E learning designer – E-Learning Designer, a title that carries the weight of transforming education and training landscapes. This role is not merely about creating digital courses; it’s about crafting engaging, effective learning experiences that empower individuals and organizations to reach their full potential.
The e-Learning Designer is a strategic architect, blending pedagogical principles, technological savvy, and a deep understanding of learner needs to build dynamic, interactive, and accessible learning environments. This field is not just about delivering content; it’s about fostering meaningful connections, igniting curiosity, and driving knowledge acquisition in a rapidly evolving digital world.
The e-Learning Designer is a crucial figure in the modern educational ecosystem, navigating a complex landscape of learning technologies, pedagogical trends, and evolving learner expectations. They are tasked with bridging the gap between traditional learning methods and the dynamic possibilities of the digital age, creating immersive experiences that captivate and empower learners.
The Role of an E-Learning Designer
E-learning designers are the architects of online learning experiences. They are responsible for creating engaging, effective, and accessible digital learning materials that meet the specific needs of learners and organizations. Their work involves a blend of creativity, technical skills, and instructional design principles.
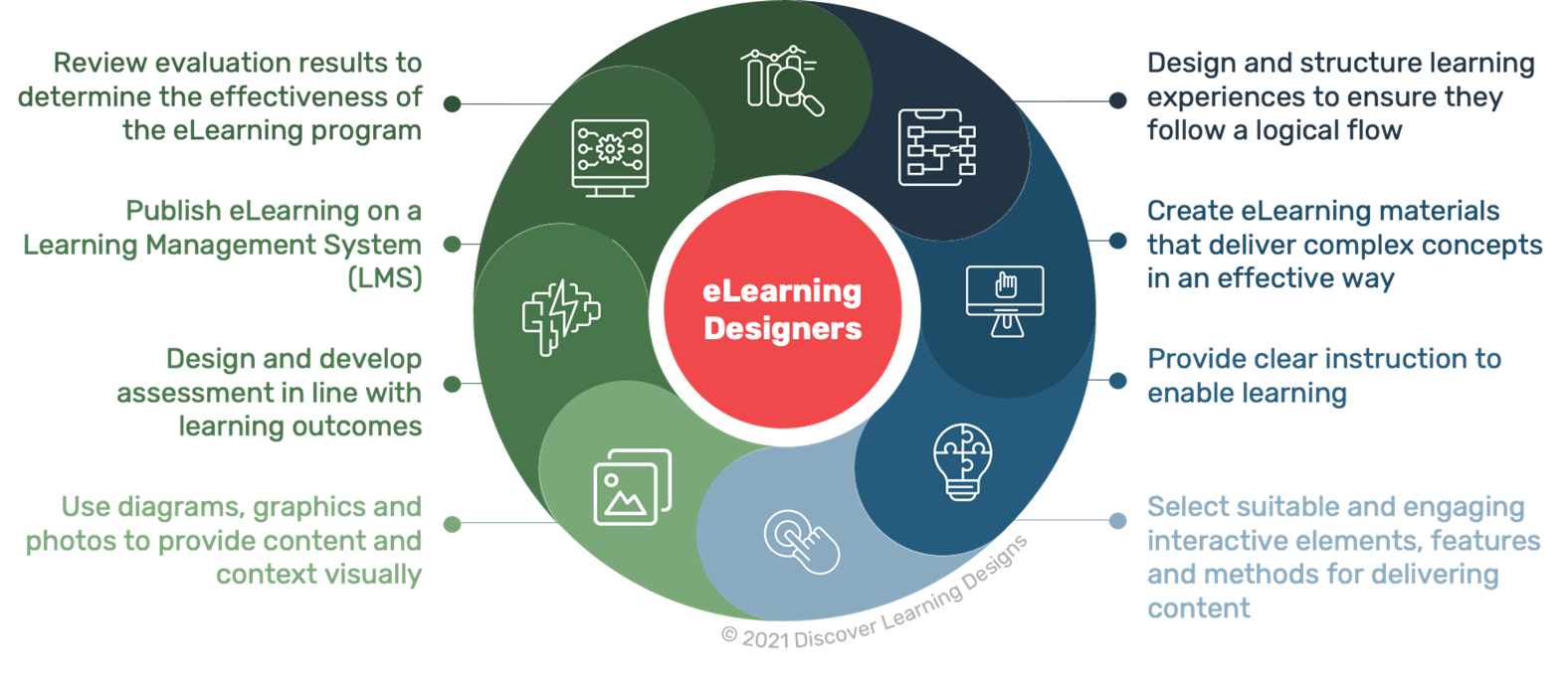
Primary Responsibilities
E-learning designers play a crucial role in the development and delivery of online learning programs. Their responsibilities encompass various aspects of the e-learning process, including:
- Needs Analysis:Identifying the learning needs and goals of the target audience, understanding their existing knowledge, and determining the desired learning outcomes.
- Instructional Design:Developing the learning content, structuring it logically, and incorporating effective instructional strategies to facilitate knowledge acquisition and skill development.
- Content Creation:Designing and creating various types of e-learning content, such as interactive simulations, videos, quizzes, and assessments.
- Technology Selection:Choosing the appropriate e-learning platform, authoring tools, and multimedia resources based on the learning objectives and budget.
- Development and Production:Using authoring tools to develop the e-learning course, integrating multimedia elements, and ensuring technical functionality.
- Testing and Evaluation:Conducting pilot testing to ensure the course’s effectiveness and usability, gathering feedback from learners, and making necessary revisions.
- Implementation and Deployment:Launching the e-learning course, providing technical support to learners, and monitoring course performance.
Key Skills and Qualifications
E-learning designers require a unique blend of skills and qualifications to succeed in this role. These include:
- Instructional Design Principles:A strong understanding of instructional design theories and best practices, such as ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation) and SAM (Successive Approximation Model).
- Learning Technologies:Proficiency in using e-learning authoring tools (e.g., Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate), learning management systems (LMS), and multimedia software (e.g., Adobe Photoshop, Premiere Pro).
- Content Development:Strong writing, editing, and content creation skills, with the ability to adapt content for different learning styles and formats.
- Project Management:Excellent organizational and time management skills to manage multiple projects and meet deadlines.
- Communication and Collaboration:Effective communication skills to collaborate with stakeholders, subject matter experts, and other team members.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking:The ability to analyze learning needs, identify challenges, and develop innovative solutions.
Types of E-Learning Content
E-learning designers create a wide range of digital learning materials to meet diverse learning objectives. These include:
- Interactive Courses:Linear or branched courses that engage learners with interactive elements, such as simulations, games, and assessments.
- Microlearning Modules:Short, focused learning units designed for quick and easy consumption, typically delivered through mobile devices.
- Video Tutorials:Instructional videos that demonstrate concepts, skills, or processes, often complemented with voiceover narration and visual aids.
- Interactive Assessments:Quizzes, tests, and other assessment tools that measure learner understanding and provide feedback.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Experiences:Immersive learning experiences that provide realistic simulations and enhance engagement.
Comparison with Other Roles
The role of an e-learning designer is often compared with other related roles, such as instructional designers, graphic designers, and content developers.
- Instructional Designers:Instructional designers focus on the overall learning process, designing the curriculum, and developing instructional strategies. E-learning designers specialize in translating these designs into digital learning materials.
- Graphic Designers:Graphic designers create visual elements, such as graphics, icons, and layouts, for e-learning courses. E-learning designers integrate these visual elements into the overall learning experience.
- Content Developers:Content developers focus on creating written content, such as text, scripts, and audio narrations. E-learning designers use this content to develop interactive learning materials.
E-Learning Design Process

The e-learning design process is a systematic approach to creating effective and engaging online learning experiences. It involves a series of steps that ensure the development of high-quality e-learning courses that meet the specific needs of learners.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out p. o. w. e. r learning online success now.
Steps in the E-Learning Design Process, E learning designer
The e-learning design process typically involves several key steps, each with its own specific purpose and activities:
- Needs Assessment:This step involves identifying the learning needs of the target audience and determining the goals and objectives of the e-learning course. This includes understanding the learners’ prior knowledge, skills, and learning styles, as well as the organizational context and learning objectives.
The needs assessment helps to ensure that the e-learning course is relevant, valuable, and aligned with the learners’ requirements.
- Learner Analysis:This step focuses on understanding the characteristics of the target audience, including their demographics, learning preferences, and technical skills. This information helps in tailoring the e-learning content and delivery methods to best suit the learners’ needs and preferences. For example, understanding the learners’ average age, location, and preferred learning styles can help in selecting appropriate instructional strategies, visual aids, and assessment methods.
- Learning Objectives:This step involves defining clear and measurable learning objectives that Artikel what learners should be able to do or know after completing the e-learning course. These objectives serve as a roadmap for the development of the e-learning content and assessment strategies.
- Content Development:This step involves creating the e-learning content, including text, images, videos, audio, and interactive elements. The content should be engaging, relevant, and aligned with the learning objectives. The choice of content format and delivery method depends on the target audience, learning objectives, and available resources.
- Instructional Design:This step involves designing the structure and flow of the e-learning course, considering the learning objectives and learner characteristics. This includes selecting appropriate instructional strategies, such as lectures, simulations, case studies, and gamification, to facilitate effective learning.
- Assessment and Evaluation:This step involves developing assessment tools and strategies to measure learner progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the e-learning course. The assessment tools should be aligned with the learning objectives and provide feedback to learners on their performance. Evaluation methods can include pre-tests, post-tests, quizzes, assignments, and performance-based assessments.
- Implementation and Delivery:This step involves launching the e-learning course and providing support to learners. This includes setting up the learning platform, providing access to the course materials, and offering technical assistance.
- Evaluation and Revision:This step involves collecting data on the effectiveness of the e-learning course and using this data to make improvements. This includes assessing learner satisfaction, tracking completion rates, and analyzing performance data. Based on the evaluation findings, the e-learning course can be revised and updated to enhance its effectiveness.
Importance of Needs Assessment and Learner Analysis
Needs assessment and learner analysis are crucial steps in the e-learning design process as they provide valuable insights into the target audience and their learning needs. This information helps in creating relevant, engaging, and effective e-learning courses that meet the specific needs of learners.
- Needs Assessment:Identifying the learning needs of the target audience ensures that the e-learning course addresses the specific knowledge, skills, and abilities that learners need to acquire. This helps in developing a course that is relevant and valuable to the learners, increasing their motivation and engagement.
- Learner Analysis:Understanding the characteristics of the target audience allows for the development of e-learning content and delivery methods that are tailored to their learning preferences and technical skills. This includes selecting appropriate instructional strategies, visual aids, and assessment methods that are engaging and effective for the learners.
Designing a Hypothetical E-Learning Course Using the ADDIE Model
The ADDIE model is a widely used instructional design model that provides a structured framework for developing e-learning courses. It involves five phases:
- Analysis:This phase involves identifying the needs of the target audience, defining the learning objectives, and gathering information about the learning context.
- Design:This phase involves developing the learning materials, instructional strategies, and assessment tools.
- Development:This phase involves creating the e-learning course, including the content, graphics, and interactive elements.
- Implementation:This phase involves launching the e-learning course and providing support to learners.
- Evaluation:This phase involves collecting data on the effectiveness of the e-learning course and making improvements.
Hypothetical E-Learning Course: Introduction to Data AnalyticsTarget Audience:Business professionals with limited knowledge of data analytics. Learning Objectives:
- Understand the fundamentals of data analytics.
- Learn how to collect, clean, and analyze data using various tools and techniques.
- Apply data analytics principles to solve business problems.
ADDIE Model Implementation:
- Analysis:Conduct a needs assessment to identify the specific knowledge and skills gaps in the target audience. Define the learning objectives and gather information about the learners’ technical skills and learning preferences.
- Design:Develop the e-learning content, including text, videos, and interactive exercises, to cover the learning objectives. Choose appropriate instructional strategies, such as lectures, simulations, and case studies, to facilitate learning. Design assessment tools, such as quizzes and assignments, to measure learner progress.
- Development:Create the e-learning course using a learning management system (LMS) or other e-learning platform. Integrate the content, graphics, and interactive elements to create an engaging and effective learning experience.
- Implementation:Launch the e-learning course and provide support to learners. This includes providing access to the course materials, offering technical assistance, and facilitating discussions.
- Evaluation:Collect data on learner satisfaction, completion rates, and performance data. Analyze the data to identify areas for improvement and revise the e-learning course accordingly.
Role of Technology in the E-Learning Design Process
Technology plays a vital role in the e-learning design process, enabling the creation of engaging and interactive learning experiences.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS):LMS platforms provide a centralized hub for managing e-learning courses, delivering content, tracking learner progress, and facilitating communication. They offer features such as course creation tools, content delivery mechanisms, assessment tools, and reporting capabilities.
- Authoring Tools:Authoring tools allow e-learning designers to create interactive and engaging e-learning content. They provide features such as multimedia integration, branching scenarios, simulations, and gamification elements.
- Multimedia Elements:Incorporating multimedia elements such as videos, audio, and animations can enhance the learning experience by making it more engaging and accessible.
- Interactive Elements:Interactive elements, such as quizzes, simulations, and games, can promote active learning and provide immediate feedback to learners.
- Collaboration Tools:Collaboration tools, such as discussion forums, chat rooms, and virtual classrooms, enable learners to interact with each other and the instructor, fostering a sense of community and supporting learning.
- Mobile Learning:With the increasing use of mobile devices, e-learning courses should be designed to be accessible and responsive on various platforms, ensuring a seamless learning experience for learners on the go.
E-Learning Content Development: E Learning Designer

E-learning content development is the heart of any successful online learning program. It involves selecting and creating engaging, effective, and accessible materials that cater to the needs of learners. This process goes beyond simply digitizing traditional classroom content; it demands a deep understanding of learning theories, instructional design principles, and technology to deliver a rich and impactful learning experience.
E-Learning Content Formats
Different e-learning content formats serve distinct purposes and cater to various learning styles. Understanding these formats and their strengths allows e-learning designers to create a diverse and engaging learning environment.
- Video: Videos offer a dynamic and engaging way to deliver information, demonstrations, and storytelling. They can be used for lectures, tutorials, case studies, and simulations. Examples include instructional videos explaining concepts, product demos, and interviews with experts.
- Simulations: Simulations provide hands-on learning experiences that allow learners to practice skills and apply knowledge in a safe and controlled environment. They are particularly effective for teaching practical skills, decision-making, and problem-solving. Examples include flight simulators for pilots, medical simulations for healthcare professionals, and virtual labs for science students.
- Interactive Exercises: Interactive exercises promote active learning and provide immediate feedback. They can be used to test knowledge, reinforce concepts, and encourage critical thinking. Examples include quizzes, games, interactive scenarios, and drag-and-drop activities.
- Gamification: Gamification incorporates game mechanics into learning experiences to increase motivation, engagement, and retention. It uses elements like points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges to create a fun and competitive learning environment. Examples include gamified courses, learning platforms with points and rewards, and interactive games that teach specific concepts.
Comparison of E-Learning Content Formats
| Format | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Video | Engaging, dynamic, versatile, can be used for various content types | Production can be expensive, time-consuming, and require technical expertise, learners may not be actively engaged if not interactive |
| Simulations | Hands-on learning, safe and controlled environment, effective for practical skills and decision-making | Can be expensive to develop, may require specialized software, not suitable for all content types |
| Interactive Exercises | Active learning, immediate feedback, reinforces concepts, promotes critical thinking | May not be engaging for all learners, can be time-consuming to develop, requires careful design to be effective |
| Gamification | Increases motivation and engagement, promotes competition and collaboration, can be used for various content types | Can be distracting if not implemented effectively, may not be appropriate for all learning objectives, can be time-consuming to design |
Accessibility and Inclusivity in E-Learning Content Development
Accessibility and inclusivity are paramount in e-learning content development. All learners, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, should have equal access to quality learning experiences. This requires considering various factors such as:
- Alternative Text for Images: Providing alternative text for images allows screen readers to describe the image content to visually impaired learners. This ensures they can access and understand the information presented.
- Closed Captions and Transcripts: Closed captions and transcripts make audio and video content accessible to deaf or hard-of-hearing learners. They also benefit learners who prefer to read or have difficulty understanding spoken language.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensuring that all content can be navigated using only a keyboard is crucial for learners who may have difficulty using a mouse or other pointing devices. This includes providing clear keyboard shortcuts and making all interactive elements keyboard-accessible.
- Color Contrast: Using sufficient color contrast between text and background ensures readability for learners with visual impairments. It also improves the overall accessibility and readability of the content for all learners.
- Content Structure and Organization: Clear and logical content structure and organization help all learners navigate and understand the information presented. This includes using headings, subheadings, bullet points, and other formatting elements to break up the text and make it easier to read and comprehend.
E-Learning Technology
E-learning technology plays a crucial role in the success of any online learning program. It encompasses the tools, platforms, and infrastructure that facilitate the delivery, management, and interaction of online learning content. This section delves into the various types of e-learning platforms, authoring tools, learning management systems, and the influence of emerging technologies on the e-learning landscape.
E-Learning Platforms
E-learning platforms provide the foundation for online learning experiences. They offer a range of features, including content delivery, assessment tools, communication channels, and learner tracking capabilities.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS):LMS platforms are comprehensive systems designed to manage all aspects of online learning. They provide features such as course creation, content delivery, assessment, grading, communication, and learner progress tracking. Examples include Moodle, Canvas, Blackboard, and D2L.
- Learning Content Management Systems (LCMS):LCMS platforms focus specifically on managing and delivering learning content. They offer features for creating, storing, and distributing learning materials, including courses, modules, and assessments. Examples include Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, and Lectora.
- Virtual Learning Environments (VLE):VLE platforms are designed to create a virtual learning environment that replicates the experience of a traditional classroom. They provide features for online collaboration, discussion forums, and group activities. Examples include Sakai, Google Classroom, and Edmodo.
E-Learning Authoring Tools
E-learning authoring tools enable instructors and designers to create interactive and engaging learning content. They offer features for creating multimedia presentations, simulations, games, and assessments.
- Articulate Storyline:A popular authoring tool known for its user-friendly interface and robust features. It allows for the creation of interactive courses, simulations, and assessments with advanced branching scenarios and multimedia elements.
- Adobe Captivate:Another powerful authoring tool that offers a wide range of features for creating e-learning content, including screen recordings, simulations, and interactive assessments. It also provides advanced features for responsive design and accessibility.
- Lectora:An authoring tool known for its flexibility and customization options. It allows for the creation of complex learning courses with advanced branching scenarios, custom interactions, and multimedia elements.
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning management systems (LMS) are essential for managing and delivering online learning programs. They provide a centralized platform for course administration, content delivery, assessment, communication, and learner progress tracking.
| LMS | Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moodle | Open-source platform, highly customizable, robust features, large community support | Flexibility, affordability, extensive customization options, large user base | Steeper learning curve, limited support for advanced multimedia features |
| Canvas | User-friendly interface, intuitive design, strong mobile capabilities, integration with third-party tools | Ease of use, mobile accessibility, strong integration capabilities, user-friendly design | Limited customization options, higher cost compared to open-source platforms |
| Blackboard | Widely adopted in higher education, robust features, extensive integration options, strong support for assessment | Established reputation, extensive features, strong integration options, comprehensive support for assessment | Less user-friendly interface, high cost, complex setup |
| D2L | Robust features, user-friendly interface, strong mobile capabilities, comprehensive reporting and analytics | User-friendly interface, comprehensive features, strong mobile capabilities, detailed reporting and analytics | Higher cost, limited customization options |
Emerging Technologies in E-Learning
Emerging technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), are transforming the e-learning landscape. They offer immersive and interactive learning experiences that can enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
- Virtual Reality (VR):VR technology creates immersive, three-dimensional environments that allow learners to experience real-world scenarios or simulations. For example, a VR application could allow a medical student to perform surgery in a virtual operating room or a history student to explore ancient Rome.
- Augmented Reality (AR):AR technology overlays digital information onto the real world, providing learners with an interactive and engaging experience. For example, an AR application could allow a student to see a 3D model of a human heart superimposed on a real anatomy textbook.
Evaluating E-Learning Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of e-learning programs is crucial for ensuring that learning objectives are met and that resources are utilized efficiently. It involves a systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to understand the impact of e-learning initiatives on learner outcomes.
Methods for Evaluating E-Learning Effectiveness
Several methods can be employed to evaluate the effectiveness of e-learning programs. These methods can be categorized into formative and summative evaluations. Formative evaluations are conducted during the development and implementation of the program to identify areas for improvement, while summative evaluations are conducted at the end of the program to assess its overall impact.
- Kirkpatrick’s Model:This widely used model evaluates e-learning programs at four levels: reaction, learning, behavior, and results. It helps assess learner satisfaction, knowledge acquisition, behavioral changes, and the overall impact of the program on organizational goals.
- Pre- and Post-Tests:These tests measure learner knowledge and skills before and after the e-learning program. The difference in scores can indicate the effectiveness of the program in promoting learning.
- Surveys and Questionnaires:These tools collect data on learner satisfaction, engagement, and perceptions of the e-learning program. They can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the program.
- Focus Groups and Interviews:These qualitative methods allow for in-depth exploration of learner experiences and perspectives. They can provide valuable insights into the factors that contribute to or hinder e-learning effectiveness.
- Performance Data Analysis:This method involves analyzing performance data, such as sales figures, customer satisfaction ratings, or employee productivity, to assess the impact of e-learning programs on business outcomes.
Importance of Data Collection and Analysis in E-Learning Evaluation
Data collection and analysis are essential for obtaining objective and reliable evidence of e-learning effectiveness. Data can be collected through various methods, including learner performance data, survey responses, and interaction logs. The data should be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and insights that can inform program improvement and decision-making.
“Data collection and analysis provide a foundation for evidence-based decision-making in e-learning.”
- Identifying Areas for Improvement:Data analysis can help identify areas where the e-learning program is not meeting its objectives. For example, if learner performance data shows that a particular module is consistently challenging, it may need to be revised or redesigned.
- Measuring Program Impact:Data can be used to measure the overall impact of the e-learning program on learner outcomes, such as improved knowledge, skills, or performance. This information can be used to demonstrate the value of the program to stakeholders.
- Ensuring Program Quality:Data analysis can help ensure that the e-learning program is of high quality. For example, data on learner engagement and satisfaction can be used to identify areas where the program may be lacking in terms of interactivity or relevance.
Evaluating the Quality of E-Learning Content
Evaluating the quality of e-learning content is essential for ensuring that learners are receiving effective and engaging learning experiences. Here is a checklist that can be used to evaluate the quality of e-learning content:
- Relevance:Is the content relevant to the learning objectives and the needs of the learners?
- Accuracy:Is the information presented accurate and up-to-date?
- Clarity:Is the content clear, concise, and easy to understand?
- Engagement:Does the content engage learners and keep them interested?
- Accessibility:Is the content accessible to all learners, regardless of their abilities or disabilities?
- Design:Is the content visually appealing and well-organized?
- Interactivity:Does the content provide opportunities for learners to interact with the material?
- Feedback:Does the content provide learners with feedback on their progress?
Best Practices for Measuring Learner Engagement and Satisfaction
Measuring learner engagement and satisfaction is essential for understanding how learners are interacting with the e-learning program and how satisfied they are with the learning experience. Here are some best practices for measuring learner engagement and satisfaction:
- Use a Variety of Methods:Use a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to collect data on learner engagement and satisfaction. This can include surveys, questionnaires, focus groups, interviews, and interaction logs.
- Focus on Specific Behaviors:Measure learner engagement by tracking specific behaviors, such as time spent on the program, number of interactions, and completion rates. This can provide insights into how learners are interacting with the content and whether they are finding it engaging.
- Collect Feedback Regularly:Collect feedback from learners regularly throughout the e-learning program. This can be done through surveys, quizzes, or informal feedback mechanisms.
- Use Feedback to Improve the Program:Use learner feedback to identify areas where the e-learning program can be improved. This could include making changes to the content, design, or delivery methods.
Trends in E-Learning Design

The field of e-learning design is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing learner preferences, and the growing demand for accessible and engaging learning experiences. This section explores some of the most prominent trends shaping the future of e-learning.
Mobile Learning and Microlearning
Mobile learning, also known as m-learning, refers to the delivery of learning content through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. Its impact on e-learning design is significant, as it has led to a shift towards shorter, more bite-sized learning modules that can be accessed anytime, anywhere.
Check Choose Life Choose Words to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Microlearning, a key component of m-learning, focuses on delivering content in small, digestible chunks that can be easily absorbed and retained.
- Accessibility:Mobile devices have become ubiquitous, providing learners with constant access to learning materials, regardless of location or time constraints. This accessibility fosters flexibility and encourages learners to engage in learning on their own terms.
- Just-in-Time Learning:Microlearning enables learners to access specific information exactly when they need it, supporting on-the-job learning and performance improvement. This approach is particularly effective for skills-based training, where immediate application of knowledge is crucial.
- Engaging Formats:Mobile devices offer diverse multimedia formats like videos, interactive simulations, and gamified learning experiences. These formats cater to different learning styles and preferences, making learning more engaging and effective.
Personalization and Adaptive Learning
Personalization and adaptive learning are becoming increasingly central to e-learning design. These trends focus on tailoring learning experiences to individual learner needs, preferences, and learning styles.
- Personalized Learning Paths:Adaptive learning platforms use algorithms to track learner progress and tailor content delivery based on their individual performance and learning patterns. This allows learners to progress at their own pace and focus on areas where they need more support.
- Personalized Feedback and Support:Adaptive learning systems provide personalized feedback, offering targeted guidance and support based on learner performance. This personalized feedback can help learners identify their strengths and weaknesses, fostering self-directed learning and improvement.
- Increased Learner Engagement:Personalization and adaptive learning enhance learner engagement by making the learning experience more relevant and engaging. When learners feel that the content is tailored to their needs, they are more likely to be motivated and actively participate in the learning process.
Examples of Effective E-Learning Design
The success of an e-learning program depends on its ability to engage learners, deliver relevant content, and facilitate knowledge retention. This section explores effective e-learning design principles through examples of successful programs and courses.
Examples of Successful E-Learning Programs
Examining successful e-learning programs can provide valuable insights into effective design practices. Here are a few notable examples:
- Khan Academy:This non-profit organization offers a vast library of free educational videos and exercises covering various subjects. Its effectiveness stems from its engaging video format, interactive exercises, and personalized learning paths.
- Coursera:This platform hosts online courses from top universities worldwide. Its success can be attributed to its diverse course offerings, flexible learning schedules, and integration of interactive learning elements.
- Duolingo:This language learning app utilizes gamification and personalized learning paths to make language learning engaging and effective. Its success is evident in its high user engagement and positive learning outcomes.
Analyzing Design Elements
The success of these programs can be attributed to several design elements:
- Engaging Content:Effective e-learning programs use multimedia elements, interactive activities, and storytelling to make learning engaging and memorable.
- Personalized Learning:Programs that cater to individual learning styles and pace, allowing learners to progress at their own speed, are more likely to succeed.
- Interactive Learning:Interactive elements like quizzes, simulations, and collaborative activities encourage active learning and promote knowledge retention.
- Clear Learning Objectives:Well-defined learning objectives guide learners through the program and provide a clear sense of purpose.
- Regular Feedback and Assessment:Providing regular feedback and assessments helps learners track their progress and identify areas for improvement.
- User-Friendly Interface:An intuitive and user-friendly interface ensures learners can easily navigate the program and access the content they need.
Case Studies of E-Learning Design Projects
Case studies provide real-world examples of e-learning design challenges and successes. For instance, a case study on an e-learning program for medical professionals could analyze how the program incorporated interactive simulations to enhance practical skills, or how gamification elements were used to motivate learners to complete the program.
Challenges and Successes in Real-World Scenarios
E-learning designers often face challenges such as:
- Limited Engagement:Keeping learners engaged and motivated in an online environment can be challenging.
- Technical Issues:Technical difficulties can disrupt the learning experience and hinder progress.
- Accessibility Concerns:Ensuring accessibility for learners with disabilities is crucial but often presents design challenges.
- Cost Considerations:Budget constraints can limit the use of advanced technology and resources.
However, designers also experience successes, such as:
- Improved Learning Outcomes:Well-designed e-learning programs can lead to significant improvements in knowledge acquisition and skill development.
- Increased Accessibility:E-learning provides greater accessibility to education for learners who may not have access to traditional learning environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness:E-learning can be a cost-effective alternative to traditional classroom instruction.
Q&A
What are the typical job responsibilities of an e-Learning Designer?
E-Learning Designers are responsible for conducting needs assessments, developing learning objectives, designing instructional materials, selecting appropriate technologies, evaluating the effectiveness of learning programs, and staying abreast of emerging trends in e-learning.
What are the essential skills for a successful e-Learning Designer?
Strong instructional design skills, expertise in learning technologies, excellent communication and collaboration abilities, a deep understanding of adult learning principles, and a passion for creating engaging and effective learning experiences are essential.
What is the difference between an e-Learning Designer and a traditional instructional designer?
While both roles focus on designing learning experiences, e-Learning Designers specialize in creating digital learning materials and leveraging technology to enhance learning. Traditional instructional designers may work across a broader range of formats, including face-to-face instruction.