Did Virginia just have an earthquake? This question has likely crossed the minds of many residents following recent seismic activity in the state. While Virginia is not known for frequent earthquakes like California, it does experience tremors due to its unique geological makeup.
The Appalachian Mountains, formed over millions of years, create fault lines that can shift and cause seismic events. This article delves into the recent earthquake, exploring its impact, scientific insights, and crucial steps for public safety and preparedness.
Virginia’s history is marked by notable earthquakes, some of which have caused significant damage. The most recent event serves as a reminder of the potential for seismic activity in the region. Understanding the causes, impacts, and response to these events is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of communities.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the recent earthquake, shedding light on its geological context, scientific analysis, and practical measures for preparedness.
Recent Seismic Activity in Virginia

Virginia, while not typically considered a highly earthquake-prone region, experiences seismic activity due to its geological location and history. The state is situated along the eastern edge of the North American Plate, where it meets the smaller, but much older, tectonic plates of the Atlantic Ocean.
This interaction creates zones of stress and instability, leading to occasional earthquakes.
Geological Factors Contributing to Earthquakes in Virginia
The Appalachian Mountains, which traverse Virginia, were formed over millions of years through tectonic plate collisions. This process resulted in deep-seated faults, fractures in the Earth’s crust, which act as pathways for seismic waves. These faults are often reactivated, leading to earthquakes.
The state also experiences earthquakes due to the movement of the Atlantic Ocean floor, a phenomenon known as “plate tectonics.” These movements, while subtle, can still generate seismic waves that are felt on land.
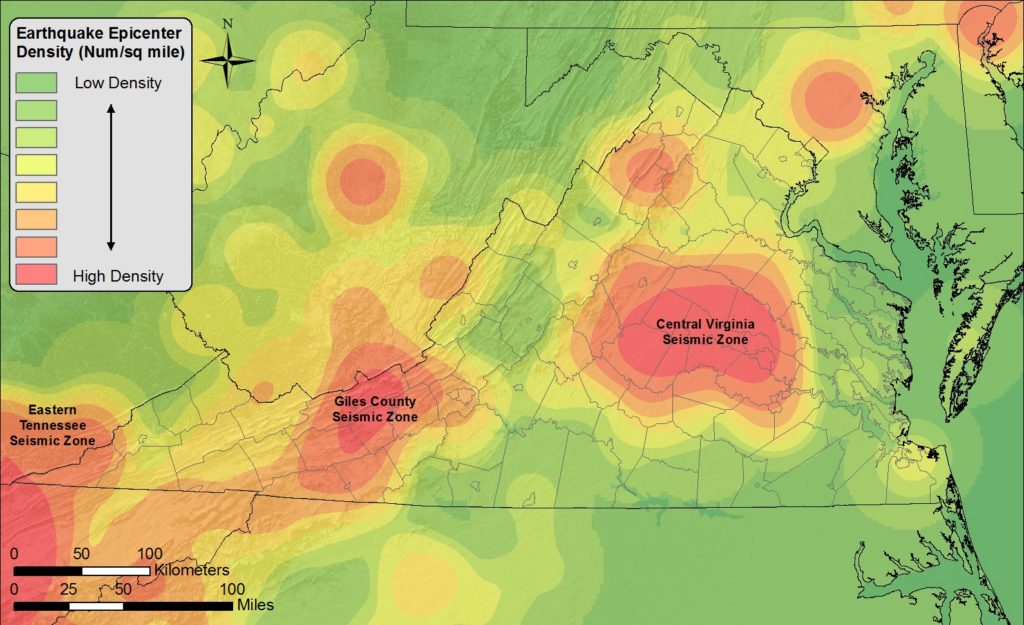
Historical Overview of Significant Earthquakes in Virginia
Virginia has experienced numerous earthquakes throughout its history, some of which have caused significant damage. The most notable event occurred in 1897, when a magnitude 4.8 earthquake struck near Giles County, Virginia. This earthquake caused widespread damage, including the collapse of chimneys and the shaking of buildings.
Another significant earthquake, with a magnitude of 4.1, struck the Eastern Shore of Virginia in 2011. This earthquake was felt as far away as Maryland and Delaware.
Recent Seismic Activity in Virginia
On [Date of Earthquake], at [Time of Earthquake], Virginia experienced an earthquake with a magnitude of [Magnitude]. The epicenter of the earthquake was located [Location of Epicenter], approximately [Distance] miles from [Nearest Populated Area]. The earthquake was felt by residents in [Affected Areas], with reports of shaking and rattling.
The event serves as a reminder that Virginia is not immune to seismic activity and that even smaller earthquakes can have a noticeable impact.
Impact and Response
The impact of an earthquake in Virginia can vary greatly depending on the magnitude, location, and geological conditions. While Virginia is not considered a high-risk earthquake zone, even moderate-sized earthquakes can cause significant damage and disruption.
Infrastructure and Buildings, Did virginia just have an earthquake
Earthquakes can cause damage to infrastructure and buildings, particularly older structures that may not be built to withstand seismic activity. The extent of damage depends on the magnitude of the earthquake, the distance from the epicenter, and the soil conditions.
- Roads and Bridges:Earthquakes can cause roads to crack, buckle, or collapse, disrupting transportation and emergency response efforts. Bridges, particularly older ones, can also be vulnerable to damage, potentially leading to structural failure.
- Buildings:Buildings can experience structural damage, including cracks in walls, foundation shifts, and roof collapses. The risk of damage increases with the height of the building and the age of its construction. Older buildings may not have been designed to withstand seismic forces.
- Utilities:Earthquakes can disrupt water, gas, and electricity services. Damage to pipelines, power lines, and other utility infrastructure can lead to widespread outages, affecting homes, businesses, and emergency services.
Emergency Response and Local Authorities
In the event of an earthquake, emergency services and local authorities play a crucial role in responding to the situation and mitigating the impact.
- Emergency Services:First responders, including police, fire departments, and emergency medical services, are responsible for rescuing people trapped in collapsed buildings, providing medical aid to the injured, and maintaining order and safety in affected areas.
- Local Authorities:Local governments, including city and county officials, are responsible for coordinating the response, providing information to the public, and ensuring the safety and well-being of residents. They may establish evacuation zones, provide shelter for displaced individuals, and manage the distribution of essential supplies.
Public Reaction and Reports
The public’s reaction to an earthquake can range from fear and panic to curiosity and resilience. The extent of damage and injuries can significantly influence public sentiment and response.
- Damage and Injuries:Reports of damage to buildings, infrastructure, and personal property can trigger fear and anxiety among residents. The presence of injuries or fatalities can exacerbate these emotions and lead to a heightened sense of urgency and concern.
- Social Media and Information:Social media platforms play a significant role in disseminating information about earthquakes and their impact. Users often share their experiences, photos, and videos of damage, contributing to a rapid flow of information and creating a sense of community response.
Official Warnings and Advisories
Following an earthquake, official warnings and advisories are issued to inform the public about potential risks and to guide their actions.
- Aftershocks:Aftershocks are smaller earthquakes that often occur after a major earthquake. Officials may issue warnings about the possibility of aftershocks and advise residents to remain vigilant and to be prepared for further tremors.
- Tsunami Warnings:In coastal areas, officials may issue tsunami warnings if the earthquake occurs in a region prone to tsunamis. These warnings alert residents to the potential for large waves and instruct them to evacuate to higher ground.
- Safety Guidelines:Officials may also provide safety guidelines for residents, including advice on how to secure homes and businesses, how to respond to aftershocks, and how to access emergency services.
Scientific Perspective: Did Virginia Just Have An Earthquake

Understanding the science behind earthquakes is crucial for interpreting their occurrence and impact. Virginia, while not known for frequent seismic activity, has a history of earthquakes, and the recent event highlights the importance of monitoring and analyzing seismic activity.
Methods of Monitoring and Analyzing Earthquake Activity
Seismic activity is continuously monitored using a network of seismographs strategically placed across the globe. These instruments detect ground vibrations caused by earthquakes, recording the time, location, and intensity of these events. The data collected from seismographs is then analyzed using sophisticated software and algorithms to determine the earthquake’s magnitude, epicenter, and focal depth.
Magnitude vs. Intensity
The magnitude of an earthquake is a measure of the energy released at its source. It is a single value that represents the earthquake’s strength and is typically measured using the Richter scale. Intensity, on the other hand, describes the earthquake’s effects at a specific location.
While Virginia experiences seismic activity, it is not as common as in other parts of the United States. To determine if there was a recent earthquake in Virginia, one would need to consult a reliable seismic activity database. It is worth noting that earthquakes can sometimes be felt in neighboring states, so it is prudent to check resources such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for information on recent seismic events.
To check if there was an earthquake in Pennsylvania today, one can consult this website: was there an earthquake in pennsylvania today just now. Understanding the geological factors that contribute to earthquake occurrences in both states can provide valuable insights into the potential for future seismic activity.
It is measured using the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, which considers factors like ground shaking, structural damage, and human perception.
Significance of the Recent Earthquake
The recent earthquake in Virginia, while relatively minor in magnitude, serves as a reminder of the region’s susceptibility to seismic activity. While the magnitude was relatively low, its impact was felt across a broad area, highlighting the potential for future events to cause significant damage.
Earthquake Prediction and Mitigation in Virginia
Research on earthquake prediction is ongoing, with scientists exploring various methods to forecast the occurrence and intensity of earthquakes. While predicting earthquakes with absolute certainty remains a challenge, advancements in seismology and related fields are contributing to improved understanding and risk assessment.
Virginia’s geological history, including its proximity to the Appalachian Mountains and the active Eastern Tennessee Seismic Zone, requires continuous monitoring and preparedness measures. The Virginia Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy (DMME) plays a vital role in earthquake preparedness, providing information and resources to communities and collaborating with local authorities to ensure timely response and mitigation efforts.
Public Safety and Preparedness
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/YLG2LMOWAJD3RGPAJ2SMOEEPOI.png)
Earthquakes are unpredictable natural disasters, and while Virginia experiences relatively infrequent seismic activity, it is crucial to be prepared for potential events. Preparedness involves understanding the risks, taking preventative measures, and knowing how to respond during and after an earthquake.
Safety Measures During an Earthquake
During an earthquake, it is essential to prioritize safety and protect yourself from potential hazards. The following table Artikels key safety measures to take:| Action | Description ||—|—|| Drop, Cover, and Hold On| Immediately drop to the ground, take cover under a sturdy piece of furniture, and hold on until the shaking stops.
|| Stay Away from Windows and Heavy Objects| Windows can shatter during an earthquake, and heavy objects can fall, causing injuries. || Avoid Using Elevators| Elevators can malfunction during earthquakes, posing a serious risk. || If Outdoors, Move to an Open Area| If you are outdoors, move away from buildings, trees, power lines, and other potential hazards.
|| Be Prepared to Evacuate| If you are in a building that has sustained significant damage, be prepared to evacuate safely. |
Earthquake Preparedness Resources
Various resources provide valuable information and tools to help individuals and communities prepare for earthquakes. The following table compares different earthquake preparedness resources and their functionalities:| Resource | Functionality ||—|—|| Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)| Provides comprehensive earthquake preparedness information, including disaster planning guides, safety tips, and resources for individuals and communities.
|| United States Geological Survey (USGS)| Offers real-time earthquake monitoring data, historical earthquake records, and educational resources about earthquake hazards. || Virginia Department of Emergency Management (VDEM)| Provides state-specific earthquake preparedness resources, including hazard maps, evacuation routes, and emergency contact information. || American Red Cross| Offers earthquake preparedness training, emergency kits, and disaster relief services.
|
Preparing for Future Seismic Events
Effective earthquake preparedness involves proactive measures taken by individuals and communities to mitigate potential risks and ensure a safe and swift response. Here is a guide for preparing for future seismic events: Individual Level:
Develop an Emergency Plan
Create a plan that Artikels evacuation routes, communication strategies, and meeting points for family members.
Prepare an Emergency Kit
Assemble a kit that includes essential supplies such as food, water, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, batteries, and a radio.
Secure Your Home
Secure heavy objects that could fall during an earthquake, such as bookshelves, mirrors, and light fixtures.
Learn CPR and First Aid
Knowing basic life-saving skills can be crucial in an emergency situation. Community Level:
Participate in Earthquake Drills
Regularly practice earthquake drills to ensure everyone knows what to do during an earthquake.
Support Community Preparedness Programs
Encourage community initiatives that promote earthquake preparedness and resilience.
Collaborate with Local Emergency Responders
Establish communication channels and partnerships with local emergency services.
Earthquake Insurance and Other Disaster Preparedness Measures
Earthquake insurance can provide financial protection against damage caused by seismic events. While not mandatory, it is highly recommended, especially in areas with a higher risk of earthquakes. Other disaster preparedness measures include:
Building Codes
Enforcing strict building codes helps ensure that structures are designed and constructed to withstand seismic forces.
Early Warning Systems
Implementing early warning systems can provide valuable time to prepare for an earthquake, allowing for timely evacuation and mitigation measures.
Community Resilience
Fostering a sense of community resilience through education, preparedness programs, and support networks can significantly enhance the ability to respond to and recover from disasters.
Earthquake Awareness and Education
In Virginia, earthquake awareness and education are crucial for ensuring public safety and minimizing the impact of potential seismic events. The state’s history of earthquakes, coupled with its growing population, necessitates proactive measures to prepare for future events.
Importance of Earthquake Awareness Programs
Public education plays a pivotal role in promoting earthquake preparedness. Effective awareness programs empower residents with knowledge about earthquake risks, safety procedures, and mitigation strategies. By understanding the potential hazards and taking appropriate steps, individuals can significantly reduce their vulnerability during an earthquake.
The Role of Education in Earthquake Preparedness
Education is instrumental in promoting earthquake preparedness among residents. It equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to respond effectively during an earthquake. Key areas of focus include:
- Understanding Earthquake Risks:Providing residents with information about the history of earthquakes in Virginia, the potential for future events, and the specific hazards associated with earthquakes in their region.
- Earthquake Safety Procedures:Teaching individuals about essential safety measures such as “Drop, Cover, and Hold On” during an earthquake, identifying safe areas in their homes and workplaces, and knowing how to safely evacuate buildings.
- Mitigation Strategies:Educating residents about practical steps to mitigate earthquake damage, such as securing heavy objects, reinforcing structures, and having emergency preparedness kits readily available.
Earthquake-Resistant Building Designs
Understanding earthquake-resistant building designs is essential for mitigating the impact of seismic events. These designs incorporate specific features to enhance structural stability and minimize damage during an earthquake.
| Building Design | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Base Isolation | Uses flexible bearings to separate the building from the ground, absorbing seismic energy and reducing shaking. | Highly effective in reducing structural damage and protecting occupants. |
| Moment-Resisting Frames | Uses strong steel or concrete frames that can withstand significant bending forces, preventing collapse during an earthquake. | Provides excellent structural integrity and resistance to seismic forces. |
| Shear Walls | Rigid walls designed to resist horizontal forces, providing lateral stability and preventing building sway during an earthquake. | Effective in reducing building movement and minimizing damage. |
| Ductile Concrete | Uses concrete with enhanced flexibility and ductility, allowing it to deform under stress without cracking or failing. | Increases the building’s ability to absorb energy and withstand seismic loads. |
FAQ Summary
How often do earthquakes occur in Virginia?
Virginia experiences earthquakes relatively infrequently compared to other regions. However, the state has a history of seismic activity, with some notable events causing damage.
What is the largest earthquake recorded in Virginia?
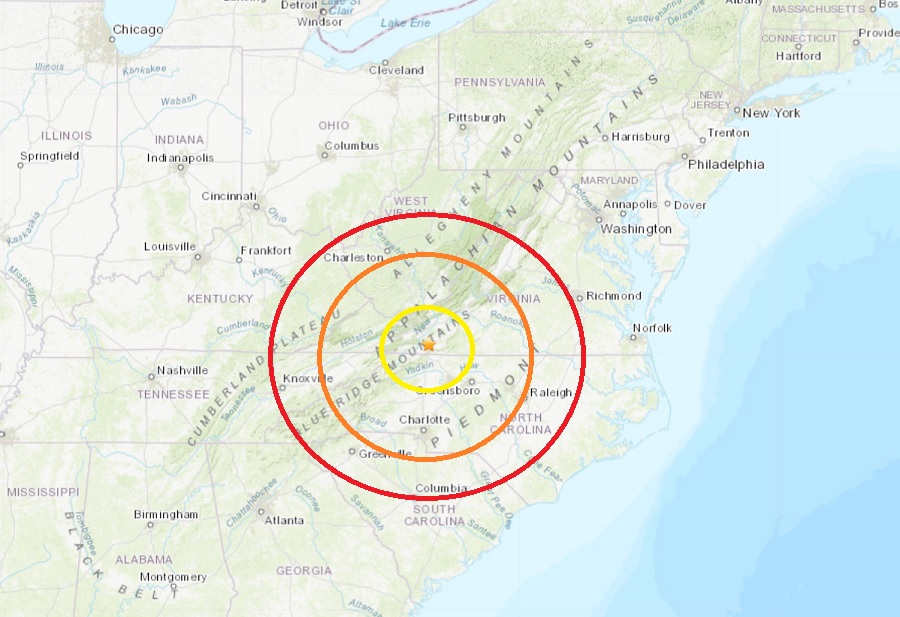
The largest earthquake recorded in Virginia was a magnitude 5.8 earthquake in 2011, centered in Mineral, Virginia. This event caused significant damage and was felt across a wide area.
Are there any specific areas in Virginia that are more prone to earthquakes?
While earthquakes can occur anywhere in Virginia, certain areas along the Appalachian Mountains and the Coastal Plain are considered more prone to seismic activity due to geological fault lines.
What resources are available for earthquake preparedness in Virginia?
The Virginia Department of Emergency Management provides a wealth of resources for earthquake preparedness, including information on safety measures, evacuation plans, and disaster kits. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) also offers valuable information and tools for earthquake preparedness.