What grade do you learn geometry? It’s a question that has puzzled students for generations. The answer, however, is not as straightforward as you might think. In this article, we will explore the different grade levels at which geometry is typically introduced in educational systems around the world, as well as the variations that exist across different countries and educational models.
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of shapes and their relationships. It is a fundamental subject that helps students develop their spatial reasoning skills, problem-solving abilities, and critical thinking skills.
Grade Level Introduction
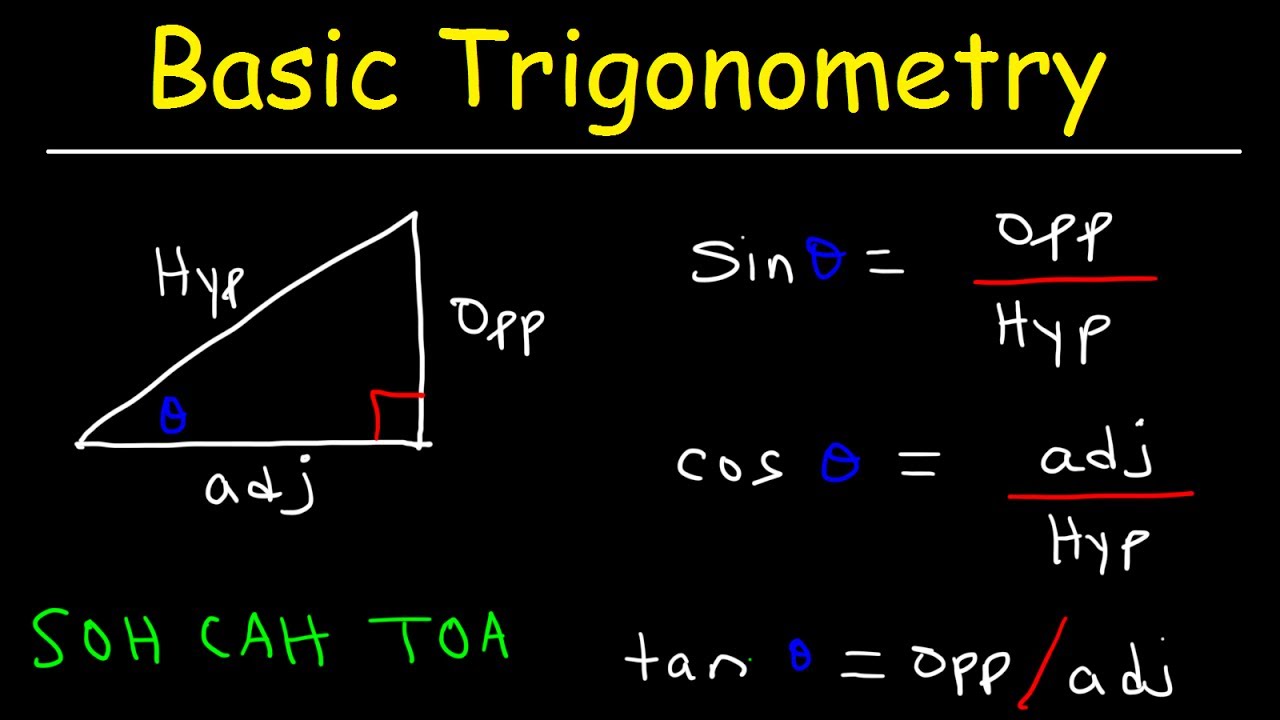
Geometry, the study of shapes and their properties, is typically introduced in the educational systems of many countries during middle or secondary school. However, the specific grade level at which geometry is first taught can vary depending on the educational model and the country in question.
Variations in Grade Levels
In some countries, such as the United States, geometry is typically introduced in the eighth or ninth grade, corresponding to students aged 13-15 years old. In other countries, such as the United Kingdom, geometry is often introduced earlier, around the age of 11 or 12 in the seventh grade.
In certain educational models, such as the International Baccalaureate (IB) program, geometry may be introduced as early as the sixth grade for students aged 11-12 years old.
Curriculum Standards

Geometry curriculum standards introduce foundational concepts and skills that prepare students for higher-level mathematics. These standards vary slightly across different educational systems, but generally cover core topics such as:
The study of geometry involves exploring the properties of shapes, their relationships, and spatial reasoning. It develops critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and visual-spatial skills.
Geometric Shapes and their Properties
- Identify and classify geometric shapes (e.g., triangles, squares, circles, cubes, spheres)
- Understand the properties of shapes, such as their sides, angles, and symmetry
- Calculate the area and perimeter of basic shapes
Transformations and Symmetry
- Recognize and perform transformations (e.g., translations, rotations, reflections)
- Identify and describe symmetry in shapes
- Apply transformations to solve problems
Measurement and Spatial Reasoning, What grade do you learn geometry
- Measure and estimate lengths, angles, and areas
- Understand the concept of volume and surface area
- Develop spatial reasoning skills (e.g., visualizing objects in 3D, understanding relationships between objects)
Learning Objectives

At the introductory grade level for geometry, students embark on a journey to acquire a solid foundation in geometric concepts, principles, and problem-solving techniques. Through engaging activities and hands-on experiences, they develop a deep understanding of geometric shapes, their properties, and their relationships with each other.
The key learning objectives for geometry at this grade level encompass the following areas:
Knowledge
- Identifying and classifying different types of geometric shapes, including polygons, circles, triangles, and quadrilaterals.
- Understanding the properties and characteristics of each shape, such as the number of sides, angles, and vertices.
- Recognizing and applying geometric vocabulary accurately.
- Visualizing and representing geometric shapes in two and three dimensions.
Skills
- Measuring and calculating the perimeter, area, and volume of geometric shapes.
- Constructing and drawing geometric shapes using tools such as rulers, protractors, and compasses.
- Solving geometry problems involving shape identification, measurement, and spatial reasoning.
- Applying geometric concepts to real-world situations and everyday objects.
Understanding
- Developing an understanding of the relationships between different geometric shapes.
- Recognizing patterns and symmetries in geometric figures.
- Applying geometric principles to analyze and solve problems.
- Communicating geometric ideas effectively through diagrams, drawings, and explanations.
al Approaches

Effective al approaches for teaching geometry at the introductory grade level emphasize hands-on experiences, visual aids, and problem-solving activities.
These approaches engage students by making geometry tangible and relatable. They foster understanding by providing multiple perspectives and representations of geometric concepts.
Inquiry-Based Learning
- Posing open-ended questions to encourage exploration and discovery.
- Guiding students through investigations and experiments to develop their understanding.
- Facilitating discussions to promote critical thinking and problem-solving.
Manipulatives and Visual Aids
- Using concrete manipulatives like blocks, shapes, and tangrams to provide hands-on experiences.
- Incorporating diagrams, charts, and models to visualize geometric concepts.
- Encouraging students to create their own representations of geometric figures.
Problem-Solving Activities
- Presenting real-world problems that require students to apply geometric concepts.
- Encouraging students to develop strategies for solving problems and explaining their reasoning.
- Providing opportunities for students to collaborate and share their problem-solving approaches.
Assessment Strategies

Evaluating student learning in geometry involves various assessment strategies tailored to the grade level where it is introduced. These strategies aim to assess students’ understanding of geometric concepts, problem-solving abilities, and communication skills.
Geometry is typically introduced in middle school, around grades 6-8. It involves the study of shapes, their properties, and their relationships. If you’re curious about learning a musical instrument, you might wonder, is the piano hard to learn ? While the piano can be challenging to master, it’s also a rewarding instrument to play.
Returning to geometry, students delve deeper into the subject in high school, exploring concepts like trigonometry and calculus.
Assessments in geometry typically fall into two main categories: formative and summative.
Geometry, the study of shapes and their properties, is typically introduced in middle school, usually around grade 7 or 8. It’s a fascinating subject that can help you understand the world around you. If you’re curious about what you can learn in geometry, check out what I learned today . You might be surprised at how much you can learn about geometry and how it applies to the real world.
Formative Assessments
Formative assessments are ongoing evaluations that provide feedback to students and teachers throughout the learning process. They help identify areas where students need additional support and adjust instruction accordingly.
- Informal Observations:Teachers observe students during class discussions, group work, and individual practice to assess their understanding and participation.
- Exit Tickets:Brief quizzes or reflections given at the end of class to assess students’ understanding of the day’s lesson.
- Homework Assignments:Regular homework assignments allow students to practice and apply geometric concepts.
- Quizzes:Short, focused assessments that cover specific topics or skills.
Summative Assessments
Summative assessments are more formal evaluations that measure student learning at the end of a unit or semester. They provide a comprehensive assessment of students’ knowledge and skills.
- Tests:Written exams that assess students’ understanding of geometric concepts, problem-solving abilities, and proof-writing skills.
- Projects:In-depth projects that allow students to apply their geometric knowledge to real-world situations or create geometric models.
- Presentations:Students present their understanding of geometric concepts or research findings to the class.
Technology Integration: What Grade Do You Learn Geometry
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing geometry learning, offering a range of tools and resources that foster student engagement, conceptual understanding, and assessment.
By incorporating technology into geometry lessons, educators can create interactive simulations, dynamic visualizations, and immersive learning experiences that bring abstract concepts to life.
Interactive Simulations
- Allow students to explore geometric shapes and their properties in a hands-on manner.
- Enable real-time manipulation and observation of transformations, rotations, and translations.
- Provide visual representations of complex geometric relationships, making them more accessible.
Dynamic Visualizations
- Create animated diagrams and 3D models that illustrate geometric concepts in a visually appealing way.
- Help students visualize abstract ideas and make connections between different aspects of geometry.
- Enhance understanding of spatial relationships and the properties of geometric figures.
Assessment Tools
- Provide interactive quizzes and assessments that offer immediate feedback on student understanding.
- Allow teachers to track student progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Enable personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs.
Query Resolution
What is geometry?
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of shapes and their relationships.
What are the benefits of learning geometry?
Geometry helps students develop their spatial reasoning skills, problem-solving abilities, and critical thinking skills.
What are the different types of geometry?
There are many different types of geometry, including Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean geometry, and algebraic geometry.
What are some examples of geometry in everyday life?
Geometry is used in architecture, engineering, art, and design.