How hard is sql to learn – In the realm of data manipulation and analysis, SQL (Structured Query Language) stands as a formidable force. But how arduous is the journey to SQL mastery? This article delves into the intricacies of SQL learning, unraveling the factors that shape its difficulty and guiding you through the optimal learning paths.
From the nuances of syntax to the intricacies of advanced features, we’ll illuminate the complexities of SQL while providing practical insights to empower your learning experience.
Difficulty Factors

Learning SQL’s difficulty depends on several factors, including prior knowledge, learning style, and the complexity of the tasks you want to perform. For beginners with no programming or data analysis experience, grasping SQL concepts may require more effort. However, those with a background in these fields often find the transition smoother.
Prior Programming Knowledge
Prior programming knowledge can be an advantage when learning SQL. Familiarity with concepts like data structures, variables, and control flow can make understanding SQL syntax and logic easier. However, even without prior programming experience, it’s possible to learn SQL with a bit more effort and practice.
Data Analysis Experience
Experience in data analysis can also aid in learning SQL. Understanding data modeling, data manipulation, and query optimization can provide a foundation for grasping SQL concepts. However, it’s not a prerequisite; those without data analysis experience can still learn SQL effectively with a dedicated approach.
Learning Methods: How Hard Is Sql To Learn
Delving into the realm of SQL mastery can be navigated through a plethora of learning avenues. Each method boasts its own distinct advantages and drawbacks, catering to diverse learning preferences and styles.
Let’s embark on an exploration of the most prevalent learning methods, dissecting their merits and shortcomings to guide you in selecting the optimal path for your SQL enlightenment.
Online Courses
Online courses offer a structured and guided approach to SQL learning, often featuring interactive exercises, quizzes, and assignments. Their flexibility allows you to learn at your own pace, fitting study sessions into your busy schedule.
- Pros:
- Structured curriculum with clear learning objectives
- Interactive exercises and quizzes for hands-on practice
- Flexibility to learn at your own pace
- Cons:
- Can be more expensive than other methods
- May lack the personalized feedback of in-person instruction
- Requires self-discipline and motivation to stay on track
Books
Books provide a comprehensive and in-depth exploration of SQL concepts, often delving into advanced topics. They offer a self-paced learning experience, allowing you to revisit and reinforce concepts at your convenience.
- Pros:
- Comprehensive coverage of SQL topics
- Can be used as a reference guide for future use
- More affordable than online courses
- Cons:
- Can be overwhelming for beginners
- Lack interactive exercises and hands-on practice
- May not provide personalized feedback or support
Bootcamps
Bootcamps offer an intensive and immersive learning experience, typically spanning a few weeks or months. They provide hands-on training, mentorship, and project-based learning, preparing you for real-world SQL applications.
- Pros:
- Intensive and focused learning experience
- Hands-on training and project-based learning
- Mentorship and support from experienced instructors
- Cons:
- Can be expensive and time-consuming
- May not be suitable for all learning styles
- May require a significant time commitment
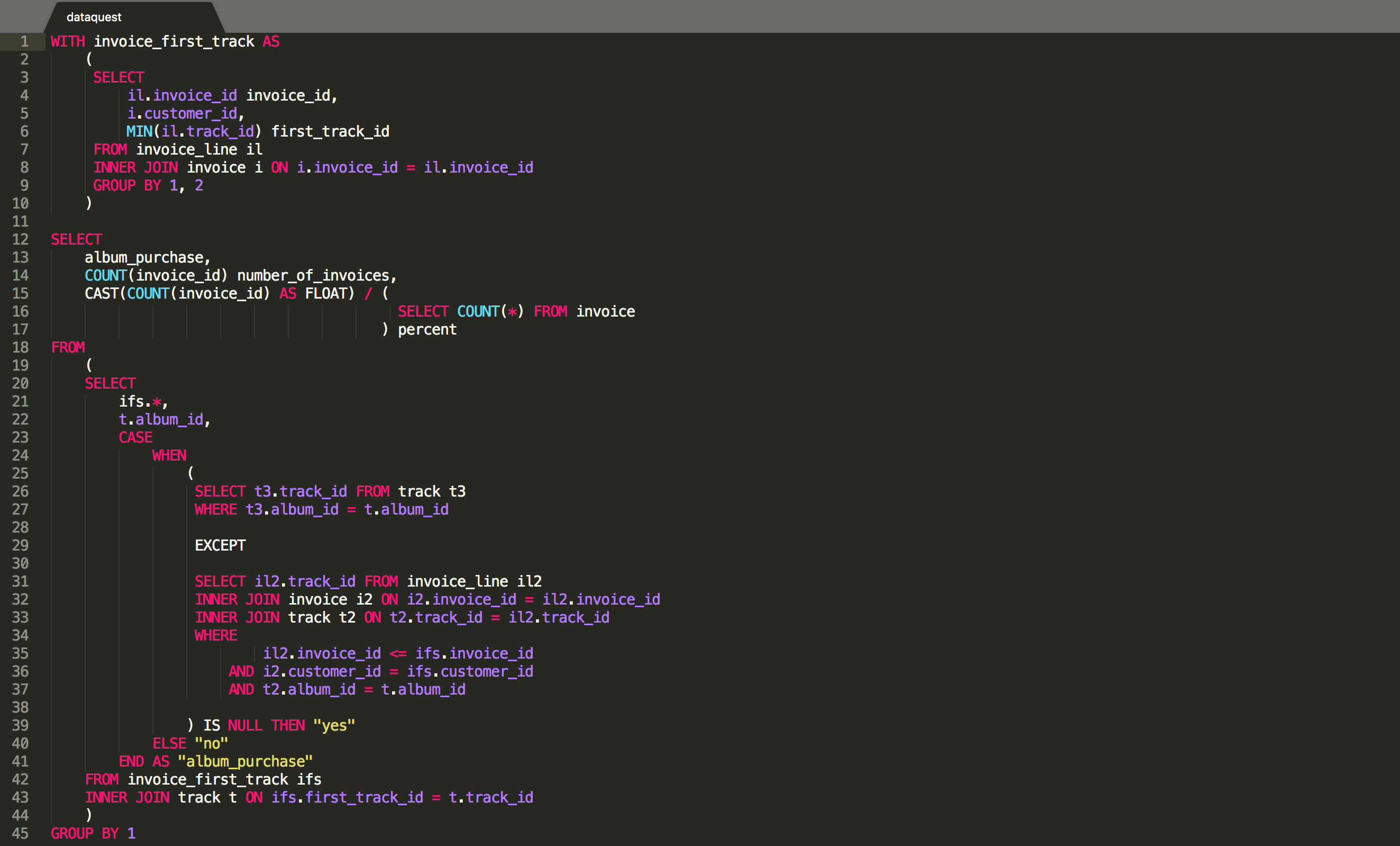
SQL Syntax and Concepts
SQL syntax is the set of rules that define how SQL statements are written. It includes the s, punctuation, and operators used in SQL. Understanding SQL syntax is essential for writing effective SQL queries.
Key concepts in SQL include:
- Data types: SQL supports a variety of data types, including numeric, character, and date types.
- Operators: SQL provides a range of operators for performing calculations, comparisons, and logical operations.
- Relational database concepts: SQL is designed to work with relational databases, which store data in tables with rows and columns. Understanding relational database concepts is essential for effective SQL usage.
Data Types
SQL supports a variety of data types, including:
- Numeric types: INTEGER, FLOAT, DECIMAL
- Character types: CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT
- Date types: DATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP
The choice of data type depends on the nature of the data being stored.
Operators
SQL provides a range of operators for performing calculations, comparisons, and logical operations. These include:
- Arithmetic operators: +, -, -, /, %
- Comparison operators: =, <>, <, >, <=, >=
- Logical operators: AND, OR, NOT
Operators are used to combine values and expressions to create more complex SQL statements.
Relational Database Concepts
SQL is designed to work with relational databases, which store data in tables with rows and columns. Each row represents a record, and each column represents a field. Tables are related to each other through foreign keys, which are columns that reference primary keys in other tables.
Understanding relational database concepts is essential for effective SQL usage. This includes understanding how to create and manage tables, how to establish relationships between tables, and how to use SQL to query and manipulate data in a relational database.
Practice and Projects

Practice is key to mastering SQL. Hands-on experience will help you solidify your understanding of concepts and improve your problem-solving abilities.
Beginners can start with small projects to apply their skills. These projects can range from simple data retrieval tasks to more complex data analysis and manipulation.
Beginner-Friendly Projects
- Create a database of your favorite books, including title, author, genre, and publication date.
- Query the database to find all books by a specific author or in a specific genre.
- Update the database to add new books or change information about existing books.
- Use SQL to generate reports on the number of books in each genre or the average publication date of books by a particular author.
Finding Practice Problems and Datasets
There are many resources available online for finding practice problems and datasets. Here are a few options:
- LeetCode: LeetCode offers a variety of SQL practice problems ranging from easy to difficult.
- HackerRank: HackerRank provides a collection of SQL challenges that can help you improve your skills.
- Kaggle: Kaggle hosts numerous datasets that you can use for practice. You can find datasets on a wide range of topics, from healthcare to finance.
Advanced SQL Features
Beyond the basics, SQL offers advanced features that unlock its full potential for data manipulation and analysis. These features include subqueries, joins, and window functions.
Subqueries, also known as nested queries, allow you to embed a query within another query. This enables you to perform complex operations, such as filtering data based on results from another query.
Joins, on the other hand, combine data from multiple tables based on common columns. This is essential for creating relationships between data sets and retrieving information across tables.
Window functions operate on a set of rows within a partition or frame. They allow you to perform calculations, such as ranking, moving averages, and cumulative sums, over a specific range of data.
Real-World Applications, How hard is sql to learn
- Subqueries: Used in data validation, filtering results based on specific criteria, and aggregating data from multiple sources.
- Joins: Essential for creating reports, analyzing customer data, and combining information from different databases.
- Window functions: Useful for ranking products, calculating moving averages in time series analysis, and finding cumulative sales over time.
Career Prospects

SQL skills open doors to various career opportunities in industries that rely on data analysis and management. These include:
-*IT and Software
Database administrators, data analysts, software engineers
-*Finance
Financial analysts, risk analysts, investment managers
-*Healthcare
Data scientists, healthcare analysts, medical researchers
-*Retail and E-commerce
Market analysts, business intelligence analysts, product managers
-*Manufacturing
Supply chain analysts, production planners, quality control engineers
Salary Expectations and Career Growth
SQL proficiency can significantly boost salary expectations. According to Glassdoor, the average annual salary for SQL developers in the United States is around $95,000. With experience and advanced skills, individuals can progress to senior roles, such as database architects or data scientists, earning even higher salaries.
FAQ Overview
Is SQL essential for data analysis?
Yes, SQL is widely recognized as a fundamental tool for data analysis, enabling efficient data retrieval, manipulation, and aggregation.
Can beginners learn SQL quickly?
While the learning curve can vary, beginners with prior programming or data analysis experience may find it easier to grasp SQL concepts. With consistent practice and dedication, beginners can achieve proficiency within a reasonable timeframe.
What are the most challenging aspects of SQL?
Understanding complex joins, subqueries, and window functions can be particularly challenging. Additionally, mastering the nuances of data modeling and optimization techniques requires significant practice and experience.