In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, popular SIEM tools have emerged as indispensable assets for organizations seeking to safeguard their networks and data. These advanced tools provide real-time monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities, empowering security teams to stay ahead of potential breaches.
As we delve into the world of SIEM tools, we’ll explore their essential features, compare leading solutions, and guide you through the selection, implementation, and management process. Get ready to enhance your cybersecurity posture and stay protected against today’s sophisticated threats.
SIEM Tools Overview

Security information and event management (SIEM) tools are designed to provide comprehensive visibility and analysis of security events across an organization’s IT infrastructure.
They collect, aggregate, and analyze data from various sources, such as logs, network traffic, and security devices, to provide a holistic view of security events and help organizations detect, investigate, and respond to potential threats.
Benefits of SIEM Tools
Using SIEM tools offers several benefits, including:
- Improved threat detection:SIEM tools use advanced analytics and correlation techniques to identify suspicious activities and potential threats that might be missed by individual security tools.
- Centralized visibility:SIEM tools provide a single, centralized platform to monitor and manage security events from across the organization’s IT infrastructure, eliminating the need to manually collect and analyze data from multiple sources.
- Faster incident response:SIEM tools can automate incident detection and response processes, allowing organizations to quickly identify and respond to security incidents, minimizing the potential impact on business operations.
- Compliance and reporting:SIEM tools can assist organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements and provide comprehensive reporting on security events and incidents, making it easier to demonstrate compliance and improve security posture.
Popular SIEM Tools
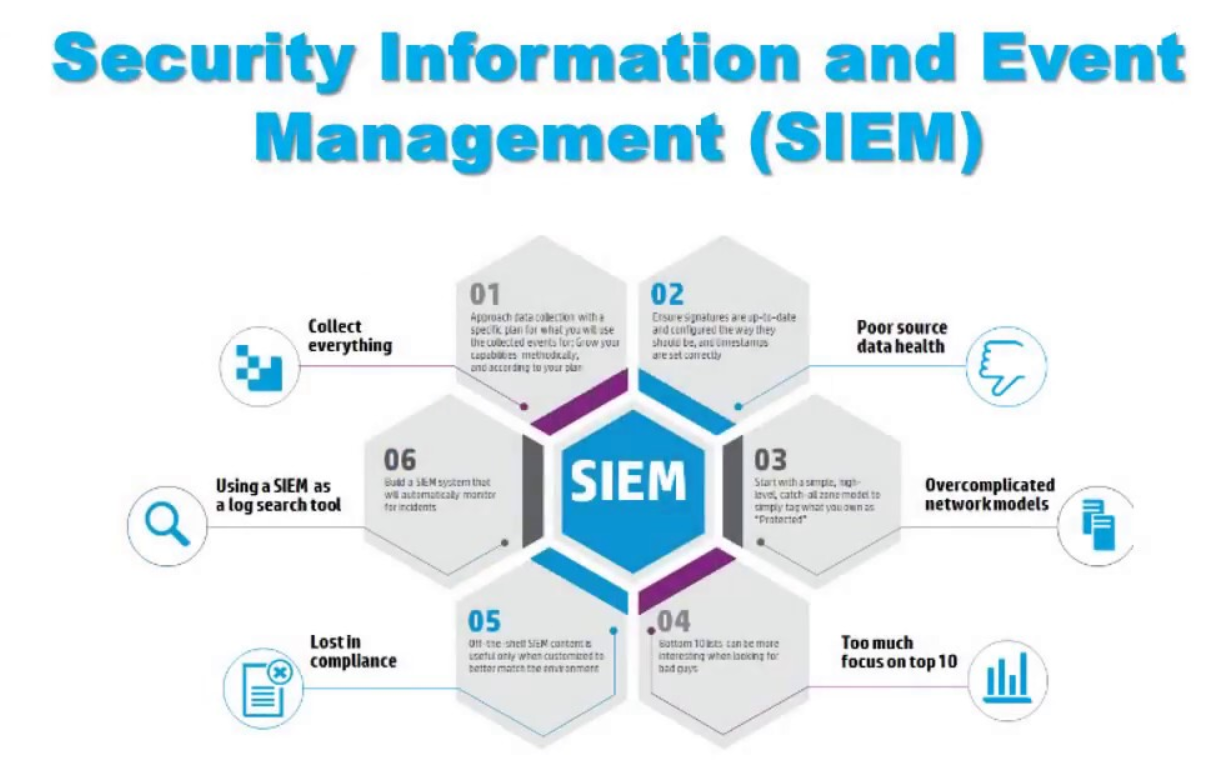
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools are essential for any organization looking to improve its security posture. These tools help organizations collect, analyze, and respond to security events in real-time.
There are many different SIEM tools available on the market, each with its own unique features and capabilities. To help you choose the right SIEM tool for your organization, we have compiled a table comparing the features and capabilities of some of the most popular SIEM tools.
Comparison of Popular SIEM Tools
| Feature | Splunk | IBM QRadar | LogRhythm | Microsoft Azure Sentinel | Elastic Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log Collection | Supports a wide range of log sources, including syslogs, Windows event logs, and custom logs | Supports a wide range of log sources, including syslogs, Windows event logs, and custom logs | Supports a wide range of log sources, including syslogs, Windows event logs, and custom logs | Supports a wide range of log sources, including syslogs, Windows event logs, and custom logs | Supports a wide range of log sources, including syslogs, Windows event logs, and custom logs |
| Log Analysis | Uses a powerful search engine to analyze logs in real-time | Uses a rule-based engine to analyze logs in real-time | Uses a machine learning engine to analyze logs in real-time | Uses a cloud-based analytics platform to analyze logs in real-time | Uses a distributed analytics platform to analyze logs in real-time |
| Threat Detection | Uses a variety of techniques to detect threats, including signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and machine learning | Uses a variety of techniques to detect threats, including signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and machine learning | Uses a variety of techniques to detect threats, including signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and machine learning | Uses a variety of techniques to detect threats, including signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and machine learning | Uses a variety of techniques to detect threats, including signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and machine learning |
| Incident Response | Provides a variety of tools to help organizations respond to security incidents, including a ticketing system, a case management system, and a reporting system | Provides a variety of tools to help organizations respond to security incidents, including a ticketing system, a case management system, and a reporting system | Provides a variety of tools to help organizations respond to security incidents, including a ticketing system, a case management system, and a reporting system | Provides a variety of tools to help organizations respond to security incidents, including a ticketing system, a case management system, and a reporting system | Provides a variety of tools to help organizations respond to security incidents, including a ticketing system, a case management system, and a reporting system |
| Reporting | Provides a variety of reports, including security reports, compliance reports, and operational reports | Provides a variety of reports, including security reports, compliance reports, and operational reports | Provides a variety of reports, including security reports, compliance reports, and operational reports | Provides a variety of reports, including security reports, compliance reports, and operational reports | Provides a variety of reports, including security reports, compliance reports, and operational reports |
| Scalability | Can be scaled to meet the needs of large organizations | Can be scaled to meet the needs of large organizations | Can be scaled to meet the needs of large organizations | Can be scaled to meet the needs of large organizations | Can be scaled to meet the needs of large organizations |
| Price | Pricing starts at $5,000 per year | Pricing starts at $10,000 per year | Pricing starts at $15,000 per year | Pricing starts at $20,000 per year | Pricing starts at $25,000 per year |
SIEM Tool Selection
Choosing the right SIEM tool for an organization is crucial for effective security monitoring and incident response. Here are some guidelines to help you make an informed decision:Consider the size and complexity of your organization. A large, complex organization with multiple locations and diverse IT systems will require a more robust SIEM tool than a small organization with a simpler IT environment.Evaluate your security requirements.
Determine the types of threats you are most concerned about and the level of protection you need. Some SIEM tools offer more advanced features, such as threat intelligence and user behavior analytics, that may be necessary for organizations facing sophisticated threats.Establish a budget for the SIEM tool.
SIEM tools can vary significantly in cost, so it’s important to set a realistic budget before you start shopping. Consider not only the initial purchase price but also the ongoing costs of maintenance, support, and upgrades.
SIEM Tool Implementation

Implementing a SIEM tool involves several key steps, including planning, deployment, configuration, and ongoing management.Planning involves defining the scope of the SIEM implementation, identifying data sources, and establishing incident response procedures. Deployment involves installing the SIEM software and connecting it to data sources.
Configuration involves customizing the SIEM to meet the organization’s specific requirements, such as defining alerts and reports. Ongoing management involves monitoring the SIEM, responding to alerts, and maintaining the system.
Best Practices for Deployment and Configuration
* Phased approach:Implement the SIEM in stages, starting with critical data sources and use cases.
Centralized deployment
Deploy the SIEM in a centralized location to provide visibility into all data sources.
Among the popular SIEM tools available, one that stands out for its unique approach is the voloom hair tool. This innovative tool utilizes advanced technology to provide a seamless and efficient hair styling experience. Despite its focus on hair styling, the voloom hair tool remains relevant to the discussion of SIEM tools, as it showcases the diverse applications of technology in various industries.
Scalability
Ensure the SIEM can handle the volume of data generated by the organization.
When working with popular SIEM tools, ensuring data quality is crucial for accurate analysis and reporting. A data quality tool can help you identify and correct data errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates, ensuring that your SIEM tools have reliable data to work with.
By improving data quality, you can enhance the effectiveness of your SIEM tools and make more informed decisions based on accurate information.
Integration
Integrate the SIEM with other security tools, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Tuning
Regularly tune the SIEM to optimize performance and reduce false positives.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
* Data volume:SIEMs can generate large volumes of data, which can be challenging to manage and analyze.
False positives
SIEMs can generate false positives, which can lead to wasted time and resources.
Skill shortage
There is a shortage of qualified SIEM professionals.
Cost
SIEMs can be expensive to purchase and maintain.To overcome these challenges, organizations can implement the following measures:* Data management:Use data compression and aggregation techniques to reduce data volume.
False positive reduction
Use machine learning and other techniques to reduce false positives.
Training
Invest in training for SIEM professionals.
Cost optimization
Consider cloud-based SIEM solutions or managed security services to reduce costs.
SIEM Tool Management

SIEM tools require ongoing management to ensure their effectiveness and efficiency. This includes regular updates, maintenance, and security monitoring.Regular updates are essential to keep SIEM tools up-to-date with the latest threat intelligence and security patches. Maintenance tasks, such as log file rotation and system optimization, help ensure the smooth operation of SIEM tools.
Security monitoring and incident response play a crucial role in detecting and responding to security threats.
Ongoing Management Tasks
Ongoing management tasks associated with SIEM tools include:
- Regular updates to address security vulnerabilities and incorporate new threat intelligence
- Maintenance tasks such as log file rotation, system optimization, and performance tuning
- Security monitoring to detect and investigate security threats
- Incident response to contain and mitigate security breaches
Importance of Regular Updates and Maintenance
Regular updates and maintenance are crucial for the effectiveness and efficiency of SIEM tools. Updates ensure that SIEM tools are equipped with the latest threat intelligence and security patches, enabling them to detect and respond to the most recent threats.
Maintenance tasks help prevent performance degradation and ensure the smooth operation of SIEM tools.
Role of Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Security monitoring and incident response are essential for detecting and responding to security threats. Security monitoring involves continuously monitoring security logs and events to identify potential threats. Incident response involves taking appropriate actions to contain and mitigate security breaches, such as isolating infected systems, blocking malicious traffic, and notifying affected parties.
SIEM Tool Trends

The SIEM tool market is constantly evolving, with new technologies and capabilities emerging all the time. These trends are shaping the future of SIEM tools, and organizations need to be aware of them in order to make informed decisions about their SIEM investments.
One of the most important trends in the SIEM tool market is the move towards cloud-based SIEM solutions. Cloud-based SIEM tools offer a number of advantages over on-premises SIEM tools, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. As a result, many organizations are moving their SIEM deployments to the cloud.
Another important trend in the SIEM tool market is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. AI and ML can be used to automate many of the tasks that are traditionally performed by SIEM analysts, such as threat detection and incident response.
This can free up analysts to focus on more strategic tasks, such as threat hunting and security planning.
Finally, the SIEM tool market is also seeing a trend towards convergence with other security technologies, such as network security monitoring (NSM) and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools. This convergence is driven by the need for organizations to have a more comprehensive view of their security posture.
By integrating SIEM tools with other security technologies, organizations can improve their ability to detect and respond to threats.
Emerging Technologies and Capabilities, Popular siem tools
In addition to the trends discussed above, there are a number of emerging technologies and capabilities that are shaping the future of SIEM tools. These include:
- User behavior analytics (UBA): UBA technologies can be used to detect anomalous user behavior that may indicate a security threat. UBA technologies can be used to identify insider threats, as well as external threats that have compromised a user’s account.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): SOAR technologies can be used to automate many of the tasks that are traditionally performed by security analysts, such as incident response and threat hunting. SOAR technologies can help organizations to improve their security posture by reducing the time it takes to respond to threats.
- Threat intelligence:Threat intelligence can be used to provide SIEM tools with information about the latest threats and vulnerabilities. This information can help SIEM tools to detect and respond to threats more effectively.
The Future of SIEM Tools
The future of SIEM tools is bright. SIEM tools are becoming more powerful and effective all the time, and they are playing an increasingly important role in the security of organizations. As new technologies and capabilities emerge, SIEM tools will continue to evolve to meet the needs of organizations.
Organizations need to be aware of the trends in the SIEM tool market in order to make informed decisions about their SIEM investments. By understanding the trends, organizations can ensure that they are using the most effective SIEM tools to protect their organizations from threats.
Essential FAQs
What is a SIEM tool?
A SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tool is a software solution that collects, analyzes, and correlates security events from various sources across an organization’s network. It provides a centralized platform for monitoring, detecting, and responding to potential security threats.
What are the benefits of using a SIEM tool?
SIEM tools offer numerous benefits, including: improved threat detection, faster incident response, enhanced compliance reporting, and reduced security costs.
How do I choose the right SIEM tool for my organization?
Selecting the right SIEM tool depends on factors such as the size and complexity of your organization, your security requirements, and your budget. It’s important to evaluate different solutions and consider their features, scalability, and ease of use.