a local non-profit to provide tutoring and mentoring to underprivileged youth. The program improved academic outcomes for the students and fostered a sense of connection between the university and the community.
- A CEL project in a rural community involved students working with farmers to develop sustainable farming practices. The project not only improved agricultural yields but also strengthened the community’s resilience to environmental challenges.
- A CEL initiative in an urban neighborhood brought together students, residents, and local businesses to create a community garden. The garden provided fresh produce for the community, fostered a sense of place, and created opportunities for social interaction.
Sustainability and Future Directions of CEL

Ensuring the sustainability of CEL initiatives is crucial for its long-term impact. Strategies include:
- Institutional support: Providing financial and administrative resources, incorporating CEL into curricula, and offering faculty development opportunities.
- Community partnerships: Building strong relationships with community organizations and involving them in planning and implementation.
- Student engagement: Creating opportunities for students to participate in CEL activities throughout their academic journey.
- Assessment and evaluation: Regularly evaluating CEL initiatives to identify areas for improvement and demonstrate impact.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
CEL is evolving rapidly. Emerging trends include:
- Interdisciplinary collaboration: CEL initiatives increasingly involve partnerships between different academic disciplines and community organizations.
- Technology-enhanced CEL: Technology is used to facilitate collaboration, connect students with communities, and provide virtual learning opportunities.
- Global CEL: CEL initiatives are expanding internationally, connecting students with global communities and addressing global challenges.
Future directions for CEL include:
- Focus on equity and social justice: CEL will continue to play a role in addressing social inequalities and promoting social change.
- Integration of CEL into higher education: CEL will become more integrated into the core of higher education, with a focus on experiential learning and community engagement.
- Continued research and evaluation: Research and evaluation will be crucial for understanding the impact of CEL and informing best practices.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key benefits of CEL for students?
CEL offers a multitude of benefits for students, including enhanced academic performance, increased civic engagement, and improved job prospects.
How can I get involved in CEL?
There are many ways to get involved in CEL, such as participating in service-learning courses, volunteering with community organizations, or conducting community-based research.
What are some challenges associated with CEL?
CEL can be challenging to implement due to factors such as funding constraints, logistical issues, and the need for strong community partnerships.