How much does it cost to install an HVAC system? This question often arises when homeowners or businesses consider upgrading their heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. The answer, however, is not a straightforward one, as several factors influence the overall cost of HVAC installation.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of HVAC installation costs, exploring the variables that determine the financial implications of this home improvement project.
From the type of system selected to the complexity of the installation process, this guide provides a detailed analysis of the cost factors associated with HVAC installation. Whether you’re a homeowner planning a system upgrade or a contractor seeking to provide accurate cost estimates, this guide serves as an invaluable resource, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of HVAC installation costs.
Types of HVAC Systems
HVAC systems are an essential part of any modern building, providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. There are many different types of HVAC systems available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common type of HVAC system is the central forced-air system. This system uses a central furnace or heat pump to heat or cool the air, which is then distributed throughout the building by a system of ducts. Central forced-air systems are relatively efficient and can be used to heat and cool large buildings.
Another common type of HVAC system is the packaged system. This system combines the furnace, air conditioner, and ductwork into a single unit that is installed outside the building. Packaged systems are less efficient than central forced-air systems, but they are less expensive to install and maintain.
Split systems are another type of HVAC system that is becoming increasingly popular. Split systems use an outdoor unit to cool the air and an indoor unit to distribute the cool air throughout the building. Split systems are more efficient than central forced-air systems and packaged systems, but they are also more expensive to install and maintain.
Efficiency Ratings
The efficiency of an HVAC system is measured by its SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) or HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor). The higher the SEER or HSPF, the more efficient the system. SEER ratings range from 13 to 25, while HSPF ratings range from 6 to 10.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of an HVAC system is determined by the type of refrigerant it uses. Refrigerants are chemicals that are used to cool the air. Some refrigerants, such as R-22, are harmful to the environment. Other refrigerants, such as R-410A, are more environmentally friendly.
Maintenance Requirements
HVAC systems require regular maintenance to keep them operating efficiently. Maintenance tasks include changing the air filter, cleaning the coils, and checking the refrigerant levels.
Cost Considerations
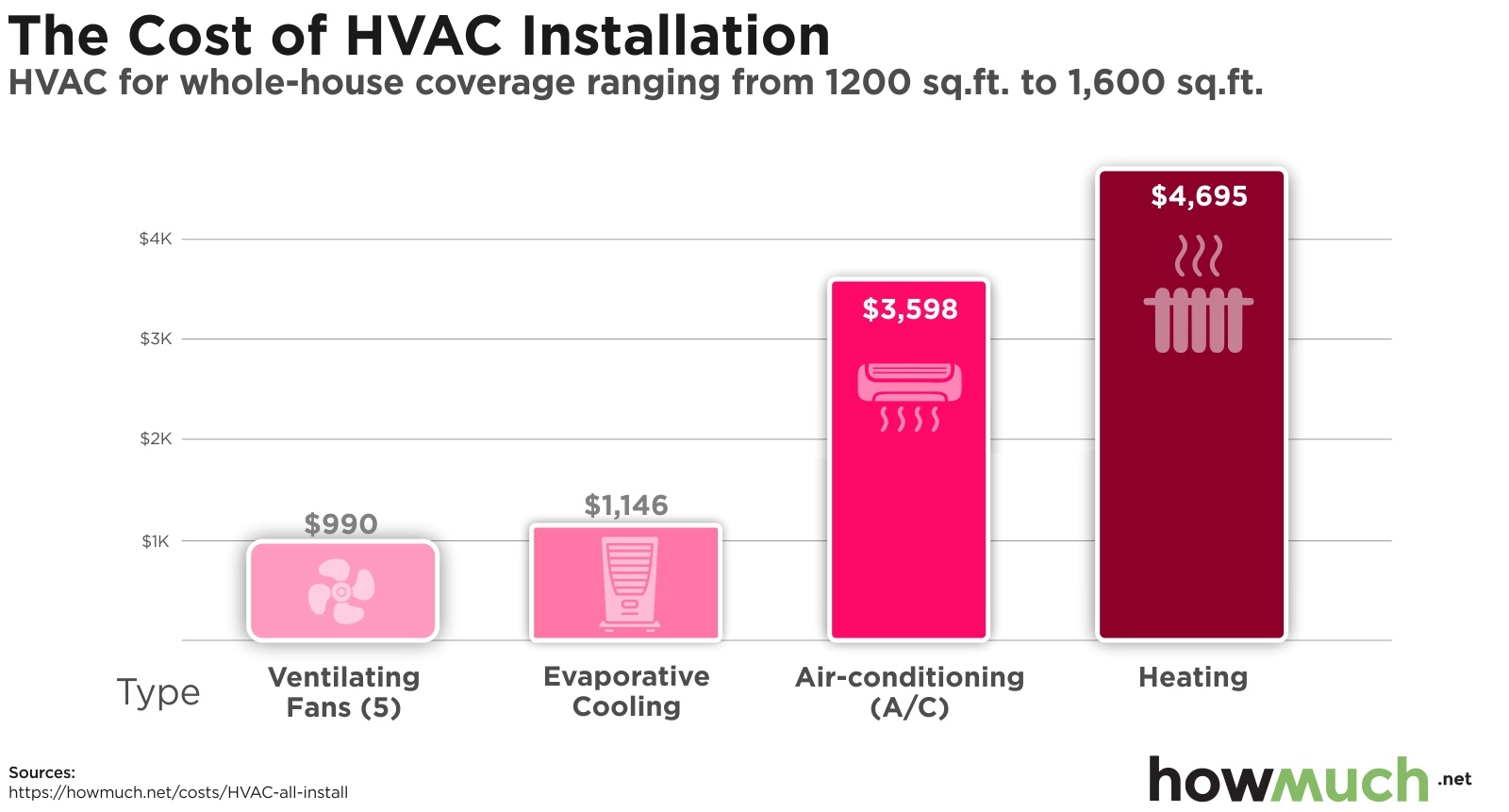
The cost of an HVAC system varies depending on the type of system, the size of the building, and the climate. Central forced-air systems are typically the most expensive to install, while packaged systems are the least expensive. Split systems fall somewhere in between.
Factors Affecting Installation Cost

The cost of installing an HVAC system can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the size of the home or building, the complexity of the ductwork, and the location of the HVAC unit.
Size of the Home or Building
The size of the home or building is a major factor that affects the cost of HVAC installation. Larger homes require larger HVAC systems, which are more expensive to purchase and install. The square footage of the home, as well as the number of rooms and stories, will all affect the size and cost of the HVAC system required.
Complexity of the Ductwork
The complexity of the ductwork is another factor that can affect the cost of HVAC installation. Homes with complex ductwork, such as those with multiple stories or multiple zones, will require more time and materials to install, which can increase the cost.
The length of the ductwork, as well as the number of bends and turns, will also affect the complexity and cost of the installation.
Location of the HVAC Unit
The location of the HVAC unit can also affect the cost of installation. Units that are located in difficult-to-reach areas, such as on a roof or in a crawl space, will require more time and effort to install, which can increase the cost.
The distance between the unit and the ductwork will also affect the cost of installation.
Labor Costs: How Much Does It Cost To Install An HVAC System?
The labor costs for HVAC installation can vary depending on the type of system, the complexity of the installation, the size of the home, and the location. It is important to hire a qualified contractor to ensure a proper and safe installation.
Range of Labor Costs
The following table provides a range of labor costs for HVAC installation, broken down by type of system:
- Central Air: $2,000-$5,000
- Heat Pump: $3,000-$6,000
- Ductless Mini-Split: $1,500-$3,000
Factors Affecting Labor Costs
The following factors can affect labor costs for HVAC installation:
- Complexity of the installation
- Size of the home
- Location
- Time of year
- Availability of contractors
Importance of Hiring a Qualified Contractor
It is important to hire a qualified contractor for HVAC installation to ensure a proper and safe installation. A qualified contractor will have the experience, licensing, and insurance to ensure that the installation is done correctly.
Tips for Finding a Reputable Contractor
The following tips can help you find a reputable contractor for HVAC installation:
- Get referrals from friends or family
- Check online reviews
- Verify their license and insurance
- Get multiple quotes
Equipment Costs
The cost of HVAC equipment varies depending on the size and type of system, as well as the brand and installation costs.
The cost of installing an HVAC system can vary greatly depending on the size and complexity of the system, as well as the location and availability of qualified contractors. For more information on cybersecurity, refer to What are the best cyber security blogs to read.
To obtain a more accurate estimate for your specific needs, it is recommended to consult with a local HVAC contractor.
Major Equipment Components
The major equipment components of an HVAC system include:
Air handler
The air handler is the indoor unit that circulates air throughout the home.
Condenser
The condenser is the outdoor unit that releases heat from the refrigerant.
Evaporator coil
The evaporator coil is the indoor unit that absorbs heat from the air.
Compressor
The compressor is the component that circulates the refrigerant through the system.
Equipment Costs
The cost of HVAC equipment can range from $2,000 to $10,000, depending on the size and type of system. Split systems are the most common type of HVAC system, and they typically cost between $2,000 and $4,000. Packaged systems are more compact than split systems, and they typically cost between $3,000 and $5,000.
Geothermal systems are the most energy-efficient type of HVAC system, and they typically cost between $5,000 and $10,000.
Factors Affecting Equipment Costs
The factors that affect equipment costs include:
System size
The larger the system, the more it will cost.
System type
Split systems are the most common and least expensive type of HVAC system. Packaged systems are more compact and more expensive than split systems. Geothermal systems are the most energy-efficient and most expensive type of HVAC system.
Brand
The brand of the HVAC equipment can also affect the cost. Some brands are more expensive than others.
Installation costs
The cost of installing an HVAC system can also vary depending on the complexity of the installation.
“The cost of HVAC equipment can vary significantly depending on the size, type, and brand of the system, as well as the complexity of the installation.”
HVAC Contractor
Permits and Inspections
Obtaining the necessary permits and inspections is crucial for HVAC installations to ensure compliance with building codes, safety regulations, and environmental standards. Failure to acquire proper permits can result in fines, delays, or even the rejection of the installation.
Types of Permits Required, How much does it cost to install an HVAC system?
The specific permits required for an HVAC installation vary depending on the municipality and the scope of the project. Generally, permits may include:
Building Permit
Required for any structural modifications or alterations to the building.
Electrical Permit
Needed for electrical wiring and connections associated with the HVAC system.
Mechanical Permit
Covers the installation and inspection of the HVAC equipment itself.
Gas Permit
Required if the HVAC system uses natural gas or propane as a fuel source.
Cost of Permits and Inspections
The cost of permits and inspections varies widely depending on the location and the complexity of the project. Typically, permit fees range from $100 to $500 per permit. Inspection fees are usually charged separately and can add another $100 to $200 per inspection.
Importance of Obtaining Proper Permits
Obtaining proper permits and inspections offers several benefits:
Ensures Compliance
Permits verify that the HVAC installation meets all applicable codes and regulations.
Protects Safety
Inspections identify potential hazards and ensure the system is installed safely and operates efficiently.
Increases Property Value
A properly permitted and inspected HVAC system can enhance the value of the property.
Avoids Legal Issues
Failure to obtain proper permits can lead to legal consequences, such as fines or even criminal charges.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in determining the installation cost and long-term expenses associated with an HVAC system. Energy-efficient systems typically have higher upfront costs due to advanced technologies and components designed to minimize energy consumption. However, these systems offer substantial savings over time by reducing energy bills.
The cost of installing an HVAC system varies depending on the size of the home, the type of system installed, and the labor costs in the area. To get a more accurate estimate, it’s best to contact a local HVAC contractor.
For instance, the Samsung Xpress M2022W Easy Printer Manager is a popular choice for small businesses and home offices. It offers a range of features, including wireless printing, mobile printing, and automatic duplex printing. Returning to our original topic, the cost of installing an HVAC system can be a significant investment, but it can also save money on energy bills in the long run.
Long-Term Savings
Energy-efficient HVAC systems can significantly reduce energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills. These savings can offset the higher installation costs over the lifespan of the system. The payback period, the time it takes for the energy savings to cover the initial investment, can vary depending on factors such as energy rates, system efficiency, and usage patterns.
Energy-Efficient Technologies
Several energy-efficient HVAC technologies can help reduce energy consumption and operating costs. These include:
Variable-speed compressors
Adjust compressor speed to match cooling or heating demand, reducing energy waste.
High-efficiency air filters
Trap more dust and allergens, improving air quality and reducing strain on the system.
Programmable thermostats
Allow users to set different temperatures for different times of day, saving energy when the home is unoccupied.
Zoning systems
Divide the home into separate zones, allowing for targeted cooling or heating only in occupied areas.
Heat pumps
Provide both heating and cooling, using a reversible refrigeration cycle to transfer heat from one area to another.By incorporating these energy-efficient technologies, homeowners can minimize energy consumption, reduce operating costs, and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19521285/air_handler.jpg)
Maintenance and repair costs for HVAC systems can vary widely depending on the type of system, its age, and the frequency of use. On average, homeowners can expect to pay between $100 and $500 per year for routine maintenance, such as cleaning and tune-ups.
Major repairs, such as replacing a compressor or blower motor, can cost several thousand dollars.Factors that affect maintenance and repair costs include:
- Type of HVAC system: Central air conditioners and heat pumps are generally more expensive to maintain and repair than window units or portable units.
- Age of the system: Older systems are more likely to require repairs.
- Frequency of use: Systems that are used more frequently are more likely to wear out and require repairs.
- Location: The cost of labor and parts can vary depending on the location of the home.
Regular maintenance is important to keep HVAC systems running efficiently and to prevent costly repairs. Maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning the air filter
- Lubricating moving parts
- Inspecting the electrical connections
- Checking the refrigerant levels
By performing regular maintenance, homeowners can extend the life of their HVAC system and save money on repairs in the long run.
DIY Installation vs. Professional Installation
HVAC systems are complex and require specialized knowledge and skills to install properly. While DIY installation may seem like a cost-effective option, it can lead to significant risks and challenges.
Costs and Benefits of DIY Installation
DIY installation can potentially save on labor costs, but it requires the purchase of tools and materials, which can add up. It also requires significant time and effort, and any mistakes made during installation can result in costly repairs.
Risks and Challenges of DIY Installation
- Improper Installation:DIY installers may not have the necessary expertise to ensure proper installation, leading to inefficiencies, reduced performance, and potential safety hazards.
- Voiding Warranties:Attempting DIY installation may void manufacturer warranties, leaving homeowners responsible for any repairs or replacements.
- Electrical Hazards:HVAC systems involve electrical connections, which can be dangerous if not handled by a qualified electrician.
- Refrigerant Handling:Refrigerants used in HVAC systems are hazardous and require proper handling and disposal, which may not be feasible for DIY installers.
Advantages of Hiring a Professional Installer
- Expertise and Experience:Professional installers have the knowledge and experience to ensure proper installation, maximizing system efficiency and lifespan.
- Warranty Protection:Hiring a licensed installer typically preserves manufacturer warranties, providing peace of mind and financial protection.
- Safety Compliance:Professionals adhere to industry standards and building codes, ensuring the safe and compliant operation of the HVAC system.
- Time and Convenience:Hiring a professional installer saves time and effort, allowing homeowners to focus on other priorities.
Regional Differences in Installation Costs

The cost of installing an HVAC system can vary significantly depending on the region in which the installation takes place. This is due to a number of factors, including the cost of labor, the availability of materials, and the local building codes.
In general, HVAC installation costs are higher in urban areas than in rural areas. This is because labor costs are typically higher in urban areas, and because the cost of materials is often higher due to the increased demand. Additionally, local building codes can also impact the cost of installation, as some codes require the use of more expensive materials or more complex installation methods.
Cost Variations Across Different Regions
The following table provides a summary of the cost variations across different regions of the United States:| Region | Average Installation Cost ||—|—|| Northeast | $6,000
$10,000 |
| Midwest | $5,000
$9,000 |
| South | $4,000
$8,000 |
| West | $5,500
$9,500 |
Factors Contributing to Regional Cost Variations
The following are some of the factors that contribute to regional cost variations in HVAC installation:* Cost of labor:Labor costs can vary significantly from one region to another. In general, labor costs are higher in urban areas than in rural areas.
Availability of materials
The availability of materials can also impact the cost of installation. In some regions, certain materials may be more difficult to obtain, which can lead to higher prices.
Local building codes
Local building codes can also impact the cost of installation. Some codes require the use of more expensive materials or more complex installation methods, which can lead to higher costs.
Impact on Overall Cost
The regional differences in HVAC installation costs can have a significant impact on the overall cost of the project. For example, a homeowner in the Northeast can expect to pay more for HVAC installation than a homeowner in the South.
This is because labor costs and material costs are typically higher in the Northeast.
Financing Options
HVAC system installation can be a significant expense, and financing options can help make it more manageable. There are several financing options available, each with its own pros and cons.
Loans
Loans are a common financing option for HVAC installations. They typically have fixed interest rates and predictable monthly payments. However, loans may require a down payment and may have prepayment penalties.
Leases
Leases offer lower monthly payments than loans, and they do not require a down payment. However, leases may not allow you to own the equipment at the end of the lease term, and they may have mileage restrictions.
Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs)
HELOCs are secured by your home, and they typically have low interest rates and tax-deductible interest. However, HELOCs may have variable interest rates, and they can be risky if your home value declines.
Credit Cards
Credit cards are a convenient financing option, and they may offer rewards or cash back. However, credit cards typically have high interest rates, and they may have balance transfer fees.The best financing option for you will depend on your individual needs and circumstances.
If you have good credit and can afford a down payment, a loan may be a good option. If you have a lower credit score or cannot afford a down payment, a lease or HELOC may be a better choice.Here are some examples of financing programs available for HVAC installations:
- The Home Depot offers a 10% discount on HVAC installations for military members and veterans.
- Wells Fargo offers a 0% APR for 12 months on HVAC loans.
- GreenSky offers a variety of financing options for HVAC installations, including loans, leases, and HELOCs.
When negotiating financing terms, it is important to compare interest rates, fees, and payment terms from multiple lenders. You should also read the loan agreement carefully before signing.
Tax Incentives and Rebates
Energy-efficient HVAC systems can qualify for various tax incentives and rebates, reducing the overall installation cost. These incentives encourage homeowners to invest in sustainable heating and cooling solutions, leading to energy savings and environmental benefits.
To qualify for these incentives, homeowners typically need to meet specific criteria, such as installing an HVAC system that meets certain energy efficiency standards or using a qualified contractor. It’s essential to check with local and federal authorities for the latest information on available incentives and eligibility requirements.
Federal Tax Incentives
- Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Tax Credit (EIHITC):This credit provides a tax deduction of up to $500 for the installation of qualifying energy-efficient HVAC systems.
- Residential Energy Efficient Property Tax Credit (REPTC):This credit offers a tax deduction of up to $2,000 for the installation of qualifying geothermal heat pumps.
State and Local Rebates
Many states and local governments offer rebates for the installation of energy-efficient HVAC systems. These rebates vary widely, so it’s important to check with local utility companies and government agencies for specific details.
By taking advantage of available tax incentives and rebates, homeowners can significantly reduce the upfront cost of installing an energy-efficient HVAC system, making it a more affordable and sustainable investment.
Return on Investment
Installing an HVAC system can be a significant investment, but it can also provide substantial long-term savings. The potential return on investment (ROI) for HVAC installation varies depending on several factors, including the type of system installed, the size of the home, and the local climate.
However, in many cases, HVAC installation can save homeowners money on their energy bills, increase the comfort of their homes, and even improve their health.
Factors Affecting ROI
The following factors can affect the ROI of HVAC installation:
- Type of HVAC system: The type of HVAC system installed will have a significant impact on the ROI. More efficient systems, such as heat pumps and geothermal systems, will have a higher upfront cost but will also provide greater long-term savings.
- Size of the home: The size of the home will also affect the ROI of HVAC installation. Larger homes will require a larger HVAC system, which will have a higher upfront cost. However, the larger system will also provide greater savings in the long run.
- Local climate: The local climate will also affect the ROI of HVAC installation. In areas with extreme temperatures, an HVAC system will be more necessary and will provide greater savings.
Examples of Long-Term Savings
HVAC installation can save homeowners money in the long run in several ways, including:
- Reduced energy bills: An efficient HVAC system can reduce energy bills by up to 50%. This is because efficient systems use less energy to heat and cool the home.
- Increased comfort: An HVAC system can make a home more comfortable by providing consistent temperatures throughout the year. This can improve sleep, reduce stress, and increase productivity.
- Improved health: An HVAC system can improve health by reducing indoor air pollution and allergens. This can help to prevent respiratory problems, allergies, and other health issues.
Cost Savings Table
The following table summarizes the potential cost savings of HVAC installation over time:
| Year | Savings |
|---|---|
| 1 | $500 |
| 2 | $1,000 |
| 3 | $1,500 |
| 4 | $2,000 |
| 5 | $2,500 |
“When considering whether or not to install an HVAC system, it is important to consider the long-term benefits. HVAC installation can save homeowners money on their energy bills, increase the comfort of their homes, and even improve their health. In many cases, the ROI of HVAC installation can be significant.”
Case Studies and Examples
To illustrate the complexities of HVAC installation costs, we present case studies and examples that showcase the impact of various factors on the overall expense.
New Construction
In new construction, HVAC installation costs can vary significantly depending on the size and complexity of the system. A single-family home with a basic system may cost around $5,000-$10,000, while a large commercial building with a complex system could exceed $1 million.
Retrofitting
Retrofitting an existing building with a new HVAC system typically involves higher costs than new construction due to the need for modifications to the building structure and existing ductwork. The cost of retrofitting can range from $10,000-$25,000 for a small residential property to hundreds of thousands of dollars for a large commercial building.
Commercial and Residential Properties
Commercial HVAC systems are generally more expensive to install than residential systems due to their larger size and more complex requirements. The cost of a commercial HVAC system can range from $50,000-$200,000, while a residential system typically costs between $5,000-$15,000.
Lessons Learned
These case studies highlight the importance of considering all relevant factors when estimating HVAC installation costs. By understanding the impact of system size, equipment type, labor costs, and other factors, homeowners and businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their HVAC investment.
Best Practices for Cost-Effective Installation
- Plan the system design carefully to minimize the need for modifications to the building structure or existing ductwork.
- Choose energy-efficient equipment to reduce operating costs over time.
- Consider DIY installation for small, simple systems to save on labor costs.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Underestimating the cost of the system and associated labor.
- Selecting equipment that is too large or too small for the space.
- Not obtaining proper permits and inspections, which can lead to fines or delays.
Infographics and Visuals
Infographics and visuals play a crucial role in simplifying complex information and making it easily understandable for users. In the context of HVAC installation costs, these tools can effectively illustrate key factors and provide a comprehensive overview of the topic.
To enhance the user experience and comprehension, it is essential to create visually appealing and informative infographics and visuals that cater to the specific needs of the audience.
Key Factors Affecting HVAC Installation Costs
- System size: The size of the HVAC system, measured in tons or British Thermal Units (BTUs), directly impacts the cost of installation. Larger systems require more materials, labor, and time to install.
- Efficiency rating: The efficiency rating of the HVAC system, measured by the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) or Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE), affects the installation cost. Higher efficiency systems typically cost more to install but offer lower operating costs over time.
- Labor costs: Labor costs vary depending on the location, availability of skilled technicians, and the complexity of the installation. Unionized labor or specialized installations may result in higher labor costs.
- Permit fees: Permits and inspections are often required for HVAC installations. The cost of permits and inspections can vary depending on the local jurisdiction and the scope of the project.
Components of an HVAC System
- Condenser: The condenser is the outdoor unit that releases heat from the refrigerant.
- Evaporator: The evaporator is the indoor unit that absorbs heat from the air.
- Ductwork: Ductwork distributes conditioned air throughout the building.
- Thermostat: The thermostat controls the temperature of the building by sending signals to the HVAC system.
Interactive Charts
Interactive charts allow users to estimate installation costs based on their specific needs and location. These charts can be customized to include factors such as system size, efficiency rating, labor costs, and permit fees.
Glossary of Terms
A glossary of terms provides definitions of technical terms related to HVAC systems. This helps users understand the concepts and components involved in the installation process.
Visual Appeal and User-Friendliness
High-quality images, graphics, animations, and videos can make infographics and visuals more visually appealing and easier to understand. By using clear and concise language, these tools can effectively convey complex information to users.
Frequently Asked Questions
Installing an HVAC system can involve significant expenses, and it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the potential costs involved. This section compiles a list of frequently asked questions related to HVAC installation costs, providing detailed answers to guide homeowners in making informed decisions.
The questions are categorized into relevant s, making it easy for readers to find the information they need.
General Questions
- What factors influence the cost of HVAC installation?
- How much does it typically cost to install an HVAC system?
- What are the differences in costs between different types of HVAC systems?
- How can I reduce the cost of HVAC installation?
- Is it possible to install an HVAC system myself?
Cost Breakdown
- What are the main components of HVAC installation costs?
- How much do labor costs contribute to the total installation cost?
- What are the typical equipment costs for different types of HVAC systems?
- Are there additional costs for permits and inspections?
- How does energy efficiency affect the cost of installation?
Maintenance and Long-Term Costs
- What are the ongoing maintenance and repair costs associated with HVAC systems?
- How can I extend the lifespan of my HVAC system and reduce maintenance costs?
- What are the potential benefits of investing in a high-efficiency HVAC system?
Financing and Incentives
- What financing options are available for HVAC installation?
- Are there any tax incentives or rebates for installing energy-efficient HVAC systems?
- How can I calculate the potential return on investment for an HVAC installation?
Regional Considerations
- How do regional differences affect HVAC installation costs?
- What are the average HVAC installation costs in different regions of the country?
Common Queries
What are the major factors that affect HVAC installation costs?
The size of the home or building, the complexity of the ductwork, the location of the HVAC unit, labor costs, equipment costs, permits and inspections, energy efficiency considerations, and regional differences all significantly impact HVAC installation costs.
How can I save money on HVAC installation costs?
Consider energy-efficient systems, compare quotes from multiple contractors, negotiate the best financing terms, and take advantage of tax incentives and rebates to reduce the overall cost of HVAC installation.
What are the benefits of hiring a qualified HVAC contractor?
Hiring a qualified HVAC contractor ensures a proper and safe installation, provides peace of mind and warranty protection, and can help avoid costly repairs down the road.
How can I estimate the cost of HVAC installation for my home?
Contact local HVAC contractors for quotes, use online cost calculators, or refer to industry averages for different system types and sizes. Keep in mind that the actual cost may vary depending on specific factors related to your property and installation requirements.
What is the average lifespan of an HVAC system?
The average lifespan of an HVAC system typically ranges from 10 to 15 years, depending on the type of system, maintenance practices, and usage patterns.