A learning theory is made up of a set of interconnected components that orchestrate the learning process. Embark on a journey to decipher these fundamental elements and their interplay, unraveling the secrets of effective learning.
From behaviorism to cognitivism, diverse learning theories have emerged, each proposing unique perspectives and applications. We’ll delve into their key principles and assumptions, comparing and contrasting their approaches to shed light on the intricacies of human learning.
Components of a Learning Theory: A Learning Theory Is Made Up Of A Set

Learning theories are frameworks that attempt to explain how individuals acquire, retain, and apply knowledge and skills. These theories consist of several fundamental components that work together to shape the learning process.
Interplay of Components
The components of a learning theory are interconnected and influence each other. For example, the learning environment can affect the learner’s motivation, which in turn impacts the learning strategies they adopt. The interplay between these components creates a complex system that influences the effectiveness of the learning process.
Examples of Learning Theories
Various learning theories exist, each emphasizing different components and processes. Some prominent examples include:
- Behaviorism:Focuses on observable behaviors and the role of reinforcement and punishment in learning.
- Cognitivism:Emphasizes the mental processes involved in learning, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving.
- Constructivism:Views learning as an active process where individuals construct their own understanding through interactions with the environment.
Theories of Learning

Theories of learning attempt to explain how individuals acquire, retain, and recall knowledge and skills. They provide a framework for understanding the learning process and can inform educational practices.
There are numerous theories of learning, each with its own unique perspective and set of assumptions. Some of the most influential theories include:
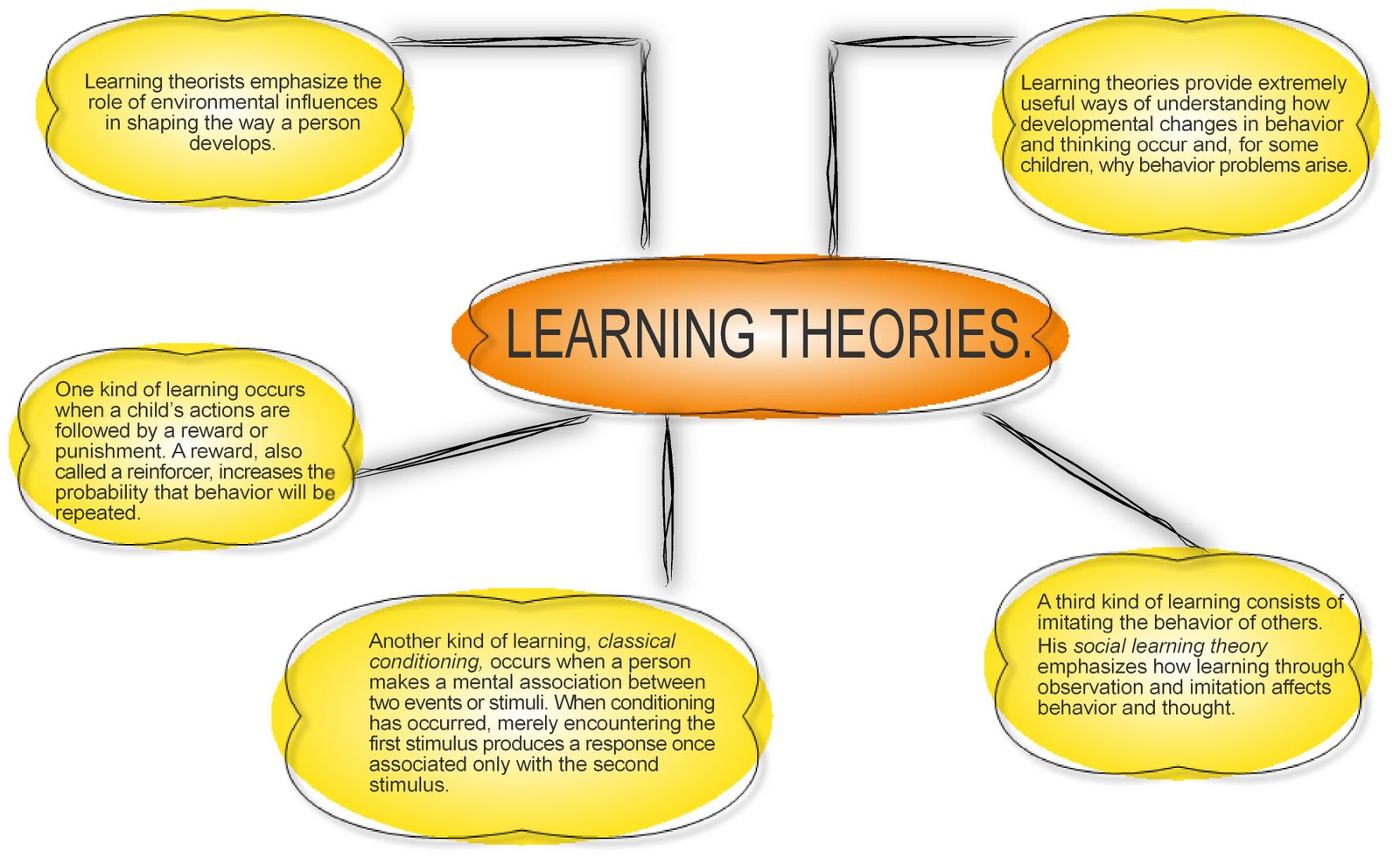
Behaviorism
Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors and the role of reinforcement and punishment in shaping those behaviors. Key principles include:
- Learning is a change in observable behavior.
- Behavior is shaped by its consequences.
- Learning occurs through association and reinforcement.
Cognitivism
Cognitivism emphasizes the role of mental processes in learning. Key principles include:
- Learning involves the acquisition and organization of knowledge.
- Learners actively construct their understanding of the world.
- Prior knowledge and experiences influence learning.
Constructivism
Constructivism builds on cognitivism, emphasizing the active role of learners in constructing their own knowledge and understanding. Key principles include:
- Learning is a social process that occurs through interaction with others.
- Learners construct their own understanding of the world based on their experiences.
- Knowledge is not passively received but actively constructed.
Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory combines elements of behaviorism and cognitivism, emphasizing the role of observation and imitation in learning. Key principles include:
- Learning occurs through observing and imitating others.
- Reinforcement and punishment can influence learning.
- Cognitive processes play a role in learning, such as attention and memory.
Humanistic Learning Theory
Humanistic learning theory focuses on the individual learner and their unique needs and experiences. Key principles include:
- Learning is a holistic process that involves the whole person.
- Learners are motivated by intrinsic factors, such as curiosity and a desire for growth.
- Learning occurs best in a supportive and nurturing environment.
Applications of Learning Theories
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/learning-study-guide-2795698_FINAL-5bec544ac9e77c005185519d.png)
Learning theories are not merely abstract concepts; they have practical applications in educational settings. Understanding the principles of learning can inform the design of instructional strategies, teaching practices, and curriculum development, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of teaching and learning.
For instance, constructivism emphasizes the active role of learners in constructing knowledge. This theory suggests that students learn best when they actively engage with the material, make connections to their prior knowledge, and collaborate with others. Consequently, teachers can create constructivist learning environments by providing hands-on activities, promoting group discussions, and encouraging students to reflect on their learning.
Instructional Strategies
- Behaviorism: Reinforcement and punishment can be used to shape desired behaviors in students.
- Cognitivism: Cognitive strategies, such as problem-solving and critical thinking, can be explicitly taught and practiced.
- Constructivism: Learning environments can be designed to foster active learning, collaboration, and reflection.
Teaching Practices
- Behaviorism: Teachers can provide immediate feedback and consequences to reinforce desired behaviors.
- Cognitivism: Teachers can scaffold learning by providing guided instruction and gradually releasing responsibility to students.
- Constructivism: Teachers can facilitate learning by creating opportunities for students to explore, collaborate, and make connections.
Curriculum Development, A learning theory is made up of a set
- Behaviorism: Curriculum can be sequenced to gradually increase difficulty and provide opportunities for reinforcement.
- Cognitivism: Curriculum can be organized around concepts and skills, allowing for transfer to new situations.
- Constructivism: Curriculum can be designed to promote active learning, inquiry, and problem-solving.
Evaluating Learning Theories
Evaluating learning theories is crucial for understanding their effectiveness and identifying the most appropriate theories for specific learning contexts. Several criteria are used to assess the effectiveness of learning theories, including:
- Predictive validity:The ability of the theory to predict learning outcomes.
- Internal consistency:The extent to which the theory’s components are logically connected and consistent.
- Generalizability:The applicability of the theory to different learning situations and contexts.
- Testability:The ability of the theory to be empirically tested and verified.
- Practicality:The ease with which the theory can be implemented in real-world learning environments.
Different learning theories have varying strengths and weaknesses. For example, behaviorism is strong in predicting and controlling observable behaviors but limited in explaining complex cognitive processes. Constructivism, on the other hand, emphasizes the active role of learners in constructing knowledge but can be challenging to implement in structured learning environments.Over
time, learning theories have been evaluated and refined through empirical research. For instance, Piaget’s theory of cognitive development was initially based on observations of his own children. However, subsequent research by other psychologists expanded and refined the theory, providing a more comprehensive understanding of cognitive development.By
evaluating learning theories, educators can make informed decisions about which theories to adopt and adapt to their specific teaching contexts. This evaluation process ensures that learning theories are grounded in research and contribute to effective teaching and learning practices.
Expert Answers
What are the key components of a learning theory?
A learning theory typically comprises elements such as goals, learners, learning environment, learning activities, and assessment methods.
How do learning theories differ from each other?
Learning theories vary in their perspectives on the nature of learning, emphasizing different aspects such as behavior, cognition, social interaction, or motivation.
What are the practical applications of learning theories?
Learning theories guide the design of educational strategies, curriculum development, and teaching practices, helping educators create effective learning environments that cater to diverse learner needs.


