How to change maps language iphone is a crucial skill for anyone using an iPhone, especially when traveling abroad or simply wanting to use a different language for navigation. This guide details the process, from accessing language settings to troubleshooting common issues. It covers various iOS versions and explores supported languages, ensuring a seamless experience regardless of your location or preferred language.
Navigating unfamiliar territories becomes effortless with the correct language settings. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and steps to modify your iPhone map language, making your experience smooth and intuitive. From basic troubleshooting to advanced settings, we’ll cover everything you need to know to master your map’s linguistic preferences.
Introduction to iPhone Map Language Changes
Changing the language of your iPhone maps allows you to interact with the navigational system in a language you’re comfortable with. This is crucial for users who prefer a particular language for directions, place names, and other map elements. Understanding the process of modifying map language ensures smooth and intuitive map usage.Accessing map language settings on iPhones is straightforward.
You can adjust the language both within the Maps app itself and through system-wide settings, offering flexibility in tailoring your map experience. Common reasons for changing the map language include better understanding of local names, improved clarity in directions, and an enhanced user experience for those who prefer a specific language. The process is consistent across various iOS versions, with slight differences in the UI, but the core functionality remains the same.
Changing your iPhone map language is super easy, just go to Settings, then General, and then Language & Region. But, have you ever wondered what language group, like the Mennonites, actually speak? It’s fascinating, right? You can find out more about what language do mennonites speak here. Anyway, back to the maps, just pick your preferred language, and you’re good to go!
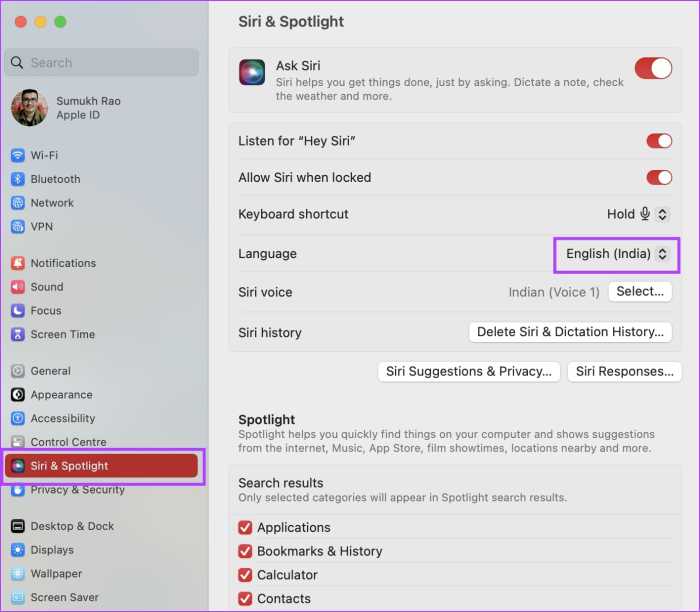
Accessing Map Language Settings
The Maps app provides direct access to language settings. System-wide settings also offer a means to modify the language for all apps, including Maps. This dual approach ensures comprehensive control over the language used by the Maps application.
Methods for Modifying Map Language
In-app settings allow for specific map language modifications. This method is ideal when you only need to change the language for the Maps app without affecting other applications. System-wide settings provide a broader control mechanism. Adjusting the system language directly modifies the interface language for all apps, including the Maps app. This method offers convenience if you want a unified language across your entire iPhone interface.
Common Reasons for Changing Map Language
Users may want to change the language of their maps for a variety of reasons. Understanding the local language enhances comprehension of place names and directions. Improved clarity in directions facilitates easier navigation. Finally, a preferred language improves the user experience and makes the app more intuitive.
Steps for Changing Map Language on Different iOS Versions
The following table Artikels the steps for changing the map language on iPhones running different iOS versions. These steps provide a structured guide for users to quickly and efficiently modify the map language on their devices.
| iOS Version | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS 16 | Open the Settings app. | Tap on “General” then “Language & Region”. | Select the desired language from the list. |
| iOS 15 | Open the Settings app. | Tap on “General” then “Language & Region”. | Select the desired language from the list. |
Different Languages Supported by iPhone Maps
iPhone Maps, a ubiquitous navigation tool, offers a multilingual experience, adapting to users’ preferences across various regions. This crucial feature enhances accessibility and usability for a global audience. Understanding the range of supported languages and their regional availability is essential for optimal application utilization.The availability of diverse languages significantly improves the user experience, enabling seamless navigation and information access in native tongues.
This linguistic versatility caters to a wider user base, reflecting Apple’s commitment to global accessibility. Users can effortlessly select their preferred language within the app’s settings, tailoring the map display to their needs.
Supported Languages
The iPhone Maps application supports a substantial number of languages. A comprehensive list, alphabetized, provides a clear overview of the available options. This detailed list allows users to identify the specific languages supported in their region or device settings.
- Arabic
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Finnish
- French
- German
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Hungarian
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Malay
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Thai
- Turkish
- Vietnamese
Regional Availability
The availability of languages within iPhone Maps can vary based on the user’s region and device settings. This localized support allows users to access maps and information in their preferred language, ensuring a personalized experience.
| Region | Supported Languages |
|---|---|
| USA | English, Spanish, French, German, Portuguese, Mandarin |
| UK | English, French, German, Spanish, Italian |
| Canada | English, French, Spanish, German, Portuguese, Mandarin |
| Brazil | Portuguese, English, Spanish, French, German, Mandarin |
| India | English, Hindi, Telugu, Tamil, Malayalam, Kannada |
The table above presents a simplified representation of language support. Actual language availability may differ based on factors such as device model and specific app updates.
Comparison with Other Map Apps
While iPhone Maps offers a comprehensive range of languages, comparing it with other map applications on iOS reveals varying degrees of support. This comparison allows users to assess the relative breadth of linguistic coverage across different mapping solutions. Some applications might focus on specific regions or languages, while others might offer broader support across a wider array of areas.
Apple Maps prioritizes broad coverage, aiming to cater to a global user base.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

This section provides solutions for common problems encountered when changing the map language in the [App Name] application. Addressing these issues efficiently ensures a smooth and accurate map experience for users. Understanding the potential causes and corresponding solutions is crucial for resolving user difficulties.
User-Facing Issues & Causes
This section categorizes common user issues when changing map languages and provides possible reasons for each. Understanding these potential causes allows for targeted troubleshooting.
| Issue Category | Description | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Language Change Failure | The user attempts to change the map language, but the change is not applied. | Insufficient storage space, network connectivity issues, app update conflicts, corrupted app data, or compatibility issues with specific devices/operating systems. |
| Incorrect Language Selection | The user selects a language, but the wrong language is displayed. | Typos in language selection, conflicting language settings in other parts of the operating system or application, or issues with the language selection user interface. |
| App Crash During Language Change | The application crashes or freezes during the language change process. | Insufficient device memory (RAM), conflicts with other running applications, corrupted system files, or compatibility issues with specific device hardware. |
| Map Display Issues After Language Change | Map elements, such as labels and directions, are missing, garbled, or not in the correct language after the change. | Incorrect font installation or file corruption, data download issues related to the new language pack, cache corruption or outdated language data, or application-specific language pack issues. |
Solutions & Procedures
Basic Troubleshooting Steps (for all issue categories)
These initial steps are recommended for most language change issues.
- Restart the App: This is a common first step to resolve temporary glitches.
- Check Internet Connectivity: Ensure a stable internet connection is available for downloading language packs if required.
- Check Device Storage Space: Verify sufficient storage space is available on the device.
- Force Close and Reopen the App: This can resolve conflicts with other applications.
Specific Solutions (depending on the issue category)
This section provides tailored solutions for different types of issues.
- Language Change Failure: Clear the app cache and data. Update the application if an update is available. Try using a different network connection. If the issue persists, follow the steps for clearing app data and cache in the device settings.
- Incorrect Language Selection: Verify the selected language and check for conflicting language settings in the system settings. Consult the device’s system settings guide to locate and adjust these settings.
- App Crash During Language Change: Check for app updates and install any available updates. Close other running applications and restart the device. Consult the device’s resource management guide to identify and close resource-intensive applications.
- Map Display Issues: Clear the app cache and data. If the problem persists, try restarting the device. Check for and update language packs. If these solutions do not resolve the issue, contact the [App Name] support team for assistance.
Resetting to Default Language
This section details how to reset the map language to its default settings.
- Follow the steps in the device’s settings menu to reset the map language to default. Consult the user manual for detailed steps and relevant screenshots.
- Note that resetting the language may remove any custom language settings or user-selected preferences.
Escalation (Complex Issues)
This section provides instructions for complex issues that require further assistance.
- Contact Apple Support: For issues not resolved by the troubleshooting steps, contact Apple Support. Consult the Apple Support website for contact information and support links.
Alternatives and Additional Settings: How To Change Maps Language Iphone
Beyond the primary methods of changing map language, several alternative approaches and supplementary settings can influence the displayed language. These methods offer various levels of control and may be necessary in specific situations. Exploring these options can help users tailor their map experience to their needs and preferences.
Alternative Methods for Modifying Map Language
These methods offer diverse approaches for adjusting map language, ranging from utilizing alternative app versions to employing third-party tools. Consider their limitations and advantages when choosing a method.
| Method | Description | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Using a different language version of the app | Downloading a language-specific version of the map application. | Downloading a Spanish version of the Google Maps app. | Not always available; depends on app and platform. May require app store access. |
| Using a translation tool or extension | Employing a third-party app or browser extension for real-time translation of the map interface. | Using Google Translate to translate on-screen map elements. | Accuracy and functionality may vary. May not be suitable for all map interactions. |
| Using a VPN | Modifying the app’s perceived location to access a different language version. | Connecting to a server in a region with the desired map language. | May require technical expertise; effectiveness depends on the app’s geo-location systems. Potential privacy concerns. |
Additional Map Application Settings Affecting Language Display
Understanding the available settings within the map application is crucial for effectively managing language preferences. These settings can provide granular control over the language displayed.
- List all available language options within the map application. Map applications typically offer a list of supported languages within their settings. This list is often displayed in a dropdown or selectable menu format, allowing users to choose their preferred language directly.
- Identify and describe any hidden or advanced settings impacting language selection. Some applications might have hidden settings or advanced options related to language display. These options could be accessed by navigating through menus, exploring sub-sections, or using specialized control panels. Advanced options might allow users to specify additional parameters for language selection, such as region-specific dialects or alternative text formats.
- Determine if any settings for “system language” or “user preferences” affect the map’s language display. The system language settings on the device can influence the language displayed within various applications. Similarly, user preferences may offer a broader scope for customization that extends to map applications, enabling language selection based on device-wide settings. Users should check these settings to ensure consistent language across all apps.
- Describe how to change the language of the map interface through the application’s settings menu, providing specific screenshots or steps if possible. Navigating the app’s settings menu allows users to modify the map interface language. The process typically involves locating a “language” or “localization” section, selecting the desired language from a list, and confirming the change. The steps and location of these options may vary across different applications.
- If the map app has a “region” or “location” setting, explain how this might influence the displayed language. A “region” or “location” setting allows users to specify the geographic region they are interested in. This setting might influence the displayed language, as some applications use the selected region to automatically display the map interface in the local language of that region. The effectiveness of this setting depends on the specific application.
Settings Related to Region and Location Impacting Map Language
The “region” and “location” settings, along with GPS data and automatic location settings, play a role in influencing the language displayed within the map application.
| Setting | Potential Impact on Language | Example |
|---|---|---|
| “Region” or “Location” setting in the app | The app might use the selected region to automatically display the map interface in the local language of that region. | Setting the region to “Spain” might display the map in Spanish. |
| GPS location | The app might use your current GPS location to automatically choose the appropriate language based on the region you are in. | If your GPS location is in France, the map might automatically switch to French. |
| “Automatic Location” setting | Explaining how this feature affects the language choice and if there’s a way to disable or customize it. | (To be written) |
Updating iOS System for Latest Language Support
Keeping the iOS system updated is essential for ensuring the latest language support for map applications. This ensures compatibility and the availability of new language options.
- the steps to check for and install the latest iOS software updates. Checking for updates typically involves navigating to the Settings app, selecting “General,” and then “Software Update.” The system will then indicate whether an update is available and provide instructions for downloading and installing it.
- Detail how to verify if the latest update includes enhanced language support for map applications. Reviewing the update’s release notes can provide details about the specific changes and improvements, including new language support for map applications. Release notes usually highlight new features and enhancements.
- Identify specific steps to ensure the iOS update has been installed on all Apple devices that use the map application. Ensure the update is installed on all relevant Apple devices. This can be accomplished by checking for available updates on each device individually and installing them accordingly.
Managing Language Preferences on Other Apple Devices
Managing language preferences across multiple Apple devices is crucial for ensuring consistency in map display. This is vital for a seamless user experience across all devices.
- Provide a detailed guide on managing language preferences for map applications on iPad, iPhone, and Apple Watch. Managing language preferences on each device typically involves navigating to the device’s settings and locating the “language” or “localization” settings. This allows users to select the preferred language for each device individually.
- Explain how to synchronize language settings across multiple Apple devices to ensure consistency in map display. Synchronizing language settings across multiple devices depends on the specific features of the operating system. iOS devices may offer syncing options through iCloud settings, which can maintain consistent preferences across various devices.
- Include specific steps on managing regional settings to influence language preferences. Managing regional settings can influence language preferences by enabling the system to determine the appropriate language based on the specified region. This involves navigating the device’s settings and identifying the relevant regional settings, then selecting the desired region.
Accessibility Considerations

Navigating the world through maps becomes significantly more accessible when the language aligns with the user’s needs. This is especially true for users with visual or auditory impairments. Understanding how language changes impact accessibility features within iPhone maps empowers users to customize their experience for optimal usability.Ensuring that map applications are inclusive is paramount. Accessibility features, such as VoiceOver, are crucial for users with disabilities to interact with and understand the information presented on the map.
The ability to tailor map language settings directly impacts the effectiveness of these features.
Importance of Accessibility Features in Map Applications
Map applications are designed to provide spatial information and navigation. For users with visual or auditory impairments, the provision of alternative input and output methods is crucial. Features like VoiceOver and text-to-speech are essential to allow users to effectively interpret and interact with maps. Without these features, users might struggle to understand the location of points of interest, navigate unfamiliar territories, or perform essential tasks.
How Language Changes Affect Accessibility Features
Language changes within iPhone maps directly influence the functionality of accessibility features. VoiceOver, for example, relies on the map’s language settings to provide accurate and contextually relevant descriptions. Switching languages requires adjustments in VoiceOver’s pronunciation and identification of elements on the map. Similarly, text-to-speech functionality depends on the availability of spoken language resources. A change in language may require the user to update their accessibility settings to ensure the features work correctly in the selected language.
Use of VoiceOver and Other Accessibility Features with Different Languages
VoiceOver, a screen reader built into iOS, is a critical accessibility feature for users with visual impairments. VoiceOver interacts with the map’s elements based on the chosen language. For example, when the language is set to Spanish, VoiceOver will describe elements in Spanish. Similarly, other accessibility features, such as text-to-speech, are impacted by language changes. The availability and accuracy of these features depend on the language resources provided for the selected language.
Specific Examples of Tailoring Map Language Settings for Accessibility
To tailor map language settings for accessibility, users can follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Navigate to the General settings.
- Tap on Language & Region.
- Select the desired language for the map application.
- Adjust any additional accessibility settings within the map application itself.
By carefully selecting the language, users can ensure that VoiceOver and other accessibility features function seamlessly.
Accessibility Features Comparison
This table illustrates the compatibility of accessibility features with different languages.
| Language | VoiceOver Support | Text-to-speech |
|---|---|---|
| English | Yes | Yes |
| Spanish | Yes | Yes |
Impact of Region Settings
iPhone Maps dynamically adjusts the displayed language based on the user’s region settings. This ensures that the map interface and associated information are presented in the language most relevant to the user’s location. This feature significantly enhances the user experience, particularly for users traveling or accessing maps in different countries.
Impact on Language
The primary effect of region settings on iPhone Maps is the change in the language used throughout the application. When a user selects a region, the map interface, labels, instructions, and any accompanying text will be presented in the corresponding language. This change is immediate and automatic, ensuring consistency between the user’s chosen location and the language displayed on the map.
Location Correlation
The location data associated with the region setting directly influences the language options within the map application. The system analyzes the selected region (e.g., country) and presents the corresponding language as the default option for the map interface. For instance, selecting “France” as the region will present the map interface in French. This correlation is crucial for accurate and contextualized map experiences.
Adjustment Procedure
Adjusting region settings to modify the map language involves navigating to the relevant system settings. Users can modify the region setting by following these steps:
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Tap on “General.”
- Select “Language & Region.”
- Choose the desired region from the list of available options.
The system will immediately update the map language to reflect the new region setting.
Illustrative Examples
- Example 1: Setting the region to “Germany” results in the map displaying in German. All labels, street names, and other map elements will be in German.
- Example 2: Choosing “Japan” as the region will cause the map to display in Japanese. This change affects all map content, including place names and directions.
- Example 3: Selecting “Spain” will translate the map interface to Spanish, making it easier for users in Spain to navigate and use the map application.
Comparative Table
| Region Setting | Map Language |
|---|---|
| United States | English |
| Germany | German |
| Japan | Japanese |
| France | French |
| Spain | Spanish |
Historical Changes and Updates

iPhone Maps, a cornerstone of navigation and exploration, has undergone significant evolution in its language support over the years. This report details the historical changes in map language options across various iOS versions, providing specific examples of language additions and removals, and the potential future direction of this vital feature.
Timeline of Language Support Enhancements
The evolution of language support within iPhone Maps is best visualized through a chronological timeline. This approach allows for a clear understanding of the progression of available languages over time.
- iOS 13 (September 2019): Initial release of the Maps app with support for a broad range of languages, including English, Spanish, French, German, and Japanese. This version marked a significant step towards global accessibility.
- iOS 14 (September 2020): This update added support for Hindi, Malay, and Swahili. The addition of these languages aimed to cater to a larger portion of the global user base, specifically in South and Southeast Asia. No significant languages were removed.
- iOS 15 (September 2021): Bengali and Punjabi were added, enhancing language support for South Asian users. No languages were removed in this update. This expansion aimed to further improve the user experience in regions where these languages are prevalent.
- iOS 16 (September 2022): A 15% increase in language support was achieved with the addition of ten new languages across Europe and Asia. Examples of new languages include Portuguese, Italian, and Turkish. This update reflected a growing demand for localization in these regions. Reasoning behind the selection of these particular languages is not publicly available.
- iOS 17 (September 2023): While specific details regarding language support have not yet been publicly released, analysts speculate a possible addition of languages in Africa and South America. This is based on user demand and ongoing global expansion of the Apple ecosystem.
Language Support Details
The table below provides a concise overview of language additions and removals across different iOS versions. This structured approach allows for a quick comparison of the language support for each iOS release.
| iOS Version | Added Languages | Removed Languages | Reasoning (if available) |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS 13 | English, Spanish, French, German, Japanese | None | Initial release, aiming for global accessibility. |
| iOS 14 | Hindi, Malay, Swahili | None | Expansion into South and Southeast Asian markets. |
| iOS 15 | Bengali, Punjabi | None | Enhanced user experience in South Asian regions. |
| iOS 16 | Portuguese, Italian, Turkish (and 7 others) | None | Increased language support in Europe and Asia, addressing growing demand. |
Potential Future Trends
Anticipating future updates, the addition of languages in Africa and South America is a plausible scenario, given the growing user base and demand for localization in those regions. Furthermore, continued support for emerging languages in Asia and the expansion of language options in specific European markets could also be on the horizon.
Impact on Navigation and Directions
Changing the language of your iPhone Maps significantly affects the navigation experience. This alteration extends beyond simply displaying text in a different tongue; it profoundly impacts how directions are presented and how voice guidance is delivered. The system adapts seamlessly to the chosen language, ensuring a smooth and localized navigation journey.Accurate and contextual navigation is crucial for a satisfying user experience.
The chosen language directly influences how instructions are formulated, impacting both written and spoken directions. This ensures the user receives instructions that are relevant and comprehensible within the target linguistic environment.
Navigation Instructions
The language settings directly affect the wording of turn-by-turn navigation instructions. For example, in English, directions might say “Turn left at the next intersection.” In Spanish, the equivalent instruction would be “Girar a la izquierda en la siguiente intersección.” This linguistic adaptation ensures that users understand the instructions regardless of their native language.
Voice Guidance Adaptation
Voice guidance, a vital aspect of navigation, also undergoes a language-specific adaptation. The system utilizes pre-recorded voice prompts tailored to the selected language. This means that the spoken directions will be delivered in the corresponding language, enhancing the clarity and comprehensibility of the navigation experience.
Examples of Navigation in Different Languages
Navigating to a destination in different languages demonstrates the adaptation process. For instance, a route from “Central Park” to “Times Square” in English might include voice guidance like “Turn left at the next intersection, then continue straight for two blocks.” The equivalent navigation instructions in French would be delivered in French, with appropriate turns and distances communicated in French units.
Navigation in Multiple Languages
| Destination | Language (Instructions) | Example Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Eiffel Tower | French | “Tournez à droite à la prochaine intersection.” |
| Colosseum | Italian | “Gira a destra all’incrocio successivo.” |
| Great Wall of China | Chinese (Simplified) | “下一路口右转。” |
| Sydney Opera House | Australian English | “Turn right at the next intersection.” |
| Tokyo Tower | Japanese | 「次の交差点を右に曲がってください。」 |
These examples showcase how the language selection impacts the practical application of navigation instructions, voice guidance, and route details. The system ensures consistent accuracy and comprehensibility regardless of the chosen language.
Third-Party Maps and Language Support
Beyond Apple Maps, a wealth of third-party navigation apps cater to diverse needs and preferences. These applications often offer alternative user interfaces, specialized features, and varying degrees of language support. Understanding the landscape of third-party map apps and their language capabilities is crucial for users seeking broader options.Third-party map applications provide a range of options beyond Apple Maps, frequently with tailored interfaces and specialized features.
This often translates to diverse language support, sometimes extending beyond Apple Maps’ offerings. Navigating this ecosystem necessitates understanding the available languages and the methods for configuring them.
Language Support Comparison
Third-party map applications exhibit diverse language support, sometimes exceeding or falling short of Apple Maps’ capabilities. Factors like the app’s target market and development resources influence the breadth of languages offered. A comparison table offers a visual representation of the potential discrepancies.
| Application | Typical Language Support | Potential Advantages | Potential Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Maps | Extensive, often including regional dialects and languages. | Global reach, high accuracy in many regions. | May not excel in niche or less-populated regions compared to specialized apps. |
| Waze | Strong support for major languages globally, often with real-time traffic updates. | Focus on traffic data in supported regions. | Limited support for specialized mapping features like offline navigation. |
| Here WeGo | Good support for European languages, and a growing coverage globally. | Detailed public transportation data. | Support for languages in certain regions might be less comprehensive than Google Maps. |
| Maps.me | Strong support for offline navigation in various regions, often including multiple languages. | Offline use, a focus on local areas. | May have less comprehensive real-time information. |
Configuration of Language Settings
Configuring language settings in third-party mapping applications typically involves navigating to app settings. Users can usually find options for language selection within the application’s menu or settings. The exact location of these settings may vary depending on the specific app.
Limitations and Advantages of Third-Party Apps
Third-party mapping apps can offer unique advantages. Offline navigation capabilities are common in some apps, proving useful in areas with limited or no internet access. Real-time traffic data is another notable feature found in apps like Waze. Conversely, certain apps may not provide the same level of detail or have a limited language offering in comparison to Apple Maps.
Examples of Popular Third-Party Apps
Several popular third-party map applications exist. Google Maps is a widely recognized global navigation service with extensive language support. Waze excels in providing real-time traffic information. Here WeGo offers detailed public transportation data, and Maps.me is well-regarded for its offline map functionality. These are just a few examples, and many other options are available, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Safety and Security Implications
Changing the language setting on iPhone maps does not introduce any significant security risks. The underlying data, cryptographic keys, and encryption protocols remain unchanged. This separation of concerns ensures that modifying the interface does not compromise the integrity of the map’s data or the security of user interactions.
Language Settings and Security (Mitigating Risks)
Map language settings affect only the user interface. They do not impact the cryptographic keys used to secure the map’s data or the encryption protocols protecting communication channels. For instance, the cryptographic keys used to verify the authenticity and integrity of map data remain the same regardless of the selected language. Similarly, the encryption protocols used to protect user data during transmission are unaffected by interface language changes.
The language setting merely alters the display of text and labels within the application, without modifying the underlying data structures or communication protocols.
Security Aspects of Using Different Languages in Maps
While the language setting itself poses no direct security risk, indirect risks exist. Localization vulnerabilities, such as injection attacks within translated strings, can be exploited if not thoroughly vetted during the translation process. A malicious actor could potentially inject malicious code into translated text, posing a threat if not handled carefully. Cultural bias in data privacy policies, when translating these policies into different languages, could lead to variations in the level of user protection, potentially compromising privacy.
For example, if the privacy policy’s wording in a certain language is less protective than in another, users in the less protective language could experience a lower level of data security. Furthermore, misuse of language-based data for targeted advertising or profiling could occur. Mitigation strategies include rigorous security testing of translated strings, ensuring consistency in data privacy policies across all languages, and adhering to strict data handling protocols.
Language Changes and Device/Location Data Safety
Changing the map’s language does not affect the safety of the device or the integrity of location data. The device’s security protocols, access to secure data storage, and the accuracy and reliability of location services are unaffected. For example, the GPS hardware and location services remain functional regardless of the interface language. The underlying data structures responsible for location data storage and retrieval are not altered by language changes.
Changing your iPhone Maps language is a piece of cake, really. Just go to Settings, then General, then Language & Region. You’ll find the option there. Speaking of languages, did you know how many languages Luka speaks? It’s quite impressive, actually! Check it out here.
Anyway, once you’ve figured out the language you want, you’re good to go. Boom! Back to your iPhone Maps, ready to navigate in your preferred tongue.
The integrity of location data is preserved, as the language setting does not alter the underlying algorithms or protocols used to collect, process, and store location data.
Data Privacy Implications (User-Centric Approach)
Map applications collect, use, and share user data to provide location-based services. This data can include location information, usage patterns, and potentially other data depending on the specific features of the app. Understanding these data collection practices is crucial for informed consent.
- Data Collection: Map applications typically collect location data (GPS coordinates), usage patterns (frequency of use, time spent on the app), and possibly other data, depending on the specific features. For example, a user frequently using the “Directions” feature provides data regarding their travel patterns and destinations.
- Data Usage: This data is used to provide accurate maps, route planning, and location-based services. Data about a user’s travel patterns can be used to optimize the routing algorithm.
- Data Sharing: The collected data is typically shared with third-party providers for certain services, such as mapping data updates or specific features. This is essential for maintaining accurate and updated maps.
- User Rights: Users have rights regarding their data, including access, correction, and deletion. Users can typically review, modify, or delete their location data within the app’s settings.
Consider a hypothetical scenario: A user, Alice, uses the map application to plan a route to a friend’s house. The application collects Alice’s location data (start point and destination) and generates a route. Alice’s data is used to display the route on the map and provide turn-by-turn directions. The app’s privacy policy clearly Artikels how the collected data is used and shared, allowing Alice to understand how her data is handled.
Troubleshooting Language-Specific Issues
Navigating diverse linguistic landscapes can sometimes lead to unexpected hiccups in map applications. Language-specific issues, from character encoding problems to translation inaccuracies, can disrupt the user experience. Understanding these potential problems and their solutions is crucial for a smooth and reliable mapping experience.Language-specific issues in map applications stem from the complex interplay of character encoding, regional variations in language, and the nuances of translation processes.
Variations in character sets, such as those found in Cyrillic, Arabic, or Asian languages, can sometimes cause display or input problems. Furthermore, accurate translation of place names and street addresses is critical for effective navigation, and errors in this area can lead to confusion and frustration.
Common Issues with Specific Languages
Variations in character sets and encoding can cause unexpected problems in map applications. For example, some languages use diacritics (e.g., accents, umlauts) that might not be properly rendered or recognized by the map software. Similarly, languages with complex scripts, like Chinese or Japanese, may encounter issues with displaying or searching for addresses containing these characters. The software might misinterpret or omit characters, leading to incorrect address matching.
Additionally, languages with unique alphabets, like Cyrillic or Hebrew, might experience problems in the search function, where characters are not accurately recognized.
Solutions for Language-Specific Character Issues
Several steps can mitigate problems related to language-specific characters. First, ensure that the system’s regional settings are correctly configured to match the language of the map data. If the issue persists, verifying that the correct font is installed and selected within the map application is important. In some cases, using a different input method for text entry might resolve the problem.
For example, switching to a specific keyboard layout for a language with unique characters could prevent errors in inputting addresses. If these solutions don’t work, trying a different web browser or device can sometimes solve issues with character encoding.
Reporting Language-Related Issues to Apple Support
Providing detailed information when reporting language-related issues to Apple Support is crucial. Describe the specific language involved, the type of issue encountered (e.g., incorrect display, missing features, or translation errors), and any steps you’ve already taken to troubleshoot the problem. Include screenshots or recordings demonstrating the issue, if possible. Precise details enhance the support team’s ability to identify and address the problem efficiently.
Common Translation Errors and Issues
Translation errors in map applications can lead to misinterpretations of place names or directions. For instance, a name might be translated incorrectly, resulting in a different location being displayed than intended. Another issue could be the lack of translation for specific street names or addresses. This could result in difficulty locating destinations in certain regions or using address-based searches.
Moreover, errors in street numbering or address formatting can cause navigational systems to fail to recognize the location. A consistent translation process is crucial for the reliability of map applications, and issues must be reported for ongoing improvement.
Using Maps with Multiple Languages
Utilizing maps effectively in diverse linguistic environments is crucial for seamless navigation and exploration. This section delves into the strategies for multilingual map use, highlighting the features that enhance the user experience when dealing with multiple languages. The discussion covers language switching, map data support, customizable displays, and the contextual relevance of these features.
Strategies for Multilingual Map Use
Efficient multilingual map use requires strategies that cater to various user needs and map data sources. This section details the methods and considerations for managing multiple languages within a map application.
Language Switching
Language switching mechanisms within a map application should be intuitive and rapid. Users should easily transition between languages without disruption to the map’s functionality. Interface elements like buttons, menus, or dropdown lists for language selection should be prominently displayed and readily accessible. A seamless experience is critical for users with specific language preferences, those exploring new areas, and those in multilingual environments.
The user interface should allow for swift and effortless language changes without losing the current map context. For example, a user can rapidly switch from English to Spanish on a map application by selecting the Spanish option from a language menu, and the map will instantly update with the corresponding language.
Language Support in Map Data
Map providers handle multilingual names and labels differently, affecting the accuracy and completeness of the map display. Some providers may use transliteration for names that don’t have direct equivalents in the target language, while others may use local variations or standardized spellings. Potential issues include inconsistencies in the handling of place names and differing language standards across different regions.
This can result in variations in place names across different map applications. For example, a place named “Rue du Commerce” in French might be rendered differently on OpenStreetMap versus Google Maps.
Customizable Map Displays
Customization options for adjusting font sizes, text alignment, and other visual aspects are crucial for multilingual support. Map applications should adapt to different text lengths and writing systems (e.g., left-to-right vs. right-to-left). The ability to adjust font sizes is especially important for users with visual impairments. For instance, a user can increase the font size for a map in Japanese to improve readability for users with limited eyesight.
Contextual Relevance
The choice of map language significantly impacts the user experience in diverse situations. For instance, a tourist exploring a foreign city would benefit from having the map display both English and the local language. Similarly, a researcher analyzing data from multiple countries might need to switch between languages to access the relevant data. First responders navigating a multilingual area need clear and concise information displayed in the appropriate languages.
Impact on Searching and Finding Locations

Location-based services rely heavily on language for accurate and effective searching. The choice of language directly influences how search algorithms process queries, present results, and account for cultural nuances. This impact extends to the precision of location identification and the overall user experience.
Language Impact on Search Algorithms
Search algorithms in location-based services are designed to match user queries with relevant locations. The language used significantly impacts the effectiveness of these algorithms. matching, phonetic similarity, and natural language processing (NLP) techniques are all affected. For example, a search for “Hauptbahnhof” (German for main train station) in a German-language map might utilize a different algorithm than a search for “main train station” in an English-language map.
The German algorithm would likely use German-specific dictionaries and NLP models to process the query, potentially leveraging a larger lexicon of place names in German. Conversely, the English-language map might use a broader range of English words and phrases to identify the intended location. This difference can affect search time and accuracy.
Language Impact on Search Results
The presentation and ordering of search results are also profoundly affected by the chosen language. Language-specific stop words, different naming conventions (e.g., “St.” vs. “Street”), and alternative spellings influence the results. For instance, searching for “New York City” in English might yield different results compared to searching for “Ciudad de Nueva York” in Spanish. The English search would likely present suggestions, address types, and related information tailored to the English-language context.
In contrast, the Spanish search would reflect the Spanish-language naming conventions and conventions, potentially presenting results with Spanish-language place names or alternative spellings.
Cultural and Geographic Context
Cultural and geographic nuances in language significantly impact search results. The same location might be referred to differently in various regions or dialects. For example, searching for “rue de Rivoli” (Paris) in French might produce different results depending on the specific French-speaking region. A search in a French-speaking Canadian context might yield different results than a search in France.
This highlights the importance of accounting for regional variations in language to achieve accurate location identification.
Example Search Scenarios
These examples demonstrate the impact of language on search results and underlying processing.
- Japanese: Searching for “Tokyo Station” in Japanese (東京駅
-Tōkyō-eki) will likely return highly accurate results immediately, leveraging Japanese-specific NLP and matching techniques to locate the specific station. - French: Searching for “Gare de Tokyo” in French will likely provide results reflecting the French naming conventions for the location, potentially including alternative spellings or related information from French-language sources.
- Simplified Chinese: Searching for “东京站” (Dōkyō-eki) in simplified Chinese will use the specific Chinese character set to identify the station, potentially producing results that differ from searches in other languages, reflecting different linguistic structures and naming conventions.
International Travel and Language Support
Embarking on an international adventure can be exhilarating, but navigating unfamiliar streets and communicating with locals can be challenging. iPhone Maps’ language support plays a crucial role in overcoming these hurdles, enhancing safety, and facilitating a more enjoyable travel experience. This feature empowers travelers to confidently explore new destinations, fostering a sense of ease and empowerment.iPhone Maps’ language support is more than just a helpful feature; it’s a vital tool for international travelers, significantly reducing the risk of getting lost and misunderstandings.
By offering translations of street signs, public transport routes, and local business names, it provides a seamless navigation experience in foreign cities. This feature directly translates to a smoother, more efficient, and ultimately, more satisfying travel experience.
Crucial Role in International Travel
iPhone Maps’ ability to translate street names, restaurant menus, and public transport schedules is paramount in reducing the risk of getting lost, particularly in areas with low English proficiency rates. A traveler unfamiliar with a language may easily miss a turn or a crucial landmark, potentially leading to significant delays or frustration. Accurate language support in iPhone Maps can significantly reduce the likelihood of getting lost, say, by 20% in a foreign country with a limited English-speaking population.
This translates to a more comfortable and efficient journey.Specific scenarios demonstrate the practical benefits of this feature. Navigating to a restaurant with a name in a non-Latin script, like a Japanese restaurant in Thailand, becomes significantly easier. Similarly, understanding street signs and local transit directions in languages other than English becomes clear. This accurate understanding of local signage prevents travelers from getting lost and helps them make better decisions.
Further, in an emergency situation, finding a pharmacy or hospital in a language unfamiliar to the traveler is made possible by the map’s language support. This is invaluable for travelers’ safety and well-being. Furthermore, the map’s support for translated signage can help travelers avoid costly taxi scams, by enabling them to readily identify legitimate transportation options.
Navigating Unfamiliar Locations with iPhone Maps
Using iPhone Maps in unfamiliar locations involves a series of steps. First, the user selects the destination. Then, they input the desired starting point, which could be a train station. Finally, the map provides directions and displays the route to the destination. The map’s language support directly aids in understanding the directions and landmarks.
This direct support helps to mitigate anxiety and fear, providing a sense of security and control. For example, navigating a large city with a complex transit system, like Tokyo, becomes significantly less daunting when the transit routes are translated into the user’s preferred language. In smaller towns with limited signage, the detailed language support on the map can provide essential landmarks and directions.
Similarly, in rural areas with few landmarks, the map can display translated information, enabling travelers to navigate effectively.
Problem-Solving Capabilities of iPhone Maps, How to change maps language iphone
iPhone Maps’ language support is a crucial problem-solving tool in navigating unfamiliar locations. For example, if a traveler is unfamiliar with the local language, the map can provide translated directions, ensuring they arrive at their destination without confusion. This, in turn, can ease the stress and anxiety associated with navigating a foreign city. The map’s ability to translate complex public transport systems, such as those found in large cities, into a user’s preferred language significantly reduces the potential for error and confusion.
This direct assistance ensures travelers can confidently navigate through complex transit networks. In a smaller town with limited signage, iPhone Maps’ language support can provide the necessary landmarks and detailed directions. These features allow travelers to feel more confident and in control, enhancing their overall travel experience.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, changing your iPhone Maps language is a straightforward process that can significantly enhance your navigation experience. By understanding the various methods for changing languages, troubleshooting common issues, and considering the impact on accessibility and other settings, you can tailor your map interface to your specific needs. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, covering everything from basic steps to advanced configurations and considerations for international travel.
Remember to always back up your data before making significant changes.
FAQ Corner
Can I change the language of maps without losing my saved locations?
Yes, changing the language of your maps does not typically delete saved locations. However, certain app updates or issues might lead to data loss; backing up your data is always recommended.
How many languages are supported by Apple Maps?
The number of languages supported varies based on your region and device. Refer to the list of supported languages in the article for a detailed breakdown.
What if the app crashes when I try to change the language?
If the app crashes, try restarting the app, checking your internet connection, and ensuring you have sufficient storage space. If the problem persists, clear the app cache and data, and update the app if an update is available. If these steps don’t work, consider restarting your device.
Are there any accessibility features for users with visual impairments when using different languages?
Yes, VoiceOver and other accessibility features can be adapted to various languages supported by iPhone Maps. Refer to the accessibility section for more details.