Is Hebrew a hard language to learn? The answer to this question is not as straightforward as one might think. While Hebrew has some unique characteristics that can make it challenging for native English speakers, it also has some features that make it easier to learn than other languages.
In this article, we will explore the factors that influence the difficulty of learning Hebrew, discuss the cognitive challenges involved, and provide effective methods for learning the language.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Overview of the Hebrew Language
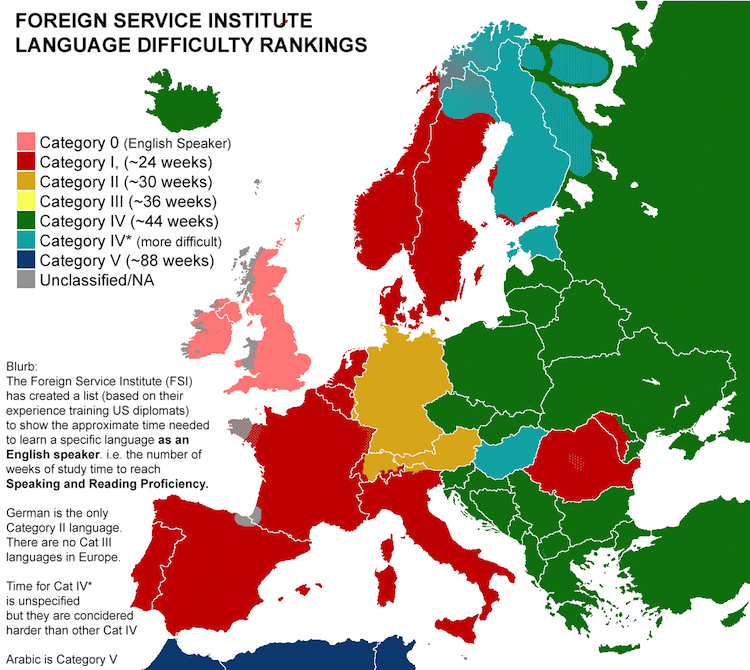
Hebrew is a fascinating language with a rich history and unique characteristics. Its ancient origins and continuous evolution make it an intriguing subject for linguists and scholars alike.
The Hebrew script, with its distinctive right-to-left orientation and lack of vowels, presents a unique challenge to learners. The grammar, too, has its complexities, with verb conjugations and noun declensions that can be tricky to master.
Dialects and Variations, Is hebrew a hard language to learn
Over time, Hebrew has evolved into several dialects and variations, each with its own nuances and peculiarities. Modern Hebrew, the official language of Israel, is based on the Biblical Hebrew of the Old Testament. However, there are also significant differences between Modern Hebrew and the Hebrew spoken in ancient times.
Factors Influencing the Difficulty of Learning Hebrew

Learning Hebrew can be influenced by various factors, including prior language knowledge and exposure, cultural and linguistic background, and learning methods and resources.
Prior Language Knowledge and Exposure
Individuals with prior knowledge of languages with similar linguistic features, such as Arabic or Aramaic, may find learning Hebrew easier due to shared vocabulary and grammatical structures. Exposure to Hebrew through immersion or media consumption can also enhance language acquisition.
Cultural and Linguistic Background
Cultural and linguistic background plays a significant role in language learning. Learners who come from cultures with similar writing systems or grammatical structures may find Hebrew more accessible. Additionally, cultural familiarity with Jewish traditions and customs can aid in understanding Hebrew texts and idioms.
Learning Methods and Resources
The effectiveness of learning methods and resources can impact the difficulty of learning Hebrew. Structured language courses, immersive programs, and interactive language learning apps can provide a supportive environment for language acquisition. The availability of comprehensive textbooks, dictionaries, and online resources can also enhance the learning process.
Cognitive Challenges in Learning Hebrew

Learning Hebrew presents cognitive challenges that stem from the distinct characteristics of the language. Acquiring the Hebrew alphabet and pronunciation requires significant effort due to their unique features, while understanding Hebrew grammar and syntax poses challenges due to their complexity and differences from Indo-European languages.
Difficulties in Acquiring the Hebrew Alphabet and Pronunciation
The Hebrew alphabet consists of 22 letters, each representing a distinct sound. However, many of these sounds are unfamiliar to native English speakers, and the pronunciation of certain letters varies depending on their position within a word. For example, the letter “het” can be pronounced as “h” or “kh,” and the letter “vav” can be pronounced as “v” or “w.”
These variations can make it challenging to accurately pronounce Hebrew words.
Challenges of Understanding Hebrew Grammar and Syntax
Hebrew grammar and syntax differ significantly from Indo-European languages, such as English. The verb-subject-object word order, the use of prefixes and suffixes to indicate tense and person, and the absence of articles and prepositions can make it difficult for learners to comprehend Hebrew sentences.
Additionally, Hebrew has a rich system of noun declensions and verb conjugations, which further adds to the complexity of the language.
Cognitive Processes Involved in Comprehending Hebrew Texts
Comprehending Hebrew texts requires the activation of multiple cognitive processes. Learners must first decode the written symbols into sounds, then process the sounds into words, and finally understand the meaning of the words in context. This process involves the use of working memory, attention, and long-term memory.
Additionally, learners must be able to make inferences and draw connections between different parts of the text to fully comprehend its meaning.
Methods for Effective Hebrew Learning: Is Hebrew A Hard Language To Learn

Mastering Hebrew requires a combination of effective strategies and consistent practice. Here are some tips to help you learn Hebrew efficiently:
Immersion and Regular Practice
Immersion in the language is crucial for fluency. Surround yourself with Hebrew by listening to music, watching movies, reading books, and interacting with native speakers. Regular practice through speaking, writing, and listening exercises strengthens your language skills.
Selecting Learning Materials and Resources
Choose learning materials that align with your learning style and goals. Textbooks, online courses, language exchange platforms, and mobile apps offer various approaches to learning Hebrew. Consider your preferred learning method and select resources that provide clear explanations, engaging exercises, and opportunities for practice.
Time and Effort Required for Hebrew Proficiency

The time and effort required to achieve Hebrew proficiency vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s learning style, prior language experience, and the intensity of their study.
On average, learners can expect to spend approximately 480 hours of classroom instruction or self-study to reach intermediate proficiency in Hebrew. This includes developing basic reading, writing, listening, and speaking skills.
Factors Influencing the Pace of Learning
- Prior language experience:Individuals with prior knowledge of other Semitic languages, such as Arabic or Aramaic, may find it easier to learn Hebrew due to similarities in grammar and vocabulary.
- Learning style:Visual learners may benefit from using flashcards and diagrams, while auditory learners may prefer listening to audio recordings and podcasts.
- Intensity of study:Consistent and regular study sessions are crucial for making progress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of dedicated study time each day.
Tips for Optimizing Time and Effort
- Set realistic goals:Break down your learning journey into smaller, achievable milestones.
- Find a structured learning program:Enroll in a Hebrew class or use a reputable online course that provides a systematic approach to learning.
- Immerse yourself in the language:Surround yourself with Hebrew by listening to music, watching movies, and reading books or articles in Hebrew.
- Practice regularly:Consistent practice is key to improving your fluency and retention.
Expert Answers
How long does it take to learn Hebrew?
The time it takes to learn Hebrew depends on a number of factors, including your prior language learning experience, your level of motivation, and the amount of time you are willing to dedicate to studying. However, most experts agree that it takes around 480 hours of study to reach intermediate proficiency in Hebrew.
Is Hebrew harder than other languages?
The difficulty of learning Hebrew depends on your native language. If your native language is English, then Hebrew will be more difficult to learn than a language like Spanish or French. However, if your native language is Arabic, then Hebrew will be much easier to learn.
