When it comes to language learning, Korean often sparks curiosity and raises the question: is Korean hard to learn for English speakers? This article delves into the intricacies of Korean, exploring its unique features and providing insights to help you make an informed decision about your language-learning journey.
From the distinct sounds of Korean phonetics to the intricate grammatical structures and the fascinating writing system, this comprehensive guide will equip you with a clear understanding of the challenges and rewards that await you in your Korean learning adventure.
Phonetics and Phonology

The Korean language features a distinct phonetic and phonological system that differs from English. Understanding these differences is crucial for English speakers learning Korean.
Korean has a smaller inventory of consonant sounds compared to English, with a notable absence of certain sounds such as /θ/ and /ð/. Additionally, Korean consonants are often pronounced with more aspiration and a stronger release of air.
Vowels
- Korean has a simpler vowel system than English, with only 10 vowel sounds compared to English’s 20.
- Korean vowels are generally shorter and more centralized than English vowels.
Tones
Unlike English, Korean is a tonal language, meaning that the pitch of the voice can change the meaning of a word. There are three main tones in Korean: high, mid, and low. The tone of a syllable can affect its pronunciation and the meaning of the word it belongs to.
Challenging Sounds
Some Korean sounds can be particularly challenging for English speakers to pronounce correctly. These include:
- The aspirated consonants /pʰ/, /tʰ/, and /kʰ/.
- The tense vowels /i/ and /u/.
- The diphthongs /ai/ and /au/.
Grammar and Syntax

Korean grammar and syntax differ significantly from English, presenting unique challenges for English speakers learning the language. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication in Korean.
Korean grammar follows a subject-object-verb (SOV) structure, unlike English’s subject-verb-object (SVO) order. This means that the subject of a sentence comes first, followed by the object and then the verb.
Verb Conjugation
Korean verbs are highly conjugated, with different forms for different tenses, moods, and speech levels. Unlike English, where verbs are typically conjugated by adding suffixes, Korean verbs undergo stem changes and use auxiliary verbs to indicate tense and mood.
Noun Declension
Korean nouns are declined, meaning they change their form depending on their grammatical function within a sentence. There are four main noun declension patterns, each with specific rules for indicating subject, object, and other grammatical roles.
Particles
Korean particles are grammatical markers that are attached to words to indicate their function in a sentence. These particles play a crucial role in conveying meaning and can significantly alter the interpretation of a sentence.
Vocabulary: Is Korean Hard To Learn For English Speakers

The Korean vocabulary system is a fascinating blend of native Korean words and Sino-Korean words, which were borrowed from Chinese. Sino-Korean words are typically used for more formal and technical concepts, while native Korean words are used for everyday speech.
This duality creates a rich and expressive vocabulary that allows for precise communication in various contexts.
Sino-Korean Words
Sino-Korean words are an essential part of the Korean vocabulary, and they make up a significant portion of the written language. These words were introduced to Korea from China during the Three Kingdoms period (57 BC – 668 AD) and have been adapted to fit the Korean sound system.
Sino-Korean words are often used in formal settings, such as in government documents, academic writing, and news reports. They are also used to express concepts that do not have a native Korean equivalent, such as scientific terms and technical jargon.
Native Korean Words
Native Korean words are those that have been developed independently in Korea and are not derived from Chinese. These words are typically used in everyday speech and informal writing. Native Korean words are often more expressive and colloquial than Sino-Korean words, and they can convey a wide range of emotions and nuances.
They are also used to express concepts that are unique to Korean culture, such as the concept of “han” (a sense of deep sorrow or regret).
Expanding Vocabulary, Is korean hard to learn for english speakers
Expanding your Korean vocabulary is essential for improving your communication skills. There are several effective strategies you can use to do this, including:
- Reading Korean texts: Reading Korean texts is a great way to expose yourself to new vocabulary and learn how it is used in context.
- Using flashcards: Flashcards are a classic tool for memorizing new vocabulary. You can create your own flashcards or use pre-made decks.
- Watching Korean movies and TV shows: Watching Korean movies and TV shows can help you learn new vocabulary in a natural and engaging way.
- Talking to native Korean speakers: Talking to native Korean speakers is a great way to practice your vocabulary and learn new words in a real-world setting.
Writing System

Korean is written using Hangul, a unique and efficient writing system created in the 15th century by King Sejong the Great. Unlike other writing systems, Hangul is not based on symbols or characters representing words or syllables but rather on the individual sounds that make up the Korean language.
Hangul consists of 24 basic letters: 14 consonants and 10 vowels. These letters are combined to form syllables, which are then combined to form words. The letters are written in blocks, with each syllable occupying one block.
Principles of Hangul Composition
- Syllable blocks:Each syllable in Korean is written as a single block, with the consonant(s) written to the left of the vowel(s).
- Consonant placement:Consonants can be written either above or below the vowel, depending on the syllable structure.
- Vowel placement:Vowels are always written in the center of the syllable block.
Principles of Hangul Pronunciation
- Consonant pronunciation:Consonants are pronounced similarly to their English counterparts, with some exceptions.
- Vowel pronunciation:Vowels are pronounced clearly and distinctly, with each vowel having its own unique sound.
- Syllable stress:Stress is typically placed on the first syllable of a word.
Challenges of Learning Hangul for English Speakers
- Unfamiliar sounds:Some Korean consonants and vowels have sounds that are not found in English, which can make pronunciation challenging.
- Syllable structure:Korean syllable structure is different from English, with consonants and vowels arranged in different ways.
- Reading speed:Hangul is a very efficient writing system, but it can take some time to get used to reading it quickly and accurately.
Cultural Influences
Understanding Korean culture and customs is crucial for effective Korean language learning. Immersion in Korean culture helps you grasp the context and nuances of the language.
Tips for Cultural Immersion
*
-*Engage with Korean media
Watch Korean movies, dramas, and TV shows to familiarize yourself with the language and culture.
-*Read Korean literature
Explore Korean novels, short stories, and poetry to delve into the written language and cultural perspectives.
-*Attend Korean cultural events
Participate in local Korean festivals, workshops, and gatherings to connect with Korean people and learn about their customs.
-*Make Korean friends
Surround yourself with native Korean speakers who can share their culture and language insights.
-*Visit South Korea
Immerse yourself in the Korean language and culture by visiting South Korea and experiencing it firsthand.
Resources and Learning Methods

Embarking on your Korean language learning journey? Dive into a treasure trove of resources and explore diverse learning methods to pave your path to fluency.
Selecting the most suitable learning method depends on your preferences, learning style, and available time. Here are some popular approaches:
Language Learning Apps and Software
- Pros:Convenient, interactive, and often gamified, making learning enjoyable and accessible.
- Cons:Can be limiting in terms of depth and personalized guidance.
Online Courses and Classes
- Pros:Structured lessons, live interactions with instructors, and feedback for improved progress.
- Cons:Can be costly and may require a fixed schedule.
Books and Workbooks
- Pros:Self-paced learning, portable, and often more comprehensive than apps or courses.
- Cons:Lack of immediate feedback, can be isolating, and may require additional resources for pronunciation.
Immersion
- Pros:Most effective way to learn a language authentically, providing exposure to real-life usage and pronunciation.
- Cons:Can be challenging to find opportunities for immersion, especially if not living in a Korean-speaking country.
Regardless of the method you choose, consistency and practice are key. Dedicate regular time to studying, immerse yourself in Korean media, and seek opportunities to converse with native speakers. Your efforts will pay off as you progress on your Korean language adventure!
Questions and Answers
Is Korean harder than other languages?
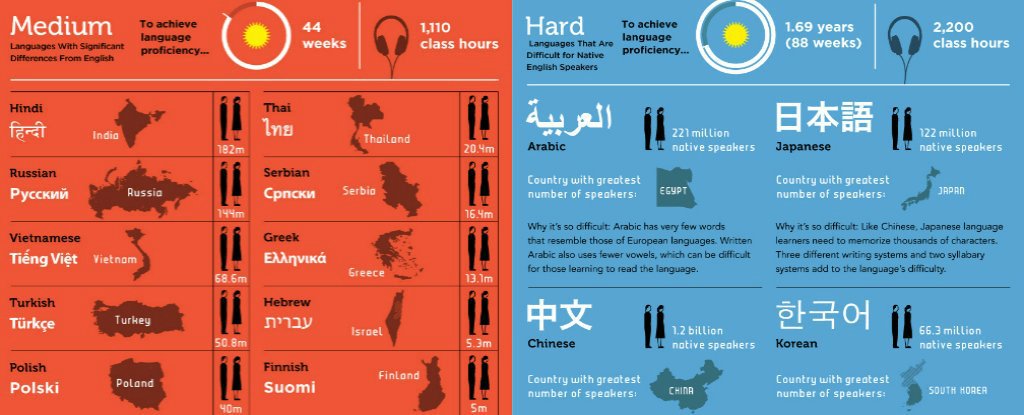
The difficulty of learning Korean depends on your native language and language learning experience. Compared to English, Korean has a different grammar structure, a unique writing system, and distinct pronunciation, which can present challenges for English speakers.
How long does it take to learn Korean?
The time it takes to learn Korean varies widely depending on factors such as your language learning goals, study intensity, and individual learning style. However, consistent practice and immersion can significantly accelerate your progress.
Is Korean pronunciation difficult?
Korean pronunciation can be challenging for English speakers due to the use of sounds that are not found in English, such as aspirated consonants and tense vowels. However, with dedicated practice and exposure to native Korean speakers, you can master the intricacies of Korean pronunciation.