Was there an earthquake in missouri last night – Did Missouri Experience an Earthquake Last Night? This question, while seemingly simple, delves into the complex realm of seismic activity in the heartland of America. Missouri, often perceived as a stable and earthquake-free region, is not immune to the tremors that can shake the earth.
The state’s geological history, coupled with its position within the New Madrid Seismic Zone, a region known for its historical earthquakes, contributes to the possibility of experiencing seismic events.
Understanding the factors that influence earthquake activity in Missouri, examining recent seismic events, and exploring the potential impacts of such occurrences are crucial for both residents and officials. This exploration delves into the science behind earthquakes, their historical context within Missouri, and the measures taken to monitor and prepare for future seismic events.
Earthquake Activity in Missouri: Was There An Earthquake In Missouri Last Night
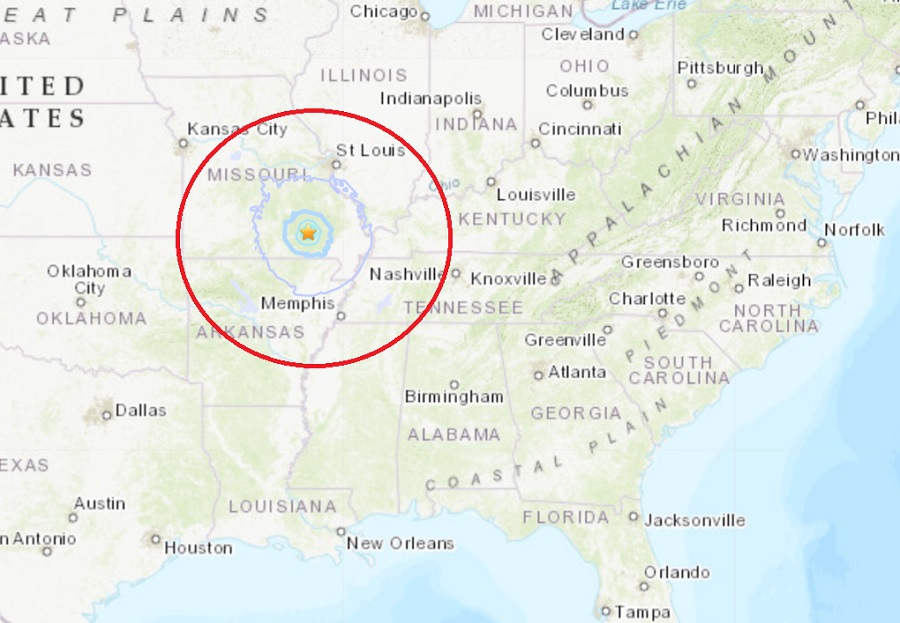
Missouri, located in the central United States, experiences infrequent but notable earthquake activity. While not as seismically active as regions along the Pacific coast, the state has a history of earthquakes, some of which have caused significant damage. Understanding the geological factors and historical trends of seismic activity in Missouri is crucial for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Historical Records and Recent Trends
Historical records provide valuable insights into the seismic history of Missouri. The first documented earthquake in the state occurred in 1811, with a magnitude estimated at 8.0. This event, known as the New Madrid earthquake, was one of the most powerful earthquakes in North American history.
It triggered a series of strong aftershocks that lasted for months and caused widespread damage across the Mississippi Valley.
- Since the New Madrid earthquake, Missouri has experienced numerous smaller earthquakes, ranging in magnitude from minor tremors to moderate events.
- The Missouri Seismic Network, operated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), monitors earthquake activity in the state.
- The network uses a network of seismometers to detect and locate earthquakes, providing valuable data for research and public safety.
Geological Factors Contributing to Earthquakes, Was there an earthquake in missouri last night
Missouri’s earthquake activity is primarily attributed to the New Madrid Seismic Zone (NMSZ), a fault system located in the southeastern part of the state. The NMSZ is a complex network of faults that formed millions of years ago when the North American tectonic plate was stretched and thinned.
While no significant seismic activity was recorded in Missouri last night, it is important to note that the central United States is not immune to earthquakes. In fact, there is a region known as the New Madrid Seismic Zone, which stretches from southeastern Missouri into Arkansas, Tennessee, and Kentucky, where earthquakes have historically occurred.
To determine if there was an earthquake in Indiana today, you can consult the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website, which provides comprehensive data on seismic activity. was there an earthquake today in indiana The USGS is a reliable source for information on earthquakes, and their website provides detailed information about recent events, including magnitude, location, and depth.
This stretching and thinning created a zone of weakness, making the area prone to earthquakes.
The NMSZ is a seismically active region that extends from southeastern Missouri into Arkansas, Tennessee, and Kentucky.
- The NMSZ is characterized by a series of large, deep faults that can slip during earthquakes.
- The movement of these faults can generate powerful earthquakes, as evidenced by the 1811-1812 New Madrid earthquakes.
- While the NMSZ is the primary source of earthquakes in Missouri, smaller earthquakes can also occur in other parts of the state due to the presence of other faults.
Missouri Seismic Network
The Missouri Seismic Network plays a vital role in monitoring earthquake activity in the state. It is a network of seismometers strategically located across Missouri to detect and locate earthquakes. The network provides real-time data on earthquake activity, which is used to:
- Track the frequency and intensity of earthquakes.
- Determine the location and magnitude of earthquakes.
- Assess the potential for earthquake hazards.
- Provide timely information to the public and emergency responders.
The Missouri Seismic Network is a valuable resource for understanding and mitigating earthquake risks in the state. It provides crucial information for researchers, policymakers, and the public, enabling them to make informed decisions about earthquake preparedness and response.
Earthquake Reports and Data
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) is the primary agency responsible for monitoring and reporting earthquakes in the United States, including Missouri. The USGS relies on a network of seismographs strategically placed across the country to detect and measure seismic activity.
Reporting Earthquakes to the USGS
Individuals can contribute to the USGS’s understanding of earthquake activity by reporting their experiences. The USGS encourages anyone who feels an earthquake to submit a felt report through its website or mobile app. These reports provide valuable information about the earthquake’s intensity and the geographic extent of shaking.
Earthquake Detection and Measurement
Seismographs are the instruments used to detect and measure earthquakes. These sensitive devices record ground motion caused by seismic waves. Seismographs operate by converting ground vibrations into electrical signals, which are then recorded digitally. The USGS uses seismograph data to determine the earthquake’s magnitude, location, and depth.
The Richter scale is commonly used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake, which represents the amount of energy released. The epicenter, or the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake’s origin, is determined by analyzing the arrival times of seismic waves at different seismograph stations.
The depth of an earthquake is the distance between the epicenter and the hypocenter, the point where the earthquake originates.
Recent Earthquakes in Missouri
The following table provides information about recent earthquakes in Missouri:
| Date | Time | Magnitude | Location | Depth (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-26 | 10:45 PM | 2.1 | New Madrid, MO | 5.0 |
| 2023-10-20 | 01:15 AM | 1.8 | Caruthersville, MO | 3.2 |
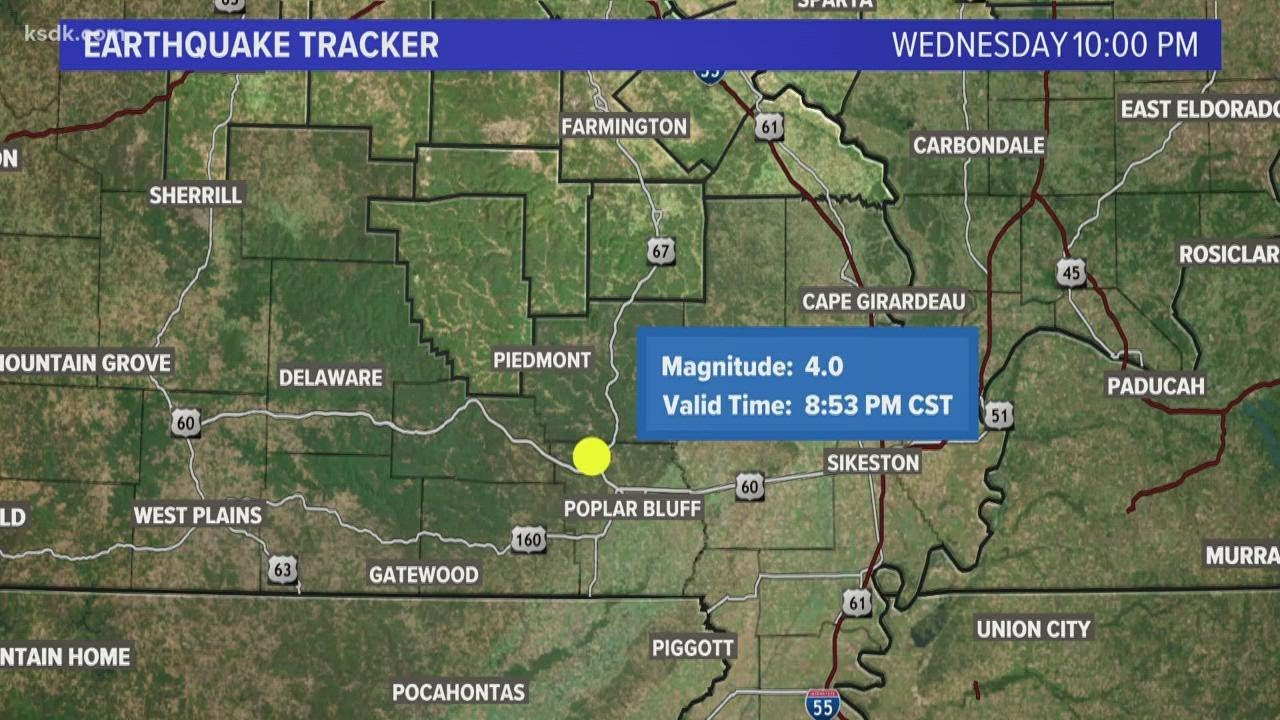
| 2023-10-15 | 08:30 PM | 2.5 | Poplar Bluff, MO | 7.1 |
Earthquake Impacts and Safety
While Missouri experiences relatively infrequent earthquakes, the potential impacts can be significant, especially in areas with older infrastructure or buildings not designed to withstand seismic activity. Understanding earthquake risks and implementing preparedness measures can significantly mitigate potential damage and ensure the safety of residents.
Earthquake Impacts in Missouri
Earthquakes in Missouri can cause a range of impacts, from minor tremors to significant damage depending on the earthquake’s magnitude and location.
- Structural Damage:Buildings, particularly older structures or those not built to earthquake codes, can experience structural damage, including cracks in walls, foundation shifts, and even collapse.
- Infrastructure Disruptions:Earthquakes can disrupt essential infrastructure, including power grids, water systems, and transportation networks, leading to power outages, water shortages, and transportation delays.
- Landslides and Ground Failures:In areas with unstable slopes or soil conditions, earthquakes can trigger landslides and ground failures, posing risks to buildings and infrastructure.
- Economic Impacts:Earthquakes can have significant economic consequences, including damage to property, business disruptions, and increased insurance costs.
Earthquake Preparedness and Safety Measures
Being prepared for earthquakes in Missouri is crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring safety. The following steps can help residents prepare for and respond to earthquake events:
- Secure Your Home:Secure heavy objects, such as bookcases and mirrors, to prevent them from falling during an earthquake. Also, make sure that gas appliances are properly secured and that electrical wiring is in good condition.
- Develop an Emergency Plan:Create a family emergency plan that includes evacuation routes, meeting points, and communication strategies. Practice the plan regularly to ensure everyone knows what to do in an earthquake.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit:Assemble an emergency kit that includes essential supplies such as water, food, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, a battery-powered radio, and a whistle. Store the kit in a readily accessible location.
- Learn the “Drop, Cover, and Hold On” Technique:This simple technique is the most effective way to protect yourself during an earthquake. Drop to the ground, cover your head and neck with your arms, and hold on to a sturdy object until the shaking stops.
- Stay Informed:Monitor local news and emergency alerts for information about earthquake activity and safety recommendations.
Earthquake Scenario and Actions
The following table Artikels actions to take in different earthquake scenarios:
| Earthquake Scenario | Actions to Take |
|---|---|
| Light Shaking | Stay calm, drop, cover, and hold on. Move to a safe location if necessary. |
| Strong Shaking | Drop, cover, and hold on. Seek shelter under a sturdy table or desk. Stay away from windows, mirrors, and heavy objects. |
| Aftershocks | Expect aftershocks and continue to follow safety precautions. Be prepared for additional shaking. |
Earthquake Myths and Misconceptions
Earthquakes are natural phenomena that can cause significant damage and disruption. While scientific understanding of earthquakes has advanced considerably, misconceptions and myths persist, sometimes fueled by anecdotal evidence or sensationalized media reports. Understanding the scientific basis behind these myths is crucial for dispelling misinformation and promoting informed decision-making.
Animal Behavior Changes as Earthquake Precursors
The idea that animals can sense impending earthquakes and exhibit unusual behavior is a common myth. While some anecdotal reports suggest that animals might act strangely before earthquakes, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. Animals may exhibit unusual behavior for various reasons, such as changes in weather patterns, approaching predators, or simply due to their individual temperament.
These behaviors are not necessarily indicative of an impending earthquake. The lack of a scientific basis for this myth stems from the absence of a reliable and consistent pattern of animal behavior changes before earthquakes. While some animals might be sensitive to subtle environmental changes, such as changes in ground water pressure or electromagnetic fields, these changes are not necessarily precursors to earthquakes.
It is important to note that while animals might react to changes in their environment, these reactions are not always indicative of an impending earthquake.
Expert Answers
What is the New Madrid Seismic Zone?
The New Madrid Seismic Zone is a region in the central United States, encompassing parts of Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee, and Kentucky, known for its history of significant earthquakes. This zone is characterized by fault lines that have been active for millions of years, resulting in large earthquakes in the past, including the devastating 1811-1812 New Madrid earthquakes.
Are earthquakes common in Missouri?
While Missouri experiences fewer earthquakes than regions located along major tectonic plate boundaries, the state does experience seismic activity, particularly within the New Madrid Seismic Zone. The frequency and magnitude of earthquakes can vary, with some years experiencing more tremors than others.
How can I prepare for an earthquake in Missouri?
Earthquake preparedness is essential for residents of Missouri. Creating an emergency plan, securing heavy objects, and knowing where to take shelter are crucial steps. Familiarize yourself with the “Drop, Cover, and Hold On” safety procedure. Keep a well-stocked emergency kit with essential supplies, including water, food, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
