How to get rid of a temple headache – Are you struggling with relentless temple headaches that leave you throbbing in pain? Our comprehensive guide will equip you with expert strategies and effective remedies to conquer these headaches and restore your well-being. From self-care measures to medical treatments, we’ll explore a range of options to help you find fast relief and long-term solutions.
Temple headaches, characterized by intense pain on one or both sides of your temples, can be debilitating. But don’t despair! By understanding the causes, triggers, and available treatments, you can effectively manage these headaches and reclaim your life.
Temple Headache Overview
Temple headaches are a common type of headache that occurs in the temples, the areas on either side of the forehead. They can range from mild to severe and can last from a few hours to several days.
Temple headaches are often caused by tension or stress, but they can also be triggered by a variety of other factors, including:
Causes and Triggers
- Fatigue
- Eye strain
- Sinus infections
- Caffeine withdrawal
- Alcohol consumption
- Certain foods, such as chocolate or cheese
Self-Care Measures
Self-care plays a vital role in managing temple headaches. Simple home remedies, lifestyle modifications, and pain management techniques can provide significant relief and prevent future episodes.
Home Remedies
- Ginger:Ginger contains anti-inflammatory compounds that can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Chamomile tea:Chamomile has calming and relaxing effects that can help soothe headaches.
- Peppermint oil:Peppermint oil applied to the temples can provide a cooling and numbing sensation.
- Cold compress:Applying a cold compress to the temples can help constrict blood vessels and reduce pain.
- Warm bath:A warm bath can relax muscles and promote blood flow, which can relieve headaches.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can help prevent temple headaches:
- Dietary changes:Avoid foods that trigger headaches, such as caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods.
- Sleep hygiene:Establish a regular sleep schedule and get enough sleep.
- Stress management:Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Regular exercise:Regular physical activity can reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Pain Management Techniques
Over-the-counter medications, cold compresses, and massage can provide effective pain relief for temple headaches.
| Technique | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, acetaminophen) | Moderate to high | Gastrointestinal upset, liver damage (with excessive use) |
| Cold compress | Moderate | None |
| Massage | Moderate to high | Bruising, skin irritation |
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if self-care measures do not provide adequate relief or if headaches are severe or persistent.
If you’re struggling with a throbbing temple headache, try applying a cold compress or taking over-the-counter pain relievers. For a deeper understanding of the term “temple,” you might want to explore the history of the Jewish Temple, destroyed in 70 AD.
when was the jewish temple destroyed Returning to your headache, consider consulting a doctor if it persists or worsens.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments for temple headaches include prescription medications, non-prescription pain relievers, and other non-medical treatments.
Prescription medications can be effective in treating temple headaches, but they may have side effects and contraindications. Non-prescription pain relievers can also be effective, but they may not be as strong as prescription medications.
Prescription Medications
Prescription medications used to treat temple headaches include:
- Triptans: Triptans are a class of medications that are specifically designed to treat migraines. They work by constricting blood vessels in the brain, which can help to relieve pain.
- Ergotamines: Ergotamines are another class of medications that are used to treat migraines. They work by stimulating the serotonin receptors in the brain, which can help to relieve pain.
- Opioids: Opioids are a class of medications that are used to treat severe pain. They work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, which can block pain signals.
Non-Prescription Pain Relievers
Non-prescription pain relievers that can be used to treat temple headaches include:
- Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen is a pain reliever that is available over-the-counter. It is effective in treating mild to moderate pain.
- Ibuprofen: Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is available over-the-counter. It is effective in treating mild to moderate pain and inflammation.
- Aspirin: Aspirin is a salicylate that is available over-the-counter. It is effective in treating mild to moderate pain and inflammation.
Other Non-Medical Treatments
Other non-medical treatments that can be used to relieve temple headaches include:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into the skin at specific points on the body. It is believed to help relieve pain by stimulating the release of endorphins.
- Massage: Massage can help to relieve muscle tension and pain in the head and neck. It can be especially helpful for tension headaches.
- Stress management techniques: Stress can trigger temple headaches. Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing, can help to reduce stress and prevent headaches.
Summary
There are a variety of medical treatments available for temple headaches. The best treatment for you will depend on the severity of your headaches and your individual needs. It is important to talk to your doctor about the best treatment options for you.
Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture and massage therapy, have gained popularity in managing temple headaches. These techniques aim to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve overall well-being.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate nerve endings and promote healing. Studies have shown that acupuncture may effectively reduce the frequency and severity of temple headaches.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy can help relieve tension in the head and neck muscles, which can contribute to temple headaches. Massage techniques, such as deep tissue massage and trigger point therapy, can improve circulation, reduce pain, and promote relaxation.
Lifestyle Factors

Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in managing temple headaches. Understanding the impact of stress, sleep hygiene, diet, exercise, and relaxation techniques can help you develop effective strategies to alleviate headaches.
Stress
Stress is a major trigger for temple headaches. Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension in the head and neck, resulting in pain. Managing stress through techniques like exercise, yoga, or meditation can help reduce headache frequency and severity.
Sleep Hygiene
Poor sleep hygiene, such as irregular sleep patterns or inadequate sleep duration, can contribute to headaches. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can improve sleep quality and reduce headaches.
Diet
Certain foods and beverages can trigger headaches in some individuals. Identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as caffeine, alcohol, or certain food additives, can help manage headaches.
Exercise
Regular exercise can be beneficial for headache management. Aerobic activities, such as running or swimming, can release endorphins that have pain-relieving effects. However, strenuous exercise or sudden changes in exercise intensity can sometimes trigger headaches.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress and muscle tension, which can alleviate headaches. These techniques promote relaxation and calmness, creating a favorable environment for headache relief.
Dietary Considerations
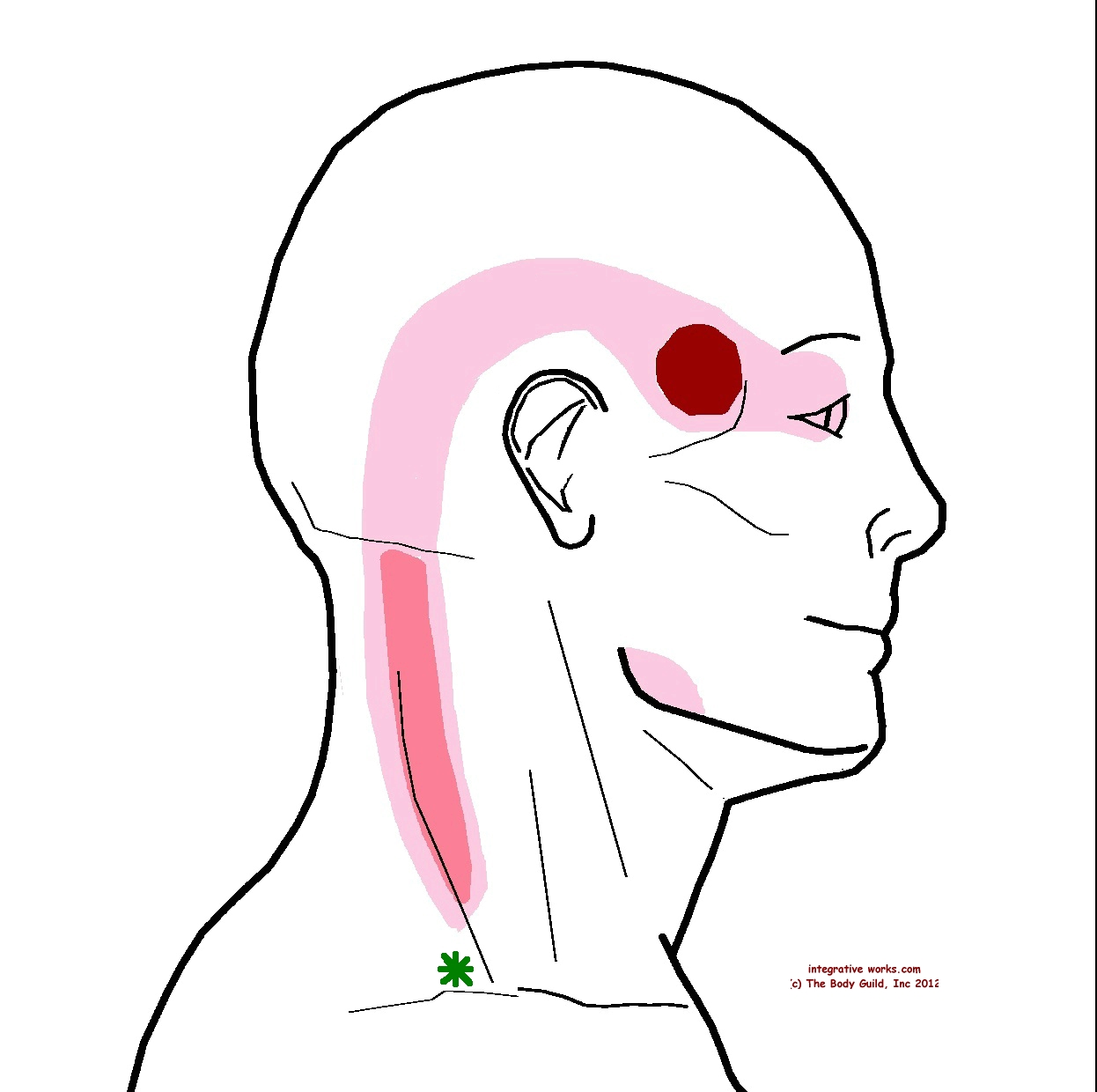
Temple headaches can be triggered or exacerbated by certain foods and drinks. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help reduce headache frequency and severity.
Common triggers include:
- Aged cheeses (e.g., cheddar, blue cheese)
- Processed meats (e.g., bacon, sausage)
- MSG (monosodium glutamate)
- Artificial sweeteners (e.g., aspartame, sucralose)
- Alcohol (especially red wine)
- Caffeine (in excess)
Dietary modifications that may alleviate temple headaches include:
- Eliminating or reducing trigger foods and drinks
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
Keeping a food diary can help identify specific triggers. By tracking what you eat and when headaches occur, you can pinpoint the foods that may be causing your pain.
Exercise and Movement: How To Get Rid Of A Temple Headache
Regular exercise has numerous benefits for overall health, including headache prevention. Physical activity helps improve blood flow, reduce stress, and release endorphins, which have pain-relieving effects. Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can help reduce the frequency and severity of temple headaches.
Proper Posture
Maintaining proper posture is crucial for preventing temple headaches. Poor posture can strain muscles in the neck and shoulders, leading to tension and pain. When sitting or standing, ensure your shoulders are relaxed, your back is straight, and your head is held high.
If you’re experiencing a temple headache, try applying a cold compress or taking over-the-counter pain medication. For more severe headaches, consider visiting the Don Ringler Temple , where you can access advanced medical care and treatments specifically designed to alleviate temple headaches.
Avoid slouching or hunching over, as this can worsen temple headaches.
Environmental Triggers

Certain environmental factors can trigger temple headaches. Identifying and managing these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
Common environmental triggers include:
- Bright lights, such as sunlight or fluorescent lights
- Loud noises
- Strong odors, such as perfumes or cleaning products
- Changes in temperature or humidity
- Barometric pressure changes
Managing Environmental Triggers
To manage environmental triggers, try the following:
- Wear sunglasses when outdoors to reduce exposure to bright light.
- Use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones to reduce exposure to loud noises.
- Avoid strong odors by using unscented products and avoiding areas with heavy scents.
- Use a humidifier or dehumidifier to regulate humidity levels in your home.
- Monitor weather forecasts and take precautions, such as staying indoors or wearing a hat, during periods of extreme temperature or barometric pressure changes.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies offer additional options for temple headache relief. Herbal remedies, essential oils, acupuncture, and massage therapy are among the popular choices.
Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs possess anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties that may help alleviate temple headaches.
| Herb | Benefits | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Feverfew | Reduces inflammation and headache frequency | May cause mouth ulcers and stomach upset |
| Ginger | Anti-nausea and pain-relieving effects | May interact with blood thinners |
| Willow bark | Contains salicin, a natural pain reliever | May cause stomach upset and bleeding |
Essential Oils
Essential oils derived from plants have been used for centuries to relieve headaches. They can be applied topically or diffused in the air.
- Lavender oil: Calming and pain-relieving
- Peppermint oil: Cooling and numbing
- Eucalyptus oil: Anti-inflammatory and decongestant
Caution:Essential oils should be diluted with a carrier oil before applying them to the skin.
Other Alternative Therapies
Other alternative therapies that may provide relief from temple headaches include:
- Acupuncture:Involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate healing.
- Massage therapy:Focuses on releasing tension and improving blood flow in the head and neck.
Chronic Temple Headaches
Chronic temple headaches are a type of persistent headache that affects the temples, the area on either side of the forehead. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, muscle tension, and underlying medical conditions.Chronic temple headaches can be debilitating, interfering with daily activities and reducing quality of life.
Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause of the headaches.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Chronic temple headaches are relatively common, affecting up to 2% of the population. They are more common in women than in men and tend to develop in adulthood. Risk factors for chronic temple headaches include:
- Stress
- Muscle tension
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Migraine
- Certain medical conditions, such as sinus infections, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, and high blood pressure
Differential Diagnosis
It is important to get an accurate diagnosis for chronic temple headaches to rule out other underlying medical conditions. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, ask about your medical history, and order tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to help determine the cause of your headaches.
Treatment Options
Treatment for chronic temple headaches depends on the underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
- Medication, such as pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, or muscle relaxants
- Physical therapy to improve posture and reduce muscle tension
- Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises
- Lifestyle modifications, such as getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep
- In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct underlying structural problems that are causing the headaches
Role of Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play an important role in managing chronic temple headaches. Some helpful lifestyle changes include:
- Getting regular exercise to reduce stress and improve overall health
- Eating a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Getting enough sleep to reduce fatigue and improve overall well-being
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises
- Avoiding triggers that may cause headaches, such as certain foods, drinks, or activities
Resources for People with Chronic Temple Headaches
If you are struggling with chronic temple headaches, there are a number of resources available to help you. These resources include:
- The National Headache Foundation: https://headaches.org/
- The American Migraine Foundation: https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/
- The Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/
Differential Diagnosis

Temple headaches share similarities with several other conditions, making accurate diagnosis crucial for effective treatment.Other conditions that can mimic temple headaches include:
- Migraines: Severe, throbbing headaches that often affect one side of the head.
- Tension headaches: Mild to moderate headaches that cause a band-like sensation around the head.
- Cluster headaches: Intense, debilitating headaches that occur in clusters.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses, which can cause pain in the temples and forehead.
- Trigeminal neuralgia: A chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, causing severe facial pain.
Accurate diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests. Proper diagnosis ensures that the underlying cause of the headaches is identified and appropriate treatment is provided.
Emergency Situations
Seeking medical attention is crucial when experiencing a temple headache accompanied by specific warning signs. These signs indicate a potential underlying medical condition requiring immediate evaluation.
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Sudden Onset and Severe Pain
- Abrupt onset of an extremely intense headache, often described as the “worst headache of your life”
- Pain that peaks within minutes or hours, reaching its maximum intensity quickly
Accompanying Neurological Symptoms
- Numbness, weakness, or paralysis on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision problems, such as blurred vision or double vision
Other Red Flags
- Fever
- Confusion or disorientation
- Loss of consciousness
li>Stiff neck
Prevention Strategies
Preventing temple headaches involves a multifaceted approach that combines lifestyle modifications, stress management, trigger identification, and regular medical checkups. By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of their headaches.
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in headache prevention. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, getting adequate sleep, and engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate the body’s natural rhythm and reduce stress levels. Avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption, as well as maintaining a healthy diet, can also contribute to headache prevention.
Stress Management
Stress is a common trigger for temple headaches. Implementing effective stress management techniques can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Some effective stress management techniques include:
- Exercise
- Yoga
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Spending time in nature
Trigger Identification and Avoidance
Identifying and avoiding triggers is essential for preventing temple headaches. Common triggers include:
- Stress
- Fatigue
- Certain foods (e.g., caffeine, alcohol, artificial sweeteners)
- Changes in weather
- Strong odors
- Bright lights
- Loud noises
By keeping a headache diary, individuals can identify their triggers and develop strategies to avoid them.
Regular Medical Checkups
Regular medical checkups are important for monitoring overall health and identifying any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to temple headaches. During these checkups, doctors can assess the patient’s symptoms, perform a physical examination, and order tests if necessary.
Alternative Therapies
Some alternative therapies may also be beneficial in preventing temple headaches. These therapies include:
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Biofeedback
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle modifications | Maintain regular sleep schedule, get adequate sleep, engage in regular physical activity, avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption, maintain a healthy diet. |
| Stress management | Implement stress management techniques such as exercise, yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, spending time in nature. |
| Trigger identification and avoidance | Identify and avoid triggers such as stress, fatigue, certain foods, changes in weather, strong odors, bright lights, loud noises. |
| Regular medical checkups | Monitor overall health, identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to temple headaches. |
| Alternative therapies | Consider alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, biofeedback. |
Resources and Support
Finding support and resources can be crucial in managing temple headaches. Joining support groups and connecting with organizations dedicated to headache awareness can provide a sense of community, shared experiences, and valuable information.
Education is essential for understanding and effectively managing headaches. Resources such as headache awareness campaigns, online forums, and patient support groups can provide reliable information on headache types, triggers, and treatment options.
Support Groups and Organizations
- American Headache Society: Provides support and advocacy for individuals with headaches, including temple headaches.
- National Headache Foundation: Offers resources, support groups, and educational materials on headache management.
- Headache Support Group Directory: A comprehensive directory of headache support groups worldwide.
Headache Education and Awareness
- Headache and Migraine Information and Resource Center (H-MIRC): Provides evidence-based information on headache disorders.
- Migraine and Headache Awareness Week: An annual event that raises awareness about headaches and migraines.
- Headache Journals: Scientific journals that publish research and clinical findings on headache disorders.
Headache Management Guide
A comprehensive guide to headache management can provide valuable information on medication, alternative therapies, and lifestyle changes. This guide should include:
- Overview of headache types and causes
- Medication options, including over-the-counter and prescription drugs
- Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and biofeedback
- Lifestyle changes that can help reduce headache frequency and severity
Symptom Tracker App
A symptom tracker app can help individuals monitor their headaches, identify triggers, and track the effectiveness of treatments. This app can include features such as:
- Headache diary to record headache frequency, duration, and severity
- Trigger identification tool to help identify potential headache triggers
- Medication and treatment tracker to monitor the effectiveness of different treatments
Headache Specialist Network, How to get rid of a temple headache
A network of headache specialists can provide personalized care and support. This network can include:
- Neurologists specializing in headache disorders
- Pain management specialists
- Behavioral health specialists
Case Studies of Successful Temple Headache Management
To illustrate the diverse approaches to managing temple headaches effectively, we present case studies of individuals who have found relief through various treatments and lifestyle modifications.
Case Study 1
- Demographics:Female, age 35, office worker
- Medical History:Chronic temple headaches for 5 years, triggered by stress and dehydration
- Lifestyle Factors:High-stress work environment, irregular sleep patterns, inadequate hydration
- Treatments and Coping Mechanisms:
- Stress management techniques (yoga, meditation)
- Regular hydration
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy to manage stress and triggers
- Effectiveness:Significant reduction in headache frequency and intensity, improved overall well-being
Case Study 2
- Demographics:Male, age 42, construction worker
- Medical History:Episodic temple headaches for 10 years, exacerbated by loud noise and bright lights
- Lifestyle Factors:Exposure to loud noise at work, sensitivity to light
- Treatments and Coping Mechanisms:
- Noise-canceling headphones or earplugs
- Sunglasses or tinted lenses to reduce light exposure
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (ibuprofen, acetaminophen)
- Effectiveness:Effective control of headache symptoms during work and in bright environments
Case Study 3
- Demographics:Female, age 28, student
- Medical History:Frequent temple headaches for 3 years, associated with hormonal fluctuations
- Lifestyle Factors:Irregular menstrual cycles, high stress levels during exams
- Treatments and Coping Mechanisms:
- Hormonal contraceptives to regulate menstrual cycles
- Stress reduction techniques (deep breathing exercises, mindfulness)
- Dietary modifications to avoid headache triggers (e.g., caffeine, alcohol)
- Effectiveness:Significant improvement in headache frequency and severity, particularly during hormonal fluctuations
FAQ Insights
What are the common causes of temple headaches?
Temple headaches can be triggered by various factors, including stress, tension, dehydration, caffeine withdrawal, sinus infections, and certain medications.
What are some effective home remedies for temple headaches?
Applying a cold compress, massaging your temples with essential oils like peppermint or lavender, and practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation can provide relief.
When should I seek medical attention for a temple headache?
If your headache is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, nausea, or vision changes, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.