The scimitar ear drum, a unique anatomical structure, plays a crucial role in hearing and balance. Its distinctive shape and characteristics set it apart from other ear drums, making it a topic of interest in both medical and scientific communities.
This detailed overview delves into the anatomy, function, clinical significance, diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis of the scimitar ear drum, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating aspect of human anatomy.
Anatomy of the Scimitar Ear Drum

The scimitar ear drum, also known as the sickle-shaped ear drum, is a unique anatomical structure found in some individuals. It is characterized by its distinctive shape, which resembles a scimitar or sickle.
The scimitar ear drum is located in the middle ear, separating the outer ear from the inner ear. It is a thin, translucent membrane that vibrates in response to sound waves, transmitting them to the inner ear.
Shape and Structure, Scimitar ear drum
The scimitar ear drum is typically crescent-shaped, with a convex upper border and a concave lower border. This shape is different from the round or oval shape of most ear drums.
The scimitar ear drum is also thinner and more delicate than a typical ear drum. It is composed of three layers: an outer layer of skin, a middle layer of fibrous tissue, and an inner layer of mucous membrane.
Function of the Scimitar Ear Drum
The scimitar ear drum plays a crucial role in hearing and sound perception. Its unique shape and structure endow it with specific acoustic properties that contribute to the overall functionality of the auditory system.
The scimitar ear drum’s curved shape acts as a sound collector, directing sound waves into the ear canal. This curvature also helps to amplify certain frequencies, enhancing the perception of speech and other important sounds.
Acoustic Properties
The scimitar ear drum’s thin and flexible nature allows it to vibrate in response to sound waves. These vibrations are then transmitted to the ossicles, a chain of small bones in the middle ear, which further amplify and transmit the sound to the inner ear.
The specific shape of the scimitar ear drum creates a resonance frequency, which is the frequency at which the drum vibrates most efficiently. This resonance frequency is tuned to match the frequencies of human speech, ensuring optimal perception of language.
A scimitar ear drum is a rare condition where the eardrum has an abnormal shape. It can cause hearing loss and other problems. To address the challenges posed by scimitar ear drum, it’s crucial to employ strategic planning tools.
These tools help healthcare professionals develop comprehensive plans to manage the condition effectively, including treatment strategies and monitoring protocols. By integrating strategic planning into the management of scimitar ear drum, patients can benefit from a tailored and optimized approach to their care.
Clinical Significance of the Scimitar Ear Drum
The scimitar ear drum is not merely a unique anatomical variation; it also holds clinical significance, as it is often associated with certain medical conditions. Understanding these associations can aid in the diagnosis and management of underlying health issues.
One of the most common clinical implications of a scimitar ear drum is its association with a rare genetic condition known as scimitar syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by a constellation of congenital heart defects, including a scimitar-shaped pulmonary vein that drains into the inferior vena cava.
Individuals with scimitar syndrome may also experience respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
In addition to scimitar syndrome, a scimitar ear drum can also be associated with other congenital heart defects, such as atrial septal defects and ventricular septal defects. These heart defects can lead to abnormal blood flow within the heart, which can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain.
Furthermore, a scimitar ear drum may affect hearing and balance. The abnormal shape of the ear drum can interfere with the transmission of sound waves, leading to hearing loss. Additionally, the scimitar ear drum can affect the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance.
This can result in symptoms such as dizziness, vertigo, and difficulty maintaining balance.
Diagnostic Evaluation of the Scimitar Ear Drum
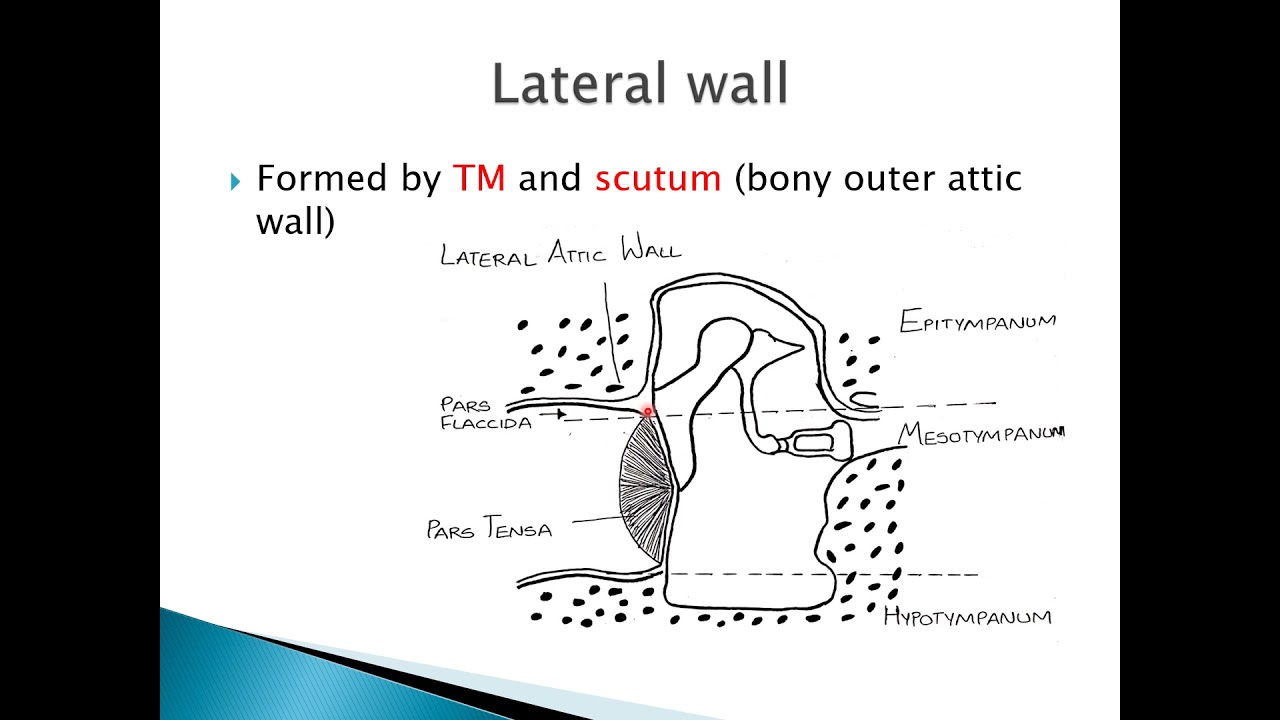
Diagnosing a scimitar ear drum involves a thorough examination of the ear to assess its structure and function.
Otoscopy
Otoscopy is a non-invasive procedure where a healthcare professional uses an otoscope, a lighted instrument, to visualize the ear canal and eardrum. This allows them to observe the shape, color, and mobility of the eardrum, as well as any abnormalities such as scarring, perforations, or the presence of fluid or debris.
The scimitar ear drum, a unique auditory structure, has a distinctive shape resembling a curved sword. Its anatomy has inspired musical instruments like the drum cymbal scimitar , where its curved form creates a distinctive sound. The scimitar ear drum’s sensitivity and response to sound waves make it an important component in hearing, allowing us to perceive a wide range of auditory stimuli.
Tympanometry
Tympanometry is a diagnostic test that measures the pressure and movement of the eardrum in response to sound waves. It can help assess the function of the middle ear, including the eardrum, ossicles, and Eustachian tube. Abnormal results may indicate a scimitar ear drum or other underlying ear conditions.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis of a scimitar ear drum is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment. It helps rule out other ear conditions with similar symptoms, such as otitis media or a perforated eardrum. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can prevent complications and improve hearing outcomes.
Treatment Options for the Scimitar Ear Drum
When dealing with a scimitar ear drum, treatment options vary depending on the severity and underlying cause. Both surgical and non-surgical approaches are available, each with its own set of benefits and risks.
Non-Surgical Approaches
- Observation:In cases where the scimitar ear drum is small and not causing any symptoms, observation may be the best course of action. The doctor will monitor the condition over time to ensure it does not worsen.
- Hearing aids:If the scimitar ear drum is affecting hearing, hearing aids can be used to amplify sound and improve hearing ability.
- Eustachian tube dilation:This procedure involves inserting a small balloon into the Eustachian tube to widen it, improving airflow and reducing pressure on the ear drum.
Surgical Approaches
- Tympanoplasty:This surgery involves repairing or replacing the damaged ear drum with a graft made from the patient’s own tissue or a synthetic material.
- Mastoidectomy:If the scimitar ear drum is caused by an infection in the mastoid bone, a mastoidectomy may be necessary to remove the infected tissue and prevent further damage.
- Stapedectomy:This surgery involves replacing the stapes bone in the middle ear, which can improve hearing in cases where the scimitar ear drum is affecting the stapes bone.
The best treatment option for a scimitar ear drum will depend on the individual patient’s condition and preferences. It’s important to discuss all options with a qualified doctor to make an informed decision.
Prognosis and Outcomes of Scimitar Ear Drum

The prognosis of a scimitar ear drum varies depending on several factors. Generally, with early diagnosis and proper treatment, the outcomes are usually positive.
Factors Influencing Outcomes
- Severity of the deformity:The extent and severity of the scimitar ear drum can affect the degree of hearing loss and other complications.
- Age of onset:Early onset of the condition, particularly in children, can result in more significant hearing loss and developmental issues.
- Associated middle ear conditions:Co-existing middle ear infections or other abnormalities can worsen the prognosis.
- Timeliness of treatment:Prompt intervention and treatment can improve outcomes and prevent further complications.
Potential Complications
- Hearing loss:Scimitar ear drum can cause varying degrees of hearing loss, ranging from mild to severe.
- Chronic ear infections:The abnormal shape of the ear drum can make it more susceptible to infections.
- Cholesteatoma:A rare but serious complication, where a cyst forms in the middle ear, can occur in severe cases.
FAQ Corner
What causes a scimitar ear drum?
The exact cause of a scimitar ear drum is unknown, but it is believed to be related to developmental abnormalities during fetal development.
Can a scimitar ear drum be treated?
Treatment options for a scimitar ear drum vary depending on the severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatments may include hearing aids or sound therapy, while surgical interventions may be necessary in some cases.
What are the long-term effects of a scimitar ear drum?
The long-term effects of a scimitar ear drum can vary. Some individuals may experience hearing loss or balance problems, while others may have no significant complications.