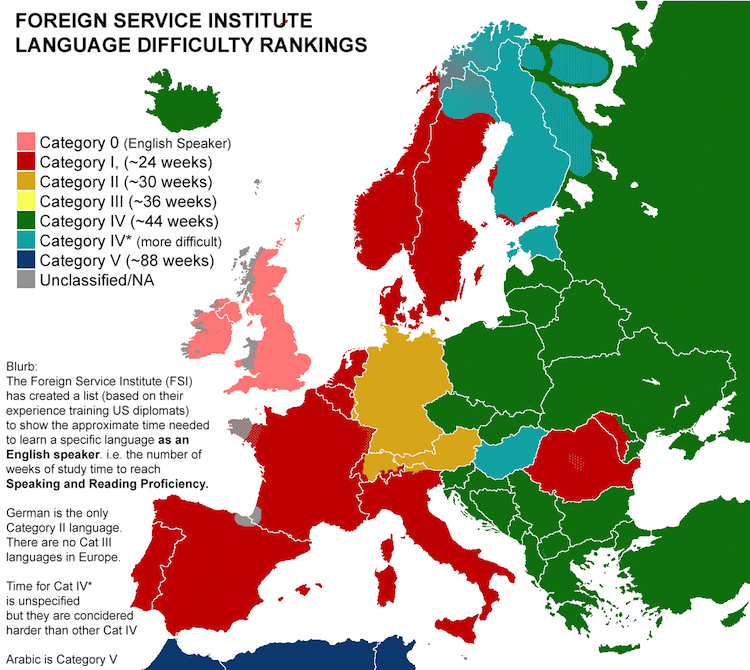
Is Russian hard to learn? For native English speakers, embarking on the journey to master this enigmatic language can be both daunting and captivating. Its unique grammar, pronunciation, and vast vocabulary present challenges that can test even the most dedicated language learners.
Yet, amidst these complexities lies a world of rich literature, vibrant culture, and profound insights. With perseverance and the right approach, Russian can unlock a treasure trove of knowledge and experiences, making the effort worthwhile.
Difficulty Level of Russian
For native English speakers, Russian is generally perceived as a difficult language to learn. This perception stems from several factors, including its complex grammar, challenging pronunciation, and extensive vocabulary.
Russian grammar is significantly different from English grammar, with a rich system of cases, declensions, and verb conjugations. This can be daunting for English speakers who are accustomed to a simpler grammatical structure.
Pronunciation
Russian pronunciation is another area of difficulty. The Russian alphabet contains many unfamiliar sounds, and the stress patterns in Russian words can be unpredictable. This can make it challenging for English speakers to pronounce Russian words correctly and to understand spoken Russian.
Vocabulary
The Russian vocabulary is vast and includes many words that have no direct equivalents in English. This can make it difficult for English speakers to expand their vocabulary and to express themselves fluently in Russian.
Similarities and Differences with English: Is Russian Hard To Learn

Russian and English belong to different language families, but they share some similarities and differences in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
Grammar:Russian grammar is more complex than English grammar, with a greater number of verb tenses, cases, and declensions. However, both languages share a similar subject-verb-object word order and use prepositions to indicate relationships between words.
Vocabulary:Russian and English share a number of common words and phrases, such as “hello,” “thank you,” and “goodbye.” However, there are also many words that are unique to each language. For example, the Russian word “здорово” (zdravstvuyte) means “hello” or “good day,” while the English word “hello” has no direct equivalent in Russian.
Pronunciation:Russian and English have different pronunciation systems. Russian has a greater number of vowel sounds than English, and its consonants are often pronounced more forcefully. Additionally, Russian has a number of unique sounds, such as the “щ” (shch) sound, which is not found in English.
Grammar
One of the most significant differences between Russian and English grammar is the use of cases. Russian has six cases, each of which indicates a different grammatical relationship between a noun and other words in a sentence. For example, the nominative case is used for the subject of a sentence, while the accusative case is used for the direct object.
English, on the other hand, has only three cases: the nominative, the possessive, and the objective.
Another difference between Russian and English grammar is the use of verb tenses. Russian has a greater number of verb tenses than English, including the past imperfect, the past perfect, and the future perfect. These tenses allow Russian speakers to express more subtle distinctions in time than English speakers can.
Vocabulary
Russian and English share a number of common words and phrases, particularly in the areas of science, technology, and mathematics. However, there are also many words that are unique to each language. For example, the Russian word “спутник” (sputnik) means “satellite,” while the English word “satellite” has no direct equivalent in Russian.
One of the challenges of learning Russian vocabulary is the use of diminutives. Diminutives are words that are formed by adding a suffix to a noun to indicate that it is small or affectionate. For example, the Russian word “дом” (dom) means “house,” while the diminutive “домик” (domik) means “little house.”
Pronunciation
Russian and English have different pronunciation systems. Russian has a greater number of vowel sounds than English, and its consonants are often pronounced more forcefully. Additionally, Russian has a number of unique sounds, such as the “щ” (shch) sound, which is not found in English.
One of the challenges of learning Russian pronunciation is the use of stress. In Russian, stress can fall on any syllable of a word, and it can change the meaning of the word. For example, the word “мука” (muka) means “flour” when the stress is on the first syllable, but it means “torment” when the stress is on the second syllable.
Case System
Russian has a complex case system, with six cases that indicate the grammatical function of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and numerals. The case system is essential for understanding the meaning of sentences and for communicating effectively in Russian.
The six cases are:
- Nominative case: This is the subject of a sentence.
- Genitive case: This is used to indicate possession, origin, or quantity.
- Dative case: This is used to indicate the indirect object of a verb or the recipient of an action.
- Accusative case: This is used to indicate the direct object of a verb.
- Instrumental case: This is used to indicate the means by which an action is performed.
- Prepositional case: This is used to indicate location or direction.
The case system can be challenging for learners of Russian, but it is essential for understanding the language. With practice, you will be able to master the case system and use it effectively in your own speech and writing.
Examples of Case Usage
- Nominative case: Я студент.(I am a student.)
- Genitive case: У меня есть книга.(I have a book.)
- Dative case: Я даю книгу другу.(I give the book to a friend.)
- Accusative case: Я вижу книгу.(I see the book.)
- Instrumental case: Я пишу ручкой.(I write with a pen.)
- Prepositional case: Я живу в Москве.(I live in Moscow.)
Verb Conjugation

Russian verbs are conjugated to indicate tense, mood, aspect, person, and number. The conjugation system is complex, but it is essential for understanding how Russian verbs work.
There are three main tenses in Russian: the present, past, and future. The present tense is used to describe actions that are happening now or that are habitual. The past tense is used to describe actions that happened in the past.
The future tense is used to describe actions that will happen in the future.
There are three main moods in Russian: the indicative, imperative, and conditional. The indicative mood is used to state facts or to describe actions that are happening or have happened. The imperative mood is used to give commands or instructions.
The conditional mood is used to express hypothetical situations or to make polite requests.
There are two main aspects in Russian: the perfective and imperfective. The perfective aspect is used to describe actions that are completed or that have a definite endpoint. The imperfective aspect is used to describe actions that are ongoing or that have no definite endpoint.
Russian verbs are also conjugated for person and number. There are three persons in Russian: the first person, second person, and third person. The first person is used to refer to the speaker, the second person is used to refer to the person being spoken to, and the third person is used to refer to someone or something that is not the speaker or the person being spoken to.
Learning Russian is renowned for its challenges, but if you’re up for the adventure, don’t let that deter you. And while we’re on the topic of learning curves, have you ever wondered about the difficulty of SQL? If you’re curious, how hard is sql to learn might shed some light.
Back to Russian, the complexities of its grammar and Cyrillic alphabet can be daunting, but the rewards of mastering this rich language are well worth the effort.
There are two numbers in Russian: the singular and plural. The singular is used to refer to one person or thing, and the plural is used to refer to two or more people or things.
The following table shows the conjugation of the verb “говорить” (to speak) in the present tense:
| Person | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| First | говорю | говорим |
| Second | говоришь | говорите |
| Third | говорит | говорят |
The following examples show how Russian verbs are used to express different meanings:
- “Я говорю по-русски.” (I speak Russian.) – present tense, indicative mood, first person singular
- “Ты говорил по-русски?” (Did you speak Russian?) – past tense, indicative mood, second person singular
- “Мы будем говорить по-русски.” (We will speak Russian.) – future tense, indicative mood, first person plural
- “Говорите по-русски!” (Speak Russian!) – imperative mood, second person plural
- “Я бы говорил по-русски, если бы мог.” (I would speak Russian if I could.) – conditional mood, first person singular
Alphabet and Pronunciation
The Russian alphabet, known as the Cyrillic script, comprises 33 letters, including 21 consonants, 10 vowels, 1 semi-vowel, and 2 modifier letters. It differs significantly from the Latin alphabet used in English, posing challenges for learners.
Russian pronunciation is characterized by its use of soft and hard consonants. Soft consonants are pronounced with a palatalized sound, giving them a slightly different articulation from their hard counterparts. This distinction is crucial for understanding and speaking Russian correctly.
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script includes several unique letters not found in English, such as “Ж” (pronounced as “zh”), “Ш” (pronounced as “sh”), and “Щ” (pronounced as “shch”). These letters represent specific sounds that can be challenging for English speakers to pronounce accurately.
Soft and Hard Consonants
Russian consonants can be either soft or hard, depending on the vowel that follows them. Soft consonants are typically indicated by an apostrophe-like mark (‘) placed after the letter. For example, the consonant “д” is pronounced as “d” when hard, but as “дь” (pronounced as “dy”) when soft.
Tips for Overcoming Pronunciation Challenges
- Practice regularly: Repetition and immersion are key to mastering Russian pronunciation.
- Listen to native speakers: Expose yourself to authentic Russian speech to familiarize yourself with the natural flow and intonation of the language.
- Use online resources: Utilize websites and apps that provide interactive pronunciation exercises and feedback.
Learning Resources and Methods

Embarking on the journey of mastering Russian requires an arsenal of resources and a tailored approach. Whether you prefer structured textbooks, interactive online courses, or engaging language exchange platforms, there’s an array of options to suit your learning style.
Different methods resonate with different learners. Some thrive in the traditional classroom setting, while others excel with self-paced online courses. Language exchange platforms offer invaluable opportunities to connect with native speakers, immersing yourself in authentic conversations.
Russian can be a challenging language to master, but don’t let that deter you. If you’re determined to learn, there are plenty of resources available to help you. Check out this article for tips on how to approach language learning effectively.
With the right mindset and consistent practice, you’ll be surprised at how quickly you can make progress in Russian.
Textbooks
Textbooks provide a comprehensive foundation, systematically covering grammar, vocabulary, and cultural insights. Consider the following:
- Russian for Dummies
- Colloquial Russian: The Complete Course for Beginners
- New Penguin Russian Course: A Complete Course for Beginners
Online Courses, Is russian hard to learn
Online courses offer flexibility and convenience, allowing you to learn at your own pace and schedule. Explore platforms such as:
- Duolingo
- Babbel
- Udemy
Language Exchange Platforms
Language exchange platforms facilitate connections with native Russian speakers. Engage in conversations, share cultural experiences, and accelerate your language acquisition:
- HelloTalk
- Tandem
- Speaky
Time Commitment and Effort

Learning Russian, like any other language, requires dedication and consistent effort. The time commitment varies based on your desired level of proficiency and your individual learning style.
For basic conversational skills, you may need around 100-150 hours of study. To become fluent, however, you’ll likely need at least 500-1000 hours or more.
Importance of Consistent Effort
Consistency is key in language learning. Regular practice helps solidify your understanding of grammar and vocabulary, and improves your pronunciation and fluency. Aim to set aside dedicated study time each day, even if it’s just for 30 minutes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Russian harder than other languages?
While difficulty is subjective, Russian is generally considered more challenging for native English speakers compared to languages like Spanish or French due to its complex grammar, unfamiliar alphabet, and extensive vocabulary.
How long does it take to learn Russian?
The time required to achieve proficiency varies greatly depending on factors such as individual learning style, practice frequency, and immersion opportunities. However, estimates suggest that reaching intermediate fluency may take around 1,100 hours of dedicated study.
Is Russian a useful language to learn?
Absolutely! Russian is the native language of over 250 million people and is widely spoken in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. It opens doors to a wealth of literature, cultural experiences, and professional opportunities in various fields.