How long does it take to learn portuguese – Embarking on the journey of learning Portuguese, one of the most intriguing questions that arises is “How long will it take?” This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Portuguese language acquisition, providing insights into the factors that influence the learning timeline and the various proficiency levels one can achieve.
Unveiling the secrets of Portuguese fluency, this guide will explore the impact of individual learning styles, prior language proficiency, and the power of immersion. We will delve into the different proficiency levels, from beginner to advanced, and provide realistic estimates of the time required to reach each milestone.
Factors Influencing Learning Duration

The time it takes to learn Portuguese varies significantly based on various factors, including individual learning styles, prior language proficiency, and the level of immersion and language exposure.
Individual Learning Styles
Different individuals have unique learning preferences and approaches. Some may excel in visual learning, relying on written materials and visual aids. Others may prefer auditory learning, benefiting from listening to native speakers and practicing pronunciation. Identifying your dominant learning style can help you optimize your study methods and accelerate progress.
Prior Language Proficiency
Prior knowledge of other languages, particularly Romance languages like Spanish, Italian, or French, can significantly reduce the learning time for Portuguese. Shared vocabulary, grammar structures, and pronunciation similarities make it easier for learners with such a background to grasp Portuguese concepts.
Immersion and Language Exposure
Immersion in the Portuguese language and culture plays a crucial role in accelerating learning. Surrounding yourself with native speakers, watching Portuguese movies and TV shows, and reading Portuguese literature can significantly enhance your proficiency. The more you expose yourself to the language, the faster you will develop fluency.
Proficiency Levels and Timeframes

Attaining proficiency in Portuguese, like any other language, is a gradual process that involves developing various skills, including speaking, listening, reading, and writing. Depending on the individual’s learning style, commitment, and exposure to the language, the time required to reach different levels of proficiency can vary.
Generally, language proficiency is divided into several levels, each with its own set of characteristics and approximate timeframes for attainment:
Beginner Level
At the beginner level, learners develop a basic understanding of Portuguese grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. They can engage in simple conversations, ask and answer basic questions, and understand short texts. Reaching this level typically requires around 100-200 hours of study.
Intermediate Level
Intermediate learners can communicate more effectively in Portuguese. They can express themselves more clearly, engage in conversations on a wider range of topics, and understand more complex texts. Achieving this level generally takes around 300-600 hours of study.
Advanced Level
Advanced learners possess a high level of fluency in Portuguese. They can express themselves with ease and accuracy, understand complex texts, and engage in nuanced conversations. Reaching this level typically requires around 800-1200 hours of study or more, depending on the individual’s goals and commitment.
It’s important to note that these timeframes are estimates and can vary depending on several factors, such as the learner’s native language, learning methods, and frequency of practice.
Case studies of individuals who have achieved fluency within specific timeframes provide valuable insights into the possible pace of progress:
- Example 1: A native English speaker with a strong foundation in Spanish learned Portuguese to an intermediate level within 6 months of consistent study.
- Example 2: A student with no prior exposure to Portuguese became fluent within 2 years of intensive language immersion and regular practice.
Learning Methods and Resources

Choosing the right learning method and resources can significantly impact your progress. Here’s a comparison of different methods and a comprehensive list of resources to help you learn Portuguese:
Self-Study
Self-study is a flexible and cost-effective option. It allows you to learn at your own pace and focus on areas that interest you. However, it requires discipline and motivation.
- Benefits:Flexibility, affordability, self-paced.
- Drawbacks:Lack of accountability, need for self-motivation.
Classes
Classes provide a structured learning environment with regular feedback and support from a teacher. They are ideal for beginners who need guidance and accountability.
- Benefits:Structured curriculum, feedback, accountability.
- Drawbacks:Cost, limited flexibility, may not align with your learning style.
Online Courses
Online courses offer a blend of self-study and structured learning. They provide interactive lessons, videos, and exercises, often with the option for live classes and teacher support.
- Benefits:Flexibility, convenience, access to expert instructors.
- Drawbacks:Can be less immersive than in-person classes, may lack accountability.
Resources for Learning Portuguese
Here’s a comprehensive list of resources to support your Portuguese learning journey:
Apps
- Duolingo:Gamified app for beginners.
- Babbel:Subscription-based app with interactive lessons.
- Memrise:App focused on vocabulary building.
Textbooks
- Practice Makes Perfect: Complete Portuguese Grammar:Comprehensive grammar reference.
- Portuguese in 10 Minutes a Day:Step-by-step guide for beginners.
- FSI Portuguese Basic Course:Free online textbook from the U.S. Foreign Service Institute.
Websites
- Forvo:Pronunciation dictionary with recordings from native speakers.
- Conjugação:Conjugation tool for Portuguese verbs.
- PortuguesePod101:Free online lessons, podcasts, and grammar explanations.
Personal Commitment and Motivation
Personal commitment and motivation are the driving forces behind successful language learning. Consistent practice, dedication, and a strong intrinsic interest can significantly influence the pace of learning and overall proficiency.
Staying motivated is crucial for overcoming challenges and achieving fluency. Setting realistic goals, finding a learning method that aligns with your preferences, and engaging in activities that spark your interest can help maintain motivation.
Strategies for Staying Motivated
- Set Achievable Goals:Break down language learning into smaller, manageable chunks to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Find a Learning Method You Enjoy:Explore different methods (e.g., apps, classes, immersion) and choose the one that best suits your learning style.
- Engage in Interesting Activities:Incorporate activities that align with your interests, such as watching movies, reading books, or listening to music in the target language.
- Celebrate Successes:Acknowledge and reward your progress, no matter how small, to stay motivated.
- Find a Language Partner or Group:Engage with others learning the same language for support and encouragement.
Language Context and Immersion
Immersion in a Portuguese-speaking environment is an invaluable asset for language learning. Surrounding yourself with the language in its natural context allows for unparalleled exposure and practice.
Cultural immersion not only enhances comprehension and fluency but also fosters a deeper understanding of the language’s nuances and cultural context. This includes experiencing local customs, traditions, and social interactions, which provide insights into the language’s usage and meaning.
Tips for Creating an Immersive Learning Experience Outside of a Portuguese-Speaking Country
- Watch Portuguese movies and TV shows with subtitles initially, then gradually transition to watching without subtitles.
- Listen to Portuguese music and podcasts, paying attention to the lyrics and pronunciations.
- Read Portuguese books, newspapers, and online articles to expand your vocabulary and grammar knowledge.
- Attend Portuguese cultural events, such as festivals, meetups, or language exchange gatherings, to connect with native speakers and immerse yourself in the culture.
li>Engage in online language exchange platforms or find a Portuguese language partner to practice speaking and listening.
Language Complexity and Similarities

Portuguese is generally considered a moderately difficult language for native English speakers to learn, but the level of difficulty can vary depending on factors such as individual aptitude, motivation, and the learner’s native language.Compared to English, Portuguese grammar is more complex, with a wider range of verb tenses, moods, and conjugations.
Portuguese vocabulary also has some unique features, such as the use of gendered nouns and a large number of false cognates (words that look similar to English words but have different meanings).However, Portuguese also shares many similarities with other Romance languages, such as Spanish, French, and Italian.
This can make learning Portuguese easier for speakers of these languages, as they can often draw on their existing knowledge of grammar and vocabulary.
Areas of Difficulty
Some of the areas where Portuguese grammar and vocabulary may pose challenges for learners include:
- The use of subjunctive mood, which is used to express uncertainty, possibility, or emotion.
- The use of personal infinitive, which is a verb form that functions as a noun.
- The use of gendered nouns, which means that every noun has a masculine or feminine gender.
- The use of false cognates, which are words that look similar to English words but have different meanings.
Similarities to Other Romance Languages
Some of the similarities between Portuguese and other Romance languages that can facilitate learning include:
- The use of similar grammar structures, such as subject-verb-object word order and the use of prepositions.
- The use of many cognates, which are words that have the same or similar meaning and spelling in multiple languages.
- The use of similar pronunciation rules, such as the use of nasal vowels and the stress on the penultimate syllable.
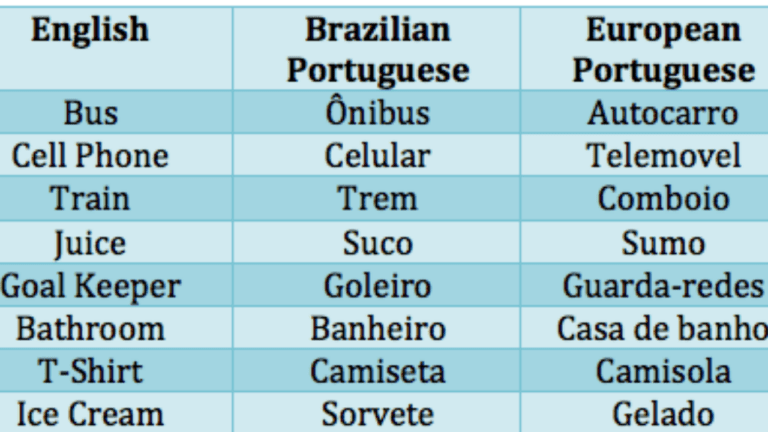
Dialects and Variations

The Portuguese language is spoken in a wide range of countries and regions worldwide, which has led to the development of various dialects and variations. These dialects can differ in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and even grammar.
Implications for Learners
Dialectal differences can have implications for learners of Portuguese. For instance, a learner who is focusing on the Brazilian dialect may encounter different pronunciation and vocabulary than a learner who is focusing on the European dialect. This can make it important for learners to be aware of the different dialects and to choose one to focus on.
Choosing a Dialect
When choosing a dialect to focus on, there are a few factors to consider. One factor is the learner’s goals. If the learner plans to travel to a specific country or region, it may be helpful to focus on the dialect spoken in that area.
Another factor to consider is the availability of resources. Some dialects may have more resources available than others, such as textbooks, dictionaries, and online materials.
Cultural Considerations

Understanding Portuguese culture is crucial for enhancing language proficiency. Cultural context heavily influences language usage and communication styles. Integrating cultural learning into the language learning process is essential.
Tips for Integrating Cultural Learning, How long does it take to learn portuguese
Immerse yourself in Portuguese media
movies, TV shows, music, and literature provide insights into cultural nuances and colloquialisms.
Engage with native speakers
Interacting with Portuguese speakers offers firsthand experience with cultural norms and communication patterns.
Attend cultural events
Participating in festivals, celebrations, and gatherings exposes you to Portuguese traditions and social interactions.
Study Portuguese history and geography
Understanding the historical and geographical context of the language enriches your comprehension of cultural references and idioms.
Q&A: How Long Does It Take To Learn Portuguese
How many hours does it take to learn Portuguese?
The number of hours required to learn Portuguese varies depending on factors such as learning style, prior language knowledge, and immersion level. On average, reaching basic proficiency may take around 240 hours of study, while achieving fluency can require up to 1,000 hours or more.
Is Portuguese easy to learn for English speakers?
For native English speakers, Portuguese is generally considered to be a moderately difficult language to learn. While it shares some similarities with English, there are also significant differences in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
What is the best way to learn Portuguese quickly?
Immersion is the most effective way to accelerate Portuguese learning. This involves surrounding yourself with the language through activities such as watching Portuguese movies, listening to music, reading books, and interacting with native speakers.