Was there an earthquake in Kentucky today? While Kentucky is not typically associated with major seismic activity, the state has a history of earthquakes, albeit less frequent and generally less intense than those experienced in other parts of the United States.
Understanding the geological factors that contribute to potential earthquakes in Kentucky is crucial for both historical perspective and present-day preparedness.
The New Madrid Seismic Zone, located just across the Mississippi River from Kentucky, is a significant source of earthquake activity in the region. This zone has been responsible for some of the most powerful earthquakes in North American history, and its tremors can be felt throughout Kentucky.
The region’s unique geological makeup, including the presence of fault lines and the movement of tectonic plates, contributes to the possibility of earthquakes in Kentucky.
Earthquake Activity in Kentucky
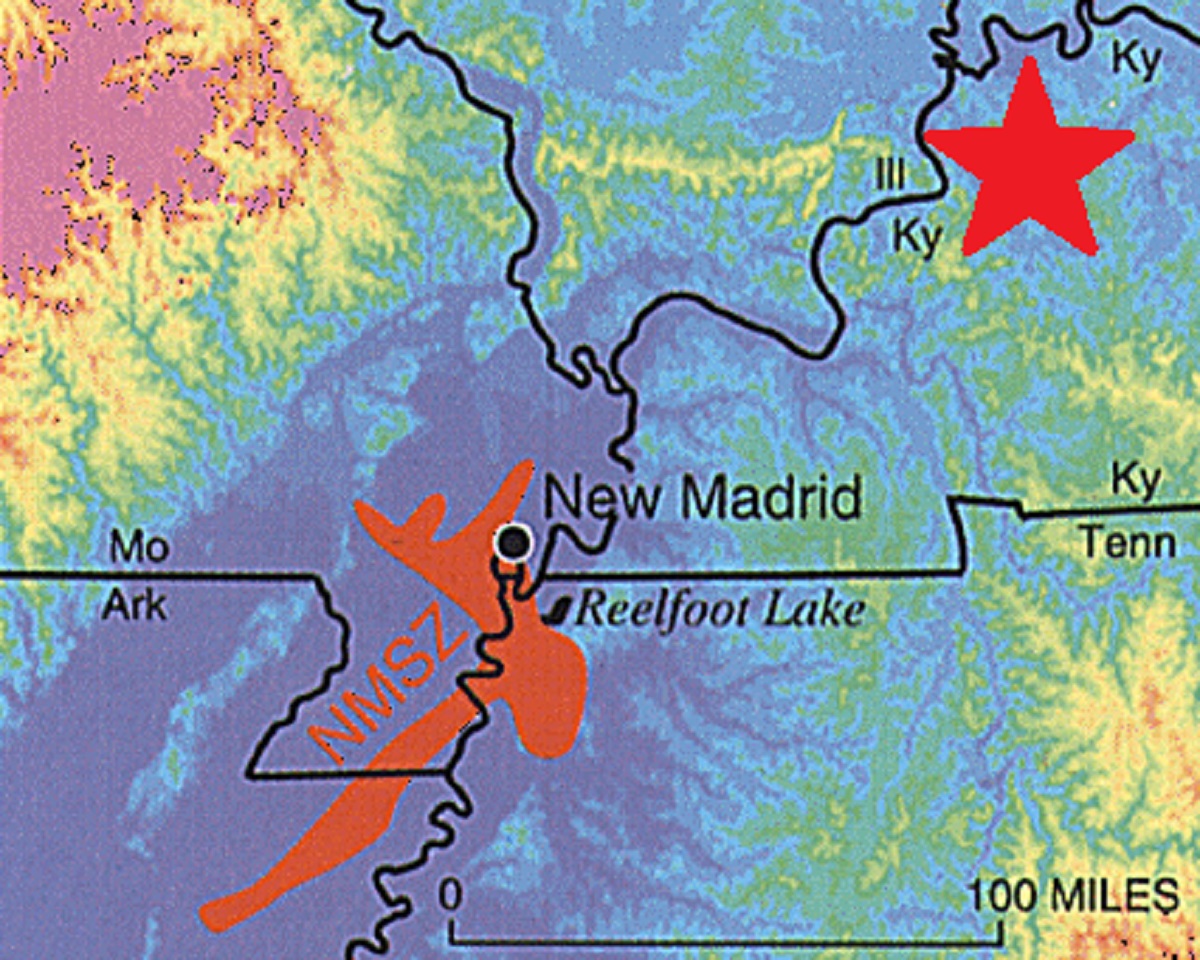
Kentucky, while not considered a highly seismic region, has experienced earthquakes throughout its history. These seismic events, though generally less intense than those in other parts of the United States, are a reminder of the dynamic geological processes shaping the Earth’s crust.
Geological Factors Contributing to Earthquakes in Kentucky
The geological features of Kentucky play a significant role in its seismic activity. The state is situated within the New Madrid Seismic Zone, a region of intense seismic activity extending from southeastern Missouri to northeastern Arkansas. This zone is characterized by a complex network of faults, remnants of ancient rifting events that occurred millions of years ago.
The movement along these faults can trigger earthquakes.
Significant Earthquakes in Kentucky’s History
Kentucky has experienced several notable earthquakes throughout its history. Some of the most significant events include:
- 1811-1812 New Madrid Earthquakes:These three massive earthquakes, centered near New Madrid, Missouri, had widespread effects throughout the Mississippi Valley, including Kentucky. These events were among the most powerful earthquakes ever recorded in the contiguous United States, and their tremors were felt as far away as Washington, D.C.
and Boston. The 1811-1812 New Madrid earthquakes caused significant changes in the landscape, altering the course of the Mississippi River and creating new lakes and swamps.
- 1989 New Madrid Earthquake:This earthquake, with a magnitude of 5.0, was centered in southeastern Missouri but caused noticeable shaking in western Kentucky. The event serves as a reminder of the potential for significant earthquakes in the region.
- 1990 Eastern Kentucky Earthquake:This earthquake, with a magnitude of 4.0, occurred near Hazard, Kentucky, and was felt in a wide area surrounding the epicenter. It was one of the largest earthquakes recorded in the state’s history.
Real-Time Earthquake Monitoring: Was There An Earthquake In Kentucky Today
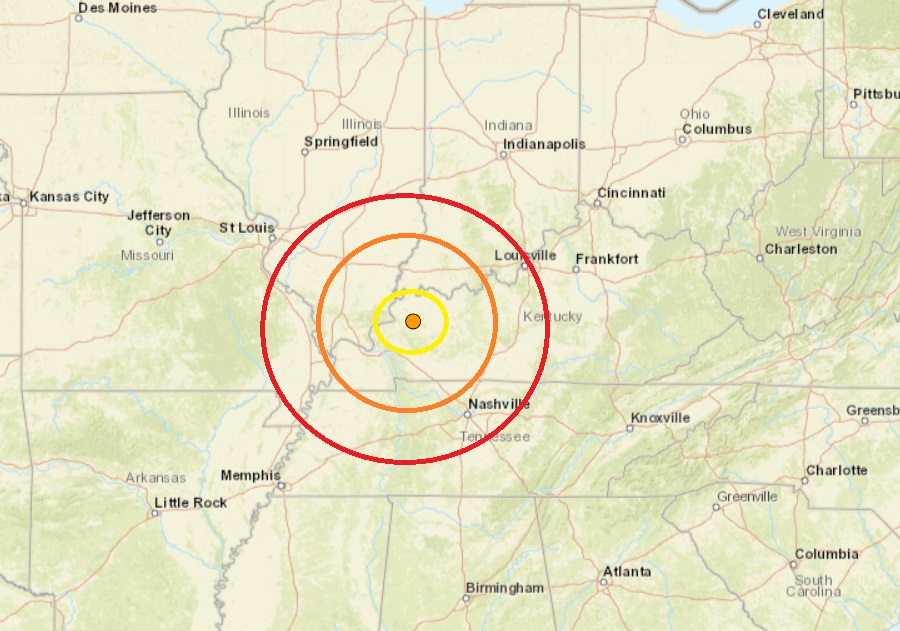
Real-time earthquake monitoring is crucial for understanding seismic activity, assessing potential hazards, and providing timely warnings to communities. The process involves a network of sensitive instruments that detect ground vibrations, followed by analysis and dissemination of information.
Earthquake Detection and Reporting
Earthquakes are detected by seismographs, instruments that measure ground motion. These devices are strategically placed across Kentucky and other regions, forming a network that captures seismic waves. When an earthquake occurs, the seismograph records the arrival time, duration, and intensity of the seismic waves.
While Kentucky is not known for its seismic activity, there is always a possibility of an earthquake occurring. The intensity of earthquakes is measured on the Richter scale, a logarithmic scale that assigns a numerical value to the magnitude of seismic waves.
To understand how earthquakes register, it is helpful to consider the article how earthquakes register 7 little words , which provides a concise explanation of the Richter scale. To determine if an earthquake occurred in Kentucky today, it is recommended to consult reliable sources such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website, which provides real-time data on earthquake activity across the country.
This data is then transmitted to monitoring centers, where it is analyzed by trained seismologists. The analysis involves determining the earthquake’s location, magnitude, and depth. This information is then disseminated to the public through various channels, including websites, social media, and news outlets.
Timely and accurate reporting of earthquake events is crucial for emergency response, disaster preparedness, and public safety.
Organizations Monitoring Seismic Activity in Kentucky
Several organizations play a vital role in monitoring seismic activity in Kentucky. These include:
- The Kentucky Geological Survey (KGS): The KGS is the official state geological survey, responsible for providing scientific and technical information on the state’s geology, including earthquake activity. They operate a network of seismographs across Kentucky and provide real-time earthquake data and reports.
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS is a federal agency that monitors earthquakes and other geological hazards nationwide. They maintain a comprehensive network of seismographs and provide real-time earthquake information, including magnitude, location, and depth.
- The National Earthquake Information Center (NEIC): The NEIC, operated by the USGS, is the primary source for earthquake information in the United States. They analyze data from seismographs worldwide and provide rapid and accurate reports on earthquake events.
Real-Time Earthquake Data for Kentucky
For real-time earthquake data specific to Kentucky, you can refer to the following website:
[https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/map/?extent=-90.475,36.45,-81.934,40.117&basemap=grayscale&maptype=earthquake&timewindow=7days&magnitude=0.0](https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/map/?extent=-90.475,36.45,-81.934,40.117&basemap=grayscale&maptype=earthquake&timewindow=7days&magnitude=0.0)
This website provides a map displaying recent earthquakes in Kentucky and other regions, along with detailed information about each event.
Earthquake Preparedness

Living in an earthquake-prone region like Kentucky requires preparedness. Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the impact of an earthquake on you and your family. This section Artikels essential preparedness measures for residents of Kentucky.
Earthquake Preparedness Tips
It is crucial to be prepared for an earthquake. The following table details steps to take before, during, and after an earthquake, along with valuable resources.
| Before an Earthquake | During an Earthquake | After an Earthquake | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Impact of Earthquakes on Infrastructure
/cdn0.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/51947965/Screen_Shot_2016_11_21_at_6.21.08_PM.0.png)
Earthquakes pose a significant threat to infrastructure in Kentucky, potentially causing widespread damage to buildings, roads, and utilities. The state’s susceptibility to seismic activity, while relatively low compared to other regions, necessitates careful consideration of earthquake-resistant design and construction practices to mitigate potential risks.
Importance of Building Codes and Earthquake-Resistant Construction Practices, Was there an earthquake in kentucky today
Building codes play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and resilience of structures during seismic events. Kentucky’s building codes are designed to minimize damage and protect lives by incorporating earthquake-resistant design principles. These codes specify requirements for structural components, foundation design, and material selection, aiming to enhance a building’s ability to withstand seismic forces.Earthquake-resistant construction practices go beyond code compliance, incorporating advanced engineering techniques to improve a structure’s seismic performance.
These practices include:
- Base Isolation:This technique separates the building from the ground, reducing the transmission of seismic energy to the structure. Base isolation systems typically use flexible bearings or sliding mechanisms to absorb and dissipate earthquake forces.
- Ductile Framing:Ductile framing utilizes materials that can deform significantly without fracturing, allowing the structure to absorb and dissipate seismic energy. Steel and reinforced concrete are commonly used in ductile framing systems.
- Shear Walls:Shear walls are designed to resist lateral forces, such as those generated by earthquakes. They are typically constructed of reinforced concrete or masonry and are strategically placed within the building to provide stability.
- Bracing:Bracing systems, such as diagonal bracing or moment-resisting frames, provide additional support and stability to the structure, helping to prevent collapse during seismic events.
Examples of Past Earthquakes and Infrastructure Damage
Although Kentucky has experienced relatively few significant earthquakes, historical events demonstrate the potential for significant infrastructure damage. The 1811-1812 New Madrid earthquakes, centered in Missouri, had widespread effects across the Mississippi Valley, including Kentucky. These earthquakes caused ground shaking and liquefaction, leading to widespread damage to buildings, bridges, and roads.The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake in California, while not directly impacting Kentucky, serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of seismic events on infrastructure.
The earthquake caused significant damage to bridges, highways, and buildings, highlighting the importance of earthquake-resistant design and construction practices.
Public Safety and Response

In the event of an earthquake, the safety and well-being of the public are paramount. Emergency responders play a critical role in mitigating the impacts of earthquakes and ensuring the safety of the affected population.
Emergency Response in Earthquake Situations
Emergency responders, including first responders, law enforcement, and medical personnel, are trained to handle various situations during and after an earthquake. Their responsibilities include:
- Search and Rescue: Locating and rescuing individuals trapped in collapsed structures or other dangerous environments.
- Medical Care: Providing immediate medical attention to those injured during the earthquake.
- Damage Assessment: Evaluating the extent of structural damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Evacuation and Sheltering: Assisting in evacuating people from unsafe areas and providing temporary shelter.
- Traffic Control: Managing road closures and traffic flow to facilitate emergency access and prevent further accidents.
- Communication and Coordination: Maintaining communication channels with other emergency services and coordinating response efforts.
Communication Protocols and Evacuation Procedures
Kentucky has established communication protocols and evacuation procedures to ensure efficient response during earthquake events. These protocols include:
- Public Alert System: Utilizing sirens, text messages, and other communication channels to warn the public about potential earthquake threats.
- Emergency Broadcast System: Broadcasting emergency information and instructions through radio and television stations.
- Social Media: Sharing updates and information about earthquake events through official social media accounts.
- Evacuation Plans: Developing and implementing evacuation plans for schools, businesses, and other public places.
- Drop, Cover, and Hold On: Educating the public on the importance of taking immediate action during an earthquake by dropping to the ground, covering their heads and necks, and holding on to a sturdy object.
Contact Information for Emergency Services
| Service | Phone Number |
|---|---|
| Kentucky State Police | (502) 782-2011 |
| Kentucky Emergency Management | (502) 564-2200 |
| Kentucky Department of Public Health | (502) 564-2200 |
| Kentucky Department of Transportation | (502) 564-2200 |
Essential FAQs
How often do earthquakes occur in Kentucky?
While earthquakes in Kentucky are less frequent than in other parts of the United States, they do occur. The state experiences an average of one or two earthquakes per year, most of which are minor and go unnoticed by the general population.
Are there any specific areas in Kentucky that are more prone to earthquakes?
Yes, the western part of Kentucky, particularly near the New Madrid Seismic Zone, is considered more prone to earthquakes than other parts of the state. The zone’s proximity to Kentucky makes the state susceptible to tremors originating from the zone’s seismic activity.
What should I do if I feel an earthquake in Kentucky?
If you feel an earthquake, it is important to stay calm and follow safety guidelines. Drop, cover, and hold on under a sturdy piece of furniture or in an interior doorway. Stay away from windows and exterior walls, and avoid using stairs or elevators.