Tools for business analysis empower organizations to delve into the intricacies of their operations, unlocking insights that drive informed decision-making. From data analysis to process modeling and collaboration, these tools provide a comprehensive toolkit for optimizing business performance.
In this guide, we will explore the vast landscape of tools for business analysis, unraveling their purpose, features, and benefits. We will delve into the criteria for selecting the right tools and uncover best practices for implementation. Moreover, we will shed light on emerging trends that are shaping the future of business analysis.
Tools Overview

Business analysis tools empower professionals to gather, analyze, and interpret data, facilitating informed decision-making and improved business outcomes. These tools encompass a wide range of functionalities, catering to diverse business analysis needs.
Tools for business analysis can be categorized into the following functional groups:
Data Analysis Tools
Data analysis tools enable the exploration, manipulation, and visualization of data. They provide capabilities for data cleansing, transformation, and statistical analysis, helping analysts uncover patterns, trends, and insights hidden within data.
When you’re working with tools for business analysis, it’s important to have the right tools for the job. If you’re looking for a way to organize your tools, you might want to consider building a wooden tool box. You can find wooden tool box blueprints online that will show you how to build a tool box that’s perfect for your needs.
Once you have your tool box built, you can start organizing your tools so that you can easily find what you need when you need it.
- Microsoft Excel:A widely used spreadsheet software with powerful data analysis capabilities, including data manipulation, statistical functions, and charting.
- Tableau:A popular data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive dashboards and visualizations, making complex data easily understandable.
- Power BI:A Microsoft product that offers data analysis, visualization, and reporting capabilities, enabling businesses to gain insights from their data.
Process Modeling Tools
Process modeling tools help analysts visualize and analyze business processes. They provide a graphical representation of the steps, activities, and relationships involved in a process, facilitating process improvement and optimization.
- Microsoft Visio:A versatile diagramming and process modeling tool that allows users to create flowcharts, org charts, and other process visualizations.
- ARIS:A comprehensive process modeling suite that supports process analysis, design, and optimization, providing a holistic view of business processes.
- Bizagi:A business process management platform that offers process modeling, automation, and monitoring capabilities, enabling businesses to streamline their processes.
Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools facilitate teamwork and communication among business analysts and stakeholders. They provide features for document sharing, version control, and real-time collaboration, ensuring that all team members are on the same page.
When it comes to business analysis, having the right tools can make all the difference. Tools like the harry josh pro tools pro dryer 2000 can help you gather data, analyze trends, and make informed decisions. These tools can streamline your workflow and provide valuable insights that can help you improve your business performance.
So, if you’re looking for ways to improve your business analysis capabilities, investing in the right tools is a great place to start.
- Microsoft Teams:A comprehensive collaboration platform that offers instant messaging, video conferencing, file sharing, and task management.
- Slack:A popular messaging and collaboration tool designed for teams, providing real-time communication, file sharing, and integration with other tools.
- Trello:A project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize and track tasks, facilitating collaboration and workflow management.
Selection Criteria
Choosing the right business analysis tools is crucial for efficient and effective analysis. Several key factors should be considered during the selection process.
First and foremost, tool compatibilityis essential. The selected tool should be compatible with existing systems and technologies within the organization. This ensures seamless integration and avoids data compatibility issues.
Scalabilityis another important consideration. The tool should be able to handle increasing data volumes and complexity as the business grows. It should also be flexible enough to adapt to changing business requirements.
Finally, ease of useis crucial. The tool should be user-friendly and intuitive, allowing analysts to quickly learn and use its features. This reduces the learning curve and increases productivity.
Evaluating Tools
To evaluate tools based on specific business requirements, consider the following:
- Data analysis capabilities: Determine the types of data the tool can analyze, including structured, unstructured, and real-time data.
- Visualization capabilities: Assess the tool’s ability to present data in various formats, such as charts, graphs, and dashboards.
- Collaboration features: Evaluate the tool’s support for collaboration among analysts, stakeholders, and teams.
- Reporting capabilities: Determine the tool’s ability to generate customizable reports and share insights.
- Integration capabilities: Assess the tool’s ability to integrate with other systems, such as data warehouses and business intelligence platforms.
Implementation Strategies: Tools For Business Analysis

To ensure successful implementation of business analysis tools, it’s crucial to follow best practices. These include defining clear objectives, selecting the right tools, and integrating them seamlessly into existing workflows.
The integration process should involve customizing the tools to meet specific business needs and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Effective training and onboarding of users are also essential to maximize adoption and utilization.
User Training and Onboarding
Effective training programs are essential for users to fully understand and utilize the capabilities of the tools. This may involve a combination of online resources, hands-on workshops, and mentorship from experienced users.
- Identify Training Needs:Determine the specific knowledge and skills users require to effectively use the tools.
- Develop Training Materials:Create comprehensive training materials that cover all aspects of the tools, including their features, functionality, and best practices.
- Provide Hands-on Experience:Offer practical exercises and simulations to allow users to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Offer Ongoing Support:Establish mechanisms for users to access ongoing support and assistance, such as online forums, documentation, and technical support.
Data Analysis and Visualization

In business analysis, data analysis and visualization tools play a pivotal role in extracting meaningful insights from complex data sets. These tools empower analysts to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that would otherwise remain hidden, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Advanced Data Visualization Capabilities
Modern data analysis tools offer a wide range of advanced data visualization capabilities that enhance the communication and presentation of findings. These capabilities include:
- Interactive dashboards and reports
- Customizable charts and graphs
- Geospatial mapping
- Data storytelling features
By leveraging these capabilities, analysts can create visually compelling and easy-to-understand representations of data, facilitating effective communication with stakeholders and decision-makers.
Process Modeling and Simulation
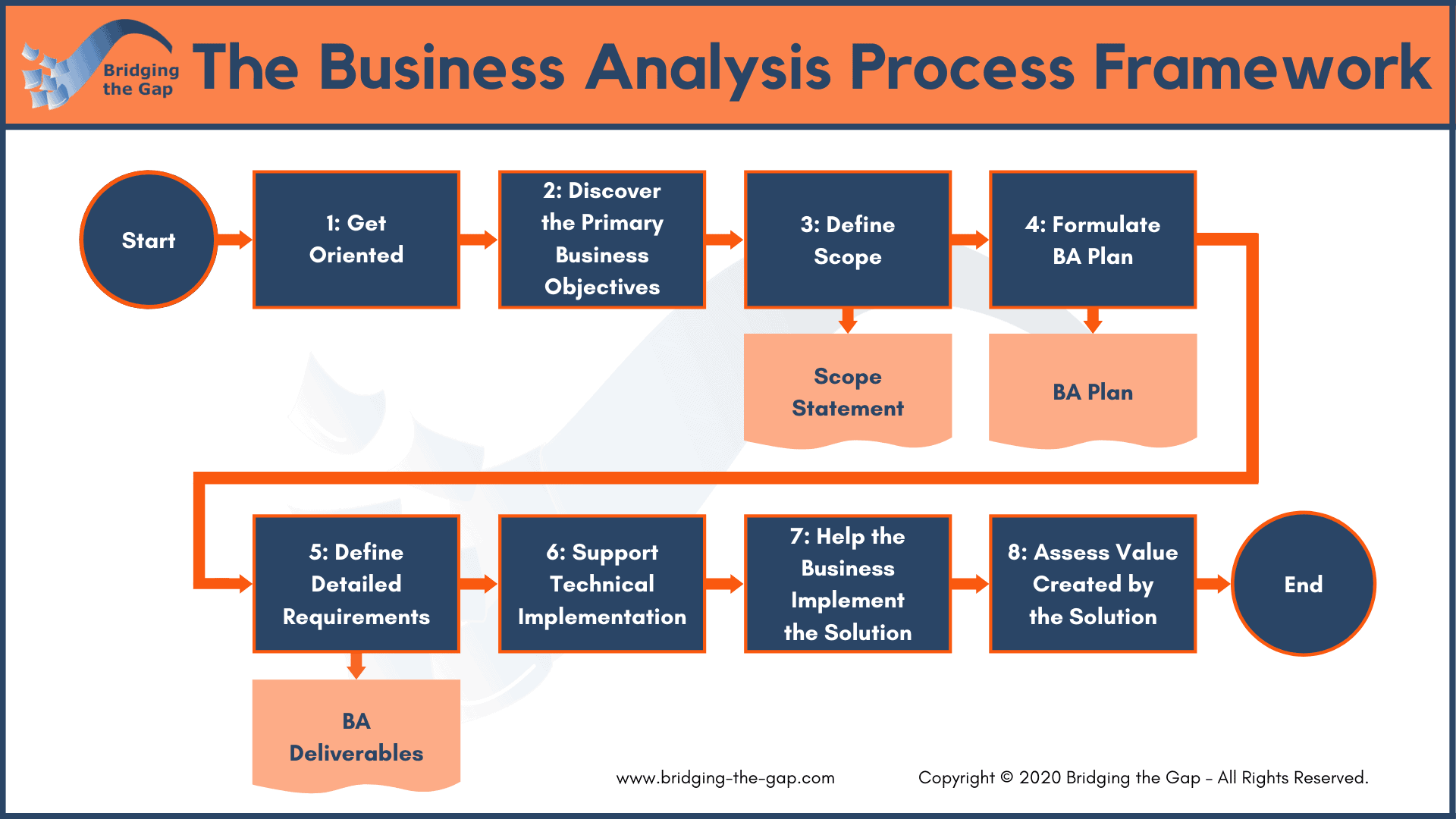
Process modeling and simulation tools are indispensable in business analysis, providing a structured approach to analyze, visualize, and optimize business processes.
These tools enable analysts to create detailed diagrams of processes, identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Through simulation, they can test different scenarios and configurations, predicting the impact of changes before implementing them in real-world systems.
BPMN and Process Modeling Notations
Many tools support the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard, a widely-used graphical language for process modeling. BPMN provides a common vocabulary and set of symbols, allowing analysts to create clear and concise diagrams that can be easily understood by stakeholders.
- Visio:A Microsoft product that offers comprehensive process modeling capabilities, including BPMN support.
- ARIS:A powerful toolset from Software AG, providing advanced features for process modeling, simulation, and optimization.
- Bizagi:A cloud-based platform that combines process modeling with workflow automation and collaboration features.
Collaboration and Communication
Business analysis tools empower teams to collaborate and communicate seamlessly, enabling them to share ideas, iterate on concepts, and make informed decisions together.
Real-Time Document Sharing
Tools like Google Docs and Microsoft Teams allow multiple users to access, edit, and comment on documents simultaneously. This real-time collaboration eliminates version conflicts and ensures everyone is working on the latest version.
Commenting and Feedback, Tools for business analysis
Built-in commenting features facilitate asynchronous communication, allowing team members to provide feedback, ask questions, and suggest improvements without interrupting the workflow. This promotes constructive discussions and ensures that diverse perspectives are considered.
Version Control
Version control systems, such as Git and Subversion, track changes made to documents over time. This allows teams to revert to previous versions if necessary, ensuring data integrity and preventing accidental overwrites.
Examples of Collaboration Tools
Slack
A messaging and collaboration platform that allows teams to communicate in real-time through channels, direct messages, and video conferencing.
Jira
A project management tool that provides features for issue tracking, task assignment, and team collaboration.
Confluence
A knowledge base and collaboration platform that allows teams to create, share, and organize documents, ideas, and project updates.
Emerging Trends
The landscape of tools for business analysis is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging all the time. These technologies are having a significant impact on the way that businesses analyze data and make decisions.
One of the most important trends is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). AI-powered tools can automate many of the tasks that were once done manually, freeing up business analysts to focus on more strategic work. For example, AI can be used to:
- Collect and clean data
- Identify patterns and trends
- Develop predictive models
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms can be used to:
- Identify customer churn
- Predict sales
- Optimize marketing campaigns
Cloud computing is another major trend that is impacting the business analysis landscape. Cloud-based tools are hosted on the internet, which makes them accessible from anywhere. This makes it easier for businesses to collaborate on projects and share data. Cloud-based tools also tend to be more scalable and affordable than on-premises tools.
Potential Benefits of Adopting New Technologies
- Improved efficiency
- Increased accuracy
- Better decision-making
- Reduced costs
Challenges of Adopting New Technologies
- Cost
- Complexity
- Data security
- Lack of expertise
Businesses that are able to successfully adopt new technologies will be well-positioned to succeed in the future. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential benefits and challenges before making any decisions.
FAQs
What are the key benefits of using tools for business analysis?
Tools for business analysis provide numerous benefits, including improved data analysis, streamlined process modeling, enhanced collaboration, and increased efficiency.
How do I select the right tools for business analysis?
Consider factors such as tool functionality, compatibility, scalability, ease of use, and alignment with specific business requirements.
What are some best practices for implementing tools for business analysis?
Establish clear goals, integrate tools into existing workflows, provide adequate training, and monitor usage to ensure adoption and effectiveness.