Software test management tools are essential for any organization looking to streamline their testing processes and improve the quality of their software. These tools provide a centralized platform for managing all aspects of the testing process, from planning and execution to defect tracking and reporting.
In this guide, we’ll explore the benefits, features, and best practices of software test management tools, helping you make informed decisions about selecting and implementing the right tool for your organization.
Software test management tools offer a wide range of benefits that can help organizations improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their testing processes. These benefits include improved test planning and execution, enhanced collaboration and communication among testing teams, increased test efficiency and effectiveness, real-time visibility into testing progress, and comprehensive test reports and analytics.
Software Test Management Tools Overview

Software test management tools are designed to assist in the planning, execution, and tracking of software testing activities. These tools help teams manage the complexities of testing, improve collaboration, and ensure the quality of software products.
Some common software test management tools include:
- Jira
- TestRail
- Zephyr
- QMetry
- Ranorex Studio
Key Features and Capabilities
Software test management tools typically offer a range of features and capabilities, including:
- Test case management: Create, organize, and manage test cases.
- Test planning: Plan and schedule testing activities.
- Test execution: Execute test cases and track results.
- Defect tracking: Track and manage defects found during testing.
- Reporting: Generate reports on test progress and results.
- Integration with other tools: Integrate with other tools such as issue trackers and version control systems.
Benefits of Using Software Test Management Tools
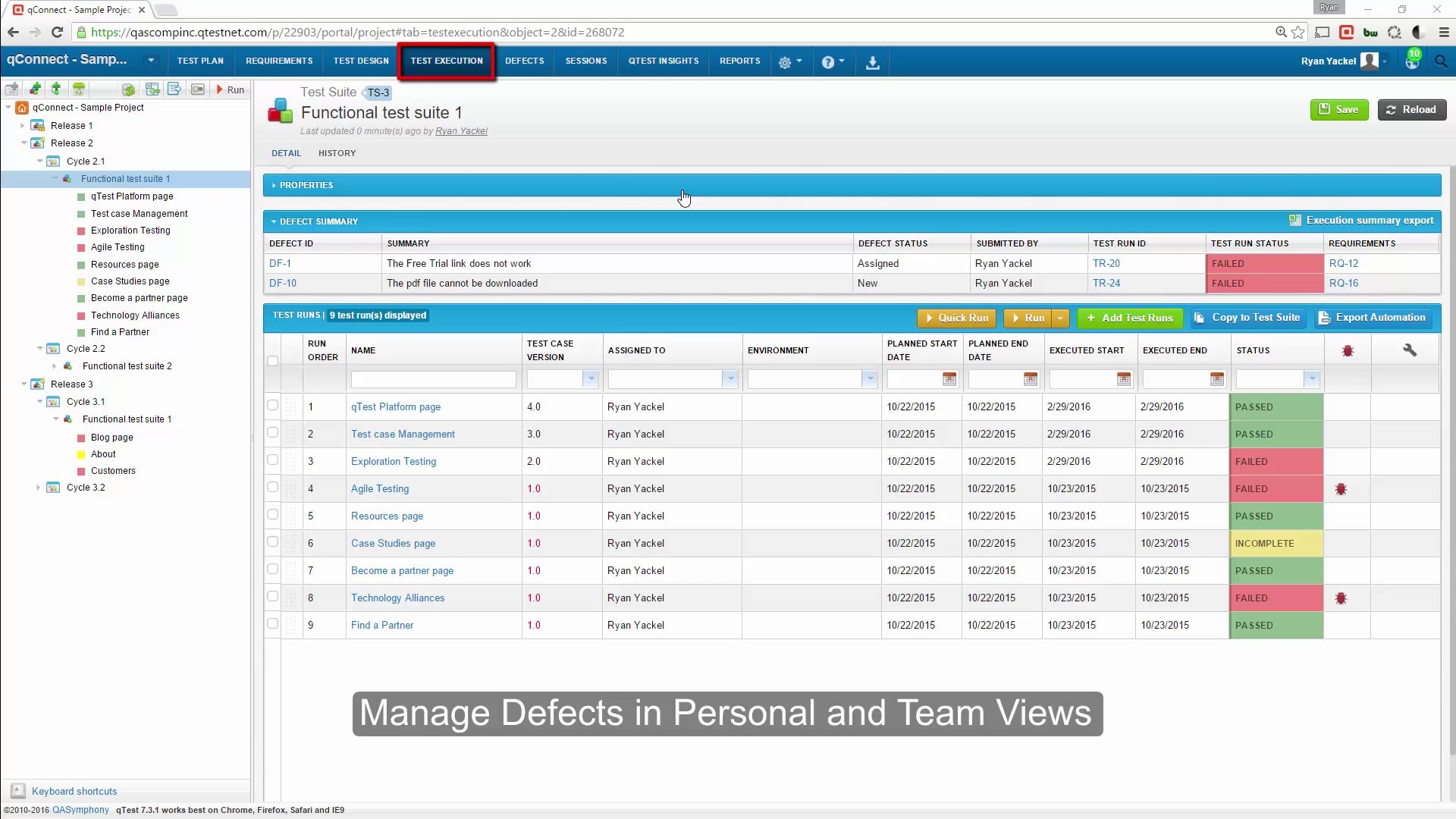
Software test management tools provide numerous advantages that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the testing process. These tools streamline test planning and execution, foster collaboration among testing teams, and offer valuable insights into testing progress.
Improved Test Planning and Execution
Test management tools facilitate the creation and management of test plans, ensuring that all testing activities are aligned with the project requirements. They enable testers to define test cases, assign them to team members, and track their progress. By centralizing test planning and execution, these tools improve coordination and reduce the risk of errors.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Test management tools provide a central platform for testing teams to collaborate and share information. They enable testers to communicate with each other, track changes to test cases, and discuss test results. This enhanced collaboration streamlines the testing process and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings.
Increased Test Efficiency and Effectiveness
Test management tools automate many tasks associated with testing, such as test case generation and execution. This automation frees up testers to focus on more complex and critical tasks. Additionally, these tools provide features such as defect tracking and reporting, which help testers identify and resolve issues quickly.
Real-Time Visibility into Testing Progress
Test management tools provide real-time visibility into the testing process. They offer dashboards and reports that track test progress, identify bottlenecks, and highlight areas for improvement. This real-time visibility enables stakeholders to make informed decisions and adjust their testing strategies as needed.
Comprehensive Test Reports and Analytics
Test management tools generate comprehensive test reports that provide insights into the quality and effectiveness of the testing process. These reports can be used to analyze test results, identify trends, and improve testing practices. The analytics provided by these tools help testers understand the performance of their tests and make data-driven decisions.
Key Features of Software Test Management Tools

Software test management tools offer a comprehensive set of features that streamline the testing process and enhance its effectiveness. These features enable testers to efficiently manage test cases, track requirements, identify and manage defects, plan and schedule testing activities, and generate reports to analyze test results.
Test Case Management
Test case management is a crucial aspect of software testing. Test management tools provide features for creating, managing, and executing test cases. Testers can create detailed test cases that define the steps to be performed, expected results, and preconditions. These test cases can be organized into test suites and assigned to specific testers or teams.
Requirements Traceability, Software test management tools
Requirements traceability is essential for ensuring that test cases are aligned with the software’s requirements. Test management tools allow testers to link test cases to specific requirements. This traceability enables testers to track which requirements have been tested and identify any gaps in coverage.
It also facilitates impact analysis when requirements change, as testers can quickly determine which test cases need to be updated.
Defect Tracking
Defect tracking is an integral part of the testing process. Test management tools provide features for identifying, tracking, and managing defects throughout the testing lifecycle. Testers can log defects, assign them to developers, and track their progress through the resolution process.
This helps ensure that defects are resolved promptly and effectively.
Test Planning and Scheduling
Test planning and scheduling are critical for managing testing activities effectively. Test management tools offer features for planning and scheduling test cycles, allocating resources, and tracking progress. Testers can create test plans that define the scope of testing, timelines, and dependencies.
They can also schedule test executions and assign testers to specific tasks.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of testing efforts. Test management tools provide features for generating reports that summarize test results, identify trends, and provide insights into the testing process. These reports can be used to improve test coverage, optimize test execution, and demonstrate the value of testing to stakeholders.
Considerations for Selecting Software Test Management Tools

Selecting the right software test management tool is crucial for effective test management. Consider the following factors to make an informed decision:
Evaluate Tool Features and Capabilities
Assess the tool’s features against your testing needs. Consider its support for different testing types (e.g., functional, performance, security), integration with other tools (e.g., bug tracking, requirements management), and reporting capabilities.
Assess Tool Compatibility with Existing Systems and Processes
Ensure the tool integrates seamlessly with your existing software development and testing processes. Consider its compatibility with your operating systems, databases, and development environments.
Consider Tool Scalability and Flexibility
Evaluate the tool’s ability to handle increasing test volumes and complexity as your projects grow. Consider its support for distributed testing, parallel execution, and automation frameworks.
Evaluate Tool Pricing and Support Options
Compare the pricing models and support options of different tools. Consider the cost of licensing, maintenance, and training. Assess the availability of technical support, documentation, and community resources.
Get Feedback from Users and Industry Experts
Seek feedback from other users and industry experts who have used the tool. Read reviews, attend webinars, and consult with experts to gather insights into the tool’s strengths and weaknesses.
Best Practices for Using Software Test Management Tools

Implementing software test management tools effectively requires adopting certain best practices to maximize their benefits. These practices ensure efficient and organized testing processes, leading to improved software quality and reduced testing timeframes.
For efficient software test management, it’s essential to utilize specialized tools. These tools streamline the testing process and enhance collaboration. Speaking of tools, if you’re tackling drywall finishing, check out the comprehensive range of tools finish drywall available. Equipping yourself with the right tools is crucial for a smooth and professional finish.
Returning to software test management tools, they offer features like test case management, defect tracking, and reporting, empowering teams to deliver high-quality software.
Establish Clear Testing Goals and Objectives
Before using the tool, it’s crucial to define the specific testing goals and objectives. This involves determining the scope of testing, identifying critical areas to focus on, and setting measurable criteria for evaluating test results. Clear goals provide a solid foundation for planning and executing test cases, ensuring that testing efforts are aligned with the project’s overall objectives.
Define Roles and Responsibilities for Testing Team Members
Assign clear roles and responsibilities to each member of the testing team. This includes defining who is responsible for creating test plans, executing test cases, reporting defects, and analyzing test results. Clearly defined roles prevent overlaps, ensure accountability, and facilitate smooth collaboration among team members.
Use the Tool to Its Full Potential
To fully leverage the capabilities of the software test management tool, explore and utilize all its available features. This may include features for test case management, defect tracking, reporting, and analytics. By maximizing the tool’s potential, teams can streamline testing processes, improve efficiency, and gain deeper insights into test results.
The use of software test management tools is crucial for ensuring the quality of software products. These tools help manage the entire testing process, from planning and execution to reporting and analysis. Additionally, they can integrate with other tools, such as press brake tooling , to provide a comprehensive solution for software testing.
By leveraging these tools, organizations can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their testing efforts, ultimately delivering higher-quality software products to their customers.
Regularly Review and Update Test Plans and Test Cases
As the software under test evolves, it’s essential to regularly review and update test plans and test cases. This ensures that tests remain relevant and effective, covering new features and addressing changes in the software’s functionality. Regular updates prevent outdated tests from skewing test results and maintain the accuracy and reliability of the testing process.
Use the Tool to Generate Reports and Analyze Test Results
Software test management tools provide robust reporting and analytics capabilities. Utilize these features to generate comprehensive reports that summarize test results, identify trends, and highlight areas for improvement. By analyzing test results, teams can gain valuable insights into the software’s quality, identify potential risks, and make informed decisions to enhance the testing process.
Case Studies and Examples
Software test management tools have been successfully implemented in various organizations, leading to improved testing processes and enhanced software quality. Here are some case studies and examples:
Case Study: Company X
- Company X, a leading software development firm, faced challenges with managing their complex testing processes. They implemented a software test management tool to streamline their testing activities, improve collaboration, and enhance test traceability.
- With the tool, Company X experienced a significant reduction in testing time, improved defect detection rate, and enhanced overall software quality.
Case Study: Company Y
- Company Y, a global e-commerce company, struggled with managing their large and distributed testing team. They adopted a software test management tool to centralize their testing processes, automate tasks, and improve communication.
- The tool enabled Company Y to achieve greater visibility and control over their testing activities, resulting in improved test efficiency, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
- Challenges:Implementing software test management tools can involve challenges such as selecting the right tool, integrating it with existing systems, and training the team.
- Lessons Learned:Organizations should carefully evaluate their needs, conduct thorough research, and involve stakeholders throughout the implementation process to overcome these challenges.
FAQs
What are the key features of software test management tools?
The key features of software test management tools include test case management, requirements traceability, defect tracking, test planning and scheduling, and reporting and analytics.
What are the benefits of using software test management tools?
The benefits of using software test management tools include improved test planning and execution, enhanced collaboration and communication among testing teams, increased test efficiency and effectiveness, real-time visibility into testing progress, and comprehensive test reports and analytics.
What are the considerations for selecting software test management tools?
The considerations for selecting software test management tools include evaluating tool features and capabilities, assessing tool compatibility with existing systems and processes, considering tool scalability and flexibility, evaluating tool pricing and support options, and getting feedback from users and industry experts.